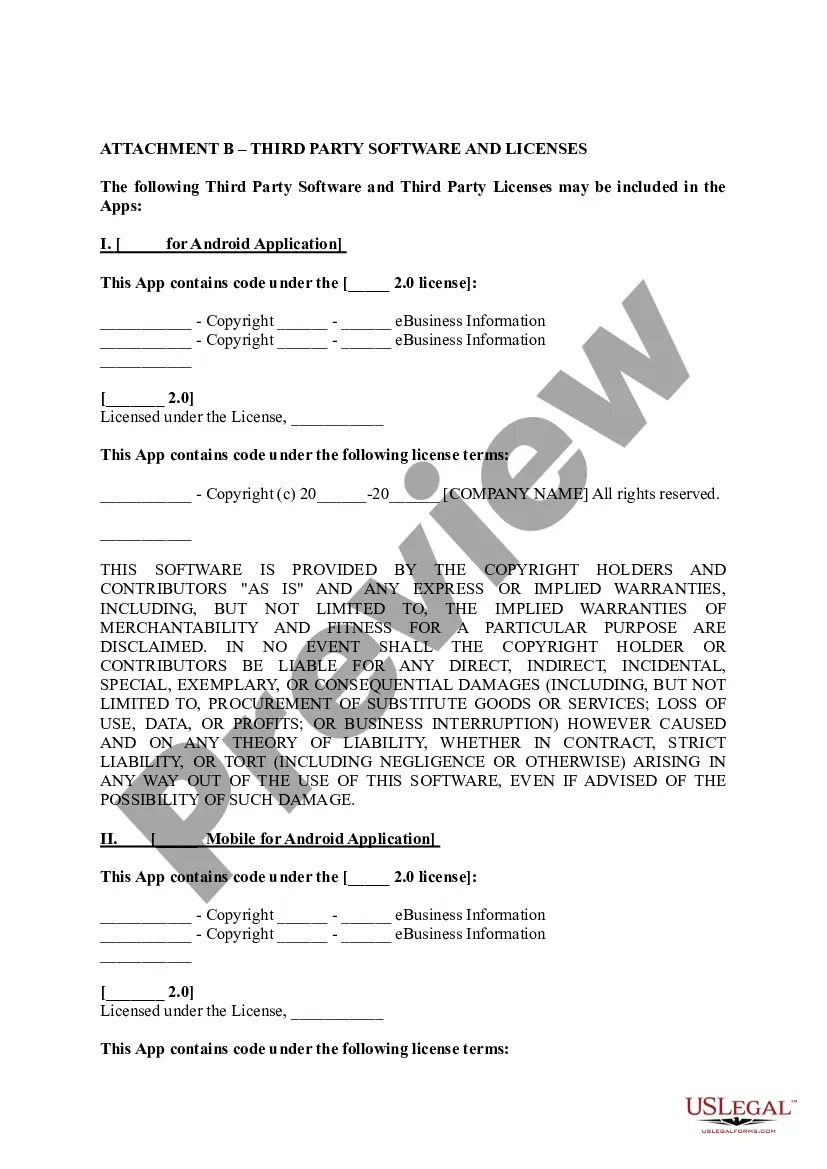
