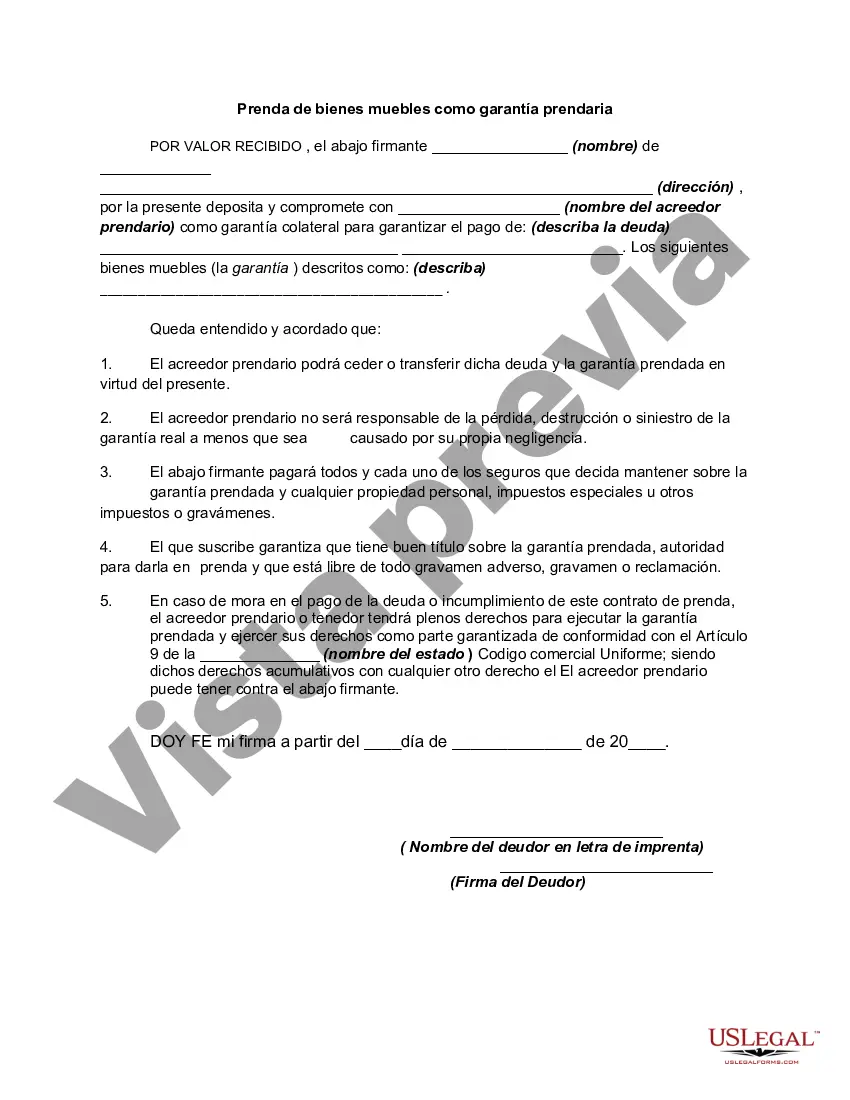
Georgia Pledge of Personal Property as Collateral Security: In Georgia, the Pledge of Personal Property as Collateral Security is a legal mechanism used to secure a loan or debt by offering personal property as collateral. This ensures that the lender has a way to recover its funds if the borrower defaults on the loan. The Georgia Pledge of Personal Property as Collateral Security is governed by the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) Article 9, which outlines the rules and regulations for secured transactions. Key features of the Georgia Pledge of Personal Property as Collateral Security include: 1. Collateral: Personal property, such as vehicles, equipment, inventory, accounts receivable, or intellectual property, can be offered as collateral for a loan. 2. Secured Interest: By pledging personal property as collateral, the lender obtains a secured interest in the assets, giving them the right to seize and sell the property if the borrower fails to repay the loan. 3. Perfection: To ensure the lender's priority over other creditors, the pledge must be perfected by filing a UCC financing statement with the Georgia Secretary of State's office. This creates a public record of the lender's claim to the collateral. 4. Default and Remedies: If the borrower defaults on the loan, the lender can enforce its rights by repossessing and selling the pledged property. The proceeds from the sale are used to repay the outstanding debt. Any remaining balance is returned to the borrower. Types of Georgia Pledge of Personal Property as Collateral Security: 1. Traditional Pledge: This is the most common type of pledge, where the borrower offers specific personal property as collateral for the loan. For example, a business owner may pledge their equipment or inventory to secure a loan. 2. Floating Lien: In certain cases, the borrower may grant the lender a floating lien over a pool of personal property. This allows the borrower to use and sell the property, while the lender maintains a security interest in the overall pool. As the borrower acquires or sells assets, the lien attaches to new property, ensuring ongoing collateral coverage. 3. Assignment of Accounts Receivable: A borrower with outstanding accounts receivable may pledge these future payments as collateral. This allows the lender to collect the funds directly from the borrower's clients if the loan defaults. 4. Intellectual Property Pledge: Intellectual property, including patents, trademarks, and copyrights, can be pledged as collateral. This protects the lender's interests if the borrower fails to repay the loan. Overall, the Georgia Pledge of Personal Property as Collateral Security is a crucial instrument for lenders and borrowers to safeguard their interests in loans. By carefully identifying and pledging appropriate collateral, borrowers can access funds while lenders can mitigate their risk. Understanding the different types of pledges available allows individuals and businesses to choose the most appropriate approach based on their specific circumstances.
Para su conveniencia, debajo del texto en español le brindamos la versión completa de este formulario en inglés. For your convenience, the complete English version of this form is attached below the Spanish version.Georgia Prenda de bienes muebles como garantía prendaria - Pledge of Personal Property as Collateral Security
Description
How to fill out Georgia Prenda De Bienes Muebles Como Garantía Prendaria?
If you need to complete, obtain, or produce authorized record layouts, use US Legal Forms, the biggest collection of authorized varieties, which can be found online. Make use of the site`s simple and handy lookup to find the documents you want. Different layouts for business and specific functions are categorized by categories and states, or key phrases. Use US Legal Forms to find the Georgia Pledge of Personal Property as Collateral Security within a handful of clicks.
If you are currently a US Legal Forms client, log in to your account and click the Acquire switch to get the Georgia Pledge of Personal Property as Collateral Security. You can also access varieties you earlier delivered electronically in the My Forms tab of your respective account.
If you use US Legal Forms the very first time, refer to the instructions beneath:
- Step 1. Ensure you have chosen the shape for the correct metropolis/country.
- Step 2. Use the Review option to look over the form`s content material. Do not neglect to see the outline.
- Step 3. If you are unhappy using the kind, use the Look for discipline at the top of the monitor to get other models of your authorized kind design.
- Step 4. Once you have discovered the shape you want, go through the Acquire now switch. Pick the pricing plan you choose and put your accreditations to register to have an account.
- Step 5. Procedure the purchase. You can utilize your Мisa or Ьastercard or PayPal account to finish the purchase.
- Step 6. Find the format of your authorized kind and obtain it in your product.
- Step 7. Total, change and produce or indication the Georgia Pledge of Personal Property as Collateral Security.
Each and every authorized record design you acquire is yours for a long time. You might have acces to every kind you delivered electronically within your acccount. Go through the My Forms section and decide on a kind to produce or obtain once again.
Contend and obtain, and produce the Georgia Pledge of Personal Property as Collateral Security with US Legal Forms. There are millions of skilled and express-certain varieties you can use to your business or specific requirements.