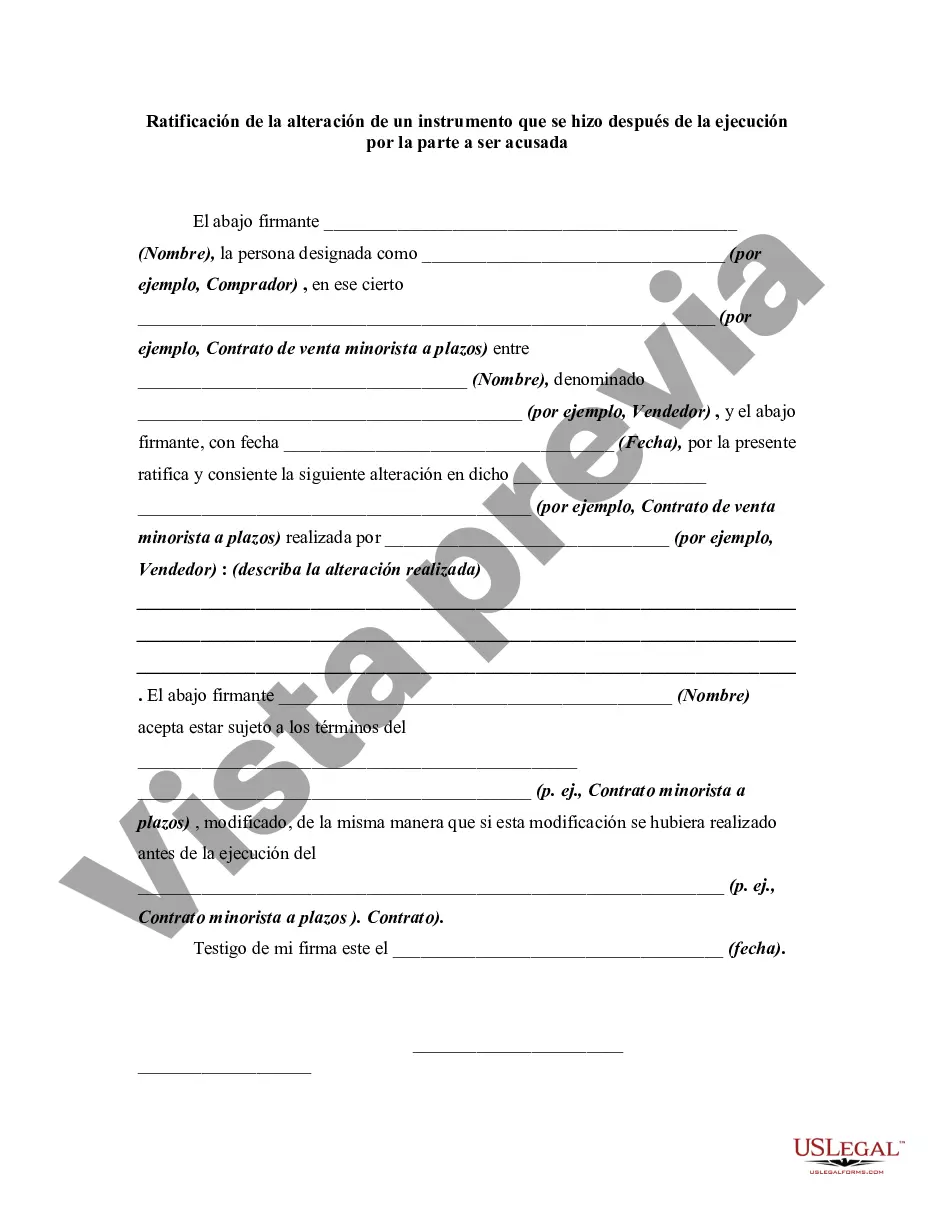
An alteration of a written instrument is a change in language of the instrument that is made by one of the parties to the instrument who is entitled to make the change. Any material alteration of a written instrument, after its execution, made by the owner or holder of the instrument, without the consent of the party to be charged, renders the instrument void as to the nonconsenting party. The party to be charged refers to that party or parties against whom enforcement of a contract or instrument is sought. If a party consents to the alteration, the instrument will not be rendered invalid as to that party.
Guam Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged refers to the legal process in which a party in Guam confirms and approves changes made to a legal document or instrument after it has been executed by the party who is being held accountable or charged. This ratification is necessary to validate any modifications made to the original document. In various legal contexts, there could be different types of ratification of alterations to an instrument in Guam. These include: 1. Ratification of Alteration of a Contract: In cases where a party made changes to a contract without the knowledge or consent of the other party, the second party may choose to ratify the alteration. This ratification confirms their acceptance of the modified terms and validates the altered contract. 2. Ratification of Alteration of a Will: If changes are made to a will after it has been executed, the party named in the document or a competent court may ratify these alterations. This ensures that the updated terms of the will are legally recognized. 3. Ratification of Alteration of a Loan Agreement: When amendments are made to a loan agreement after its execution, the parties involved may choose to ratify the changes. This ratification validates the modified terms and makes them legally binding on both parties. 4. Ratification of Alteration of a Property Deed: In cases where modifications are made to a property deed after execution, the property owner or the appropriate legal authority may ratify these alterations. This confirms the updated details and ensures the legal validity of the property transaction. In summary, Guam Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged refers to the process of confirming and approving changes made to a legal instrument after it has been executed. Different types of ratification may include those related to contracts, wills, loan agreements, and property deeds.Guam Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged refers to the legal process in which a party in Guam confirms and approves changes made to a legal document or instrument after it has been executed by the party who is being held accountable or charged. This ratification is necessary to validate any modifications made to the original document. In various legal contexts, there could be different types of ratification of alterations to an instrument in Guam. These include: 1. Ratification of Alteration of a Contract: In cases where a party made changes to a contract without the knowledge or consent of the other party, the second party may choose to ratify the alteration. This ratification confirms their acceptance of the modified terms and validates the altered contract. 2. Ratification of Alteration of a Will: If changes are made to a will after it has been executed, the party named in the document or a competent court may ratify these alterations. This ensures that the updated terms of the will are legally recognized. 3. Ratification of Alteration of a Loan Agreement: When amendments are made to a loan agreement after its execution, the parties involved may choose to ratify the changes. This ratification validates the modified terms and makes them legally binding on both parties. 4. Ratification of Alteration of a Property Deed: In cases where modifications are made to a property deed after execution, the property owner or the appropriate legal authority may ratify these alterations. This confirms the updated details and ensures the legal validity of the property transaction. In summary, Guam Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged refers to the process of confirming and approving changes made to a legal instrument after it has been executed. Different types of ratification may include those related to contracts, wills, loan agreements, and property deeds.
Para su conveniencia, debajo del texto en español le brindamos la versión completa de este formulario en inglés. For your convenience, the complete English version of this form is attached below the Spanish version.