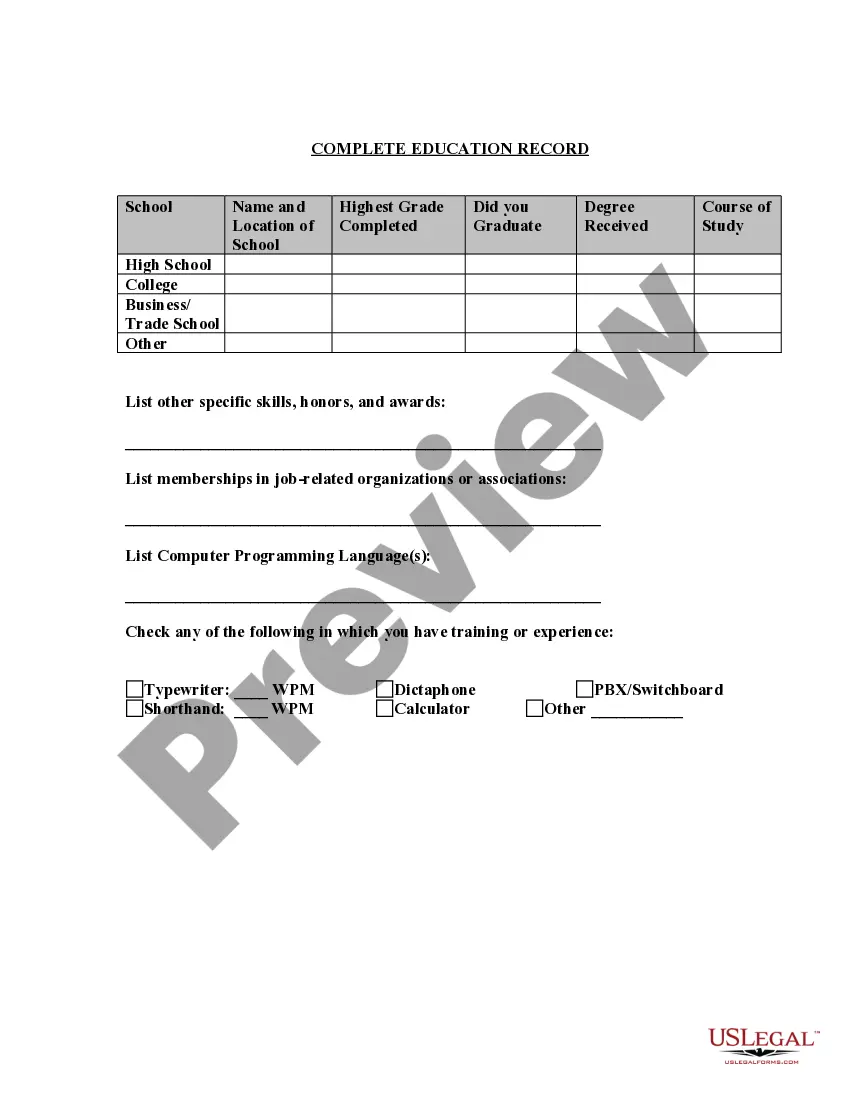
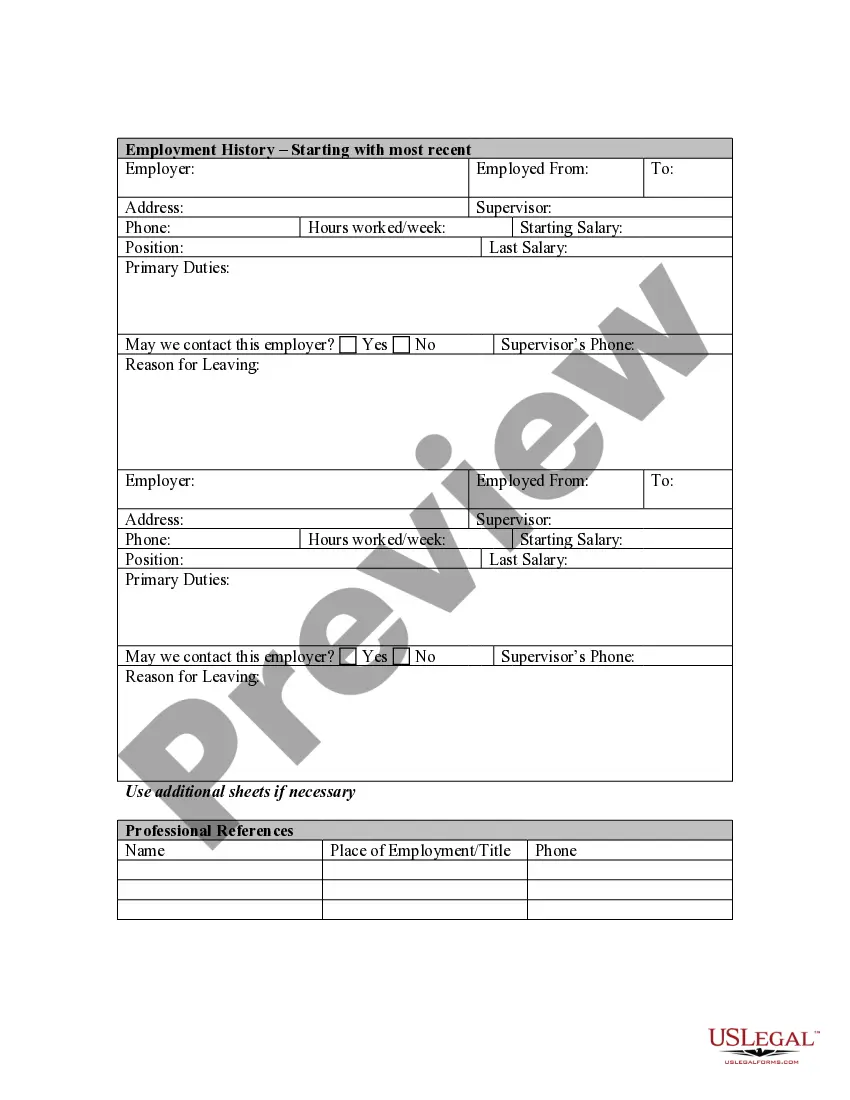
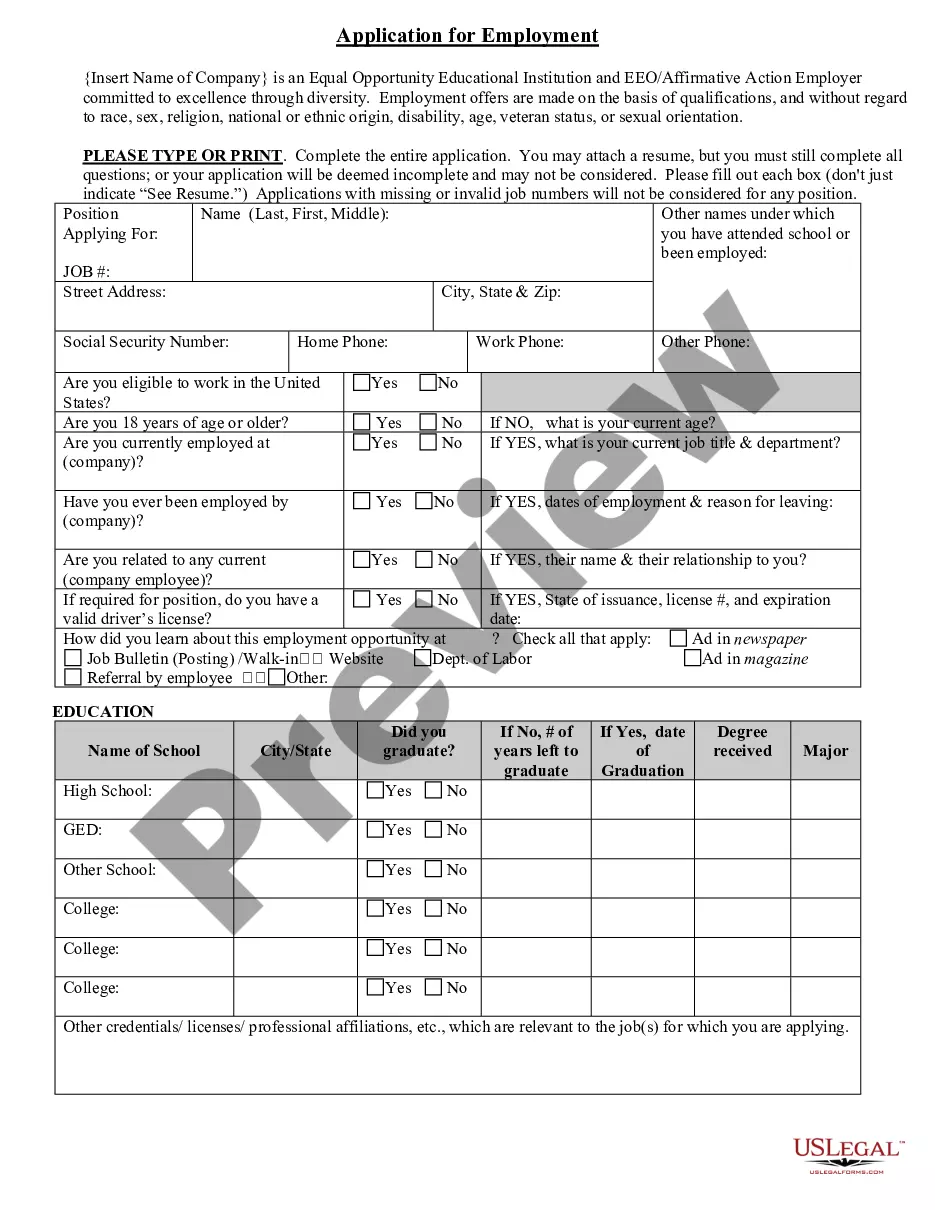
Missouri Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position
Description
How to fill out Application For Work Or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, Or Nonexempt Position?
It is feasible to spend multiple hours online attempting to discover the legal document template that meets the federal and state requirements you will require.
US Legal Forms provides thousands of legal documents that can be evaluated by professionals.
You can download or print the Missouri Application for Employment or Work - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position from the service.
If available, utilize the Preview button to review the document template as well.
- If you already have a US Legal Forms account, you can Log In and click the Obtain button.
- After that, you can complete, amend, print, or sign the Missouri Application for Employment or Work - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position.
- Every legal document template you acquire is yours permanently.
- To obtain another copy of the purchased form, go to the My documents tab and click the respective button.
- If you are using the US Legal Forms website for the first time, follow the simple instructions below.
- First, ensure that you have selected the correct document template for the state/city of your choice.
- Read the form description to ensure you have selected the right kind.
Form popularity
FAQ
When discussing the difference between exempt and non-exempt employees in Missouri, focus on compensation and hours worked. Exempt employees typically earn a predetermined salary and do not receive overtime compensation, while non-exempt employees earn hourly wages and are entitled to overtime for hours exceeding 40 in a workweek. Accessing the Missouri Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position can help you identify which classification aligns with your employment rights and expectations.
Tips For Drafting Job Descriptions for Exempt EmployeesAccuracy is King. The job description must be accurate.Accuracy Does Not Mean Exhaustion.Strong Verbs, Clear Impact.Focus on Exempt Functions.Don't Shy Away From Degree Requirements.Assist With Can Diminish a Role.Consider Requiring Acknowledgement.
Exempt Employee Rights Under the Fair Labor Standards Act, an exempt employee in Missouri and other states earns at least $455 per week and $23,600 per year. The employee must also satisfy at least one clause of the FLSA duties test. An exempt employee does not receive overtime pay.
Executives, administrators, and other professionals earning at least $455 per week do not have to be paid overtime under Section 13(a)(1) of the Fair Labor Standards Act. External salespeople (who often set their own hours) are also exempted from MO overtime requirements, as are some types of computer-related workers.
An exempt employee is not entitled overtime pay by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). These salaried employees receive the same amount of pay per pay period, even if they put in overtime hours. A nonexempt employee is eligible to be paid overtime for work in excess of 40 hours per week, per federal guidelines.
Exempt employees refer to workers in the United States who are not entitled to overtime pay. This simply implies that employers of exempt employees are not bound by law to pay them for any extra hours of work. The federal standard for work hours in the United States is 40 hours per workweek.
Executive, administrative, managerial, faculty and professional positions are classified as exempt and no overtime is paid or compensatory time earned. Because exempt employees are not eligible for overtime, they are not required to keep a record of the hours they work but must report time away from work (leave).
The FLSA includes these job categories as exempt: professional, administrative, executive, outside sales, and computer-related. The details vary by state, but if an employee falls in the above categories, is salaried, and earns a minimum of $684 per week or $35,568 annually, then they are considered exempt.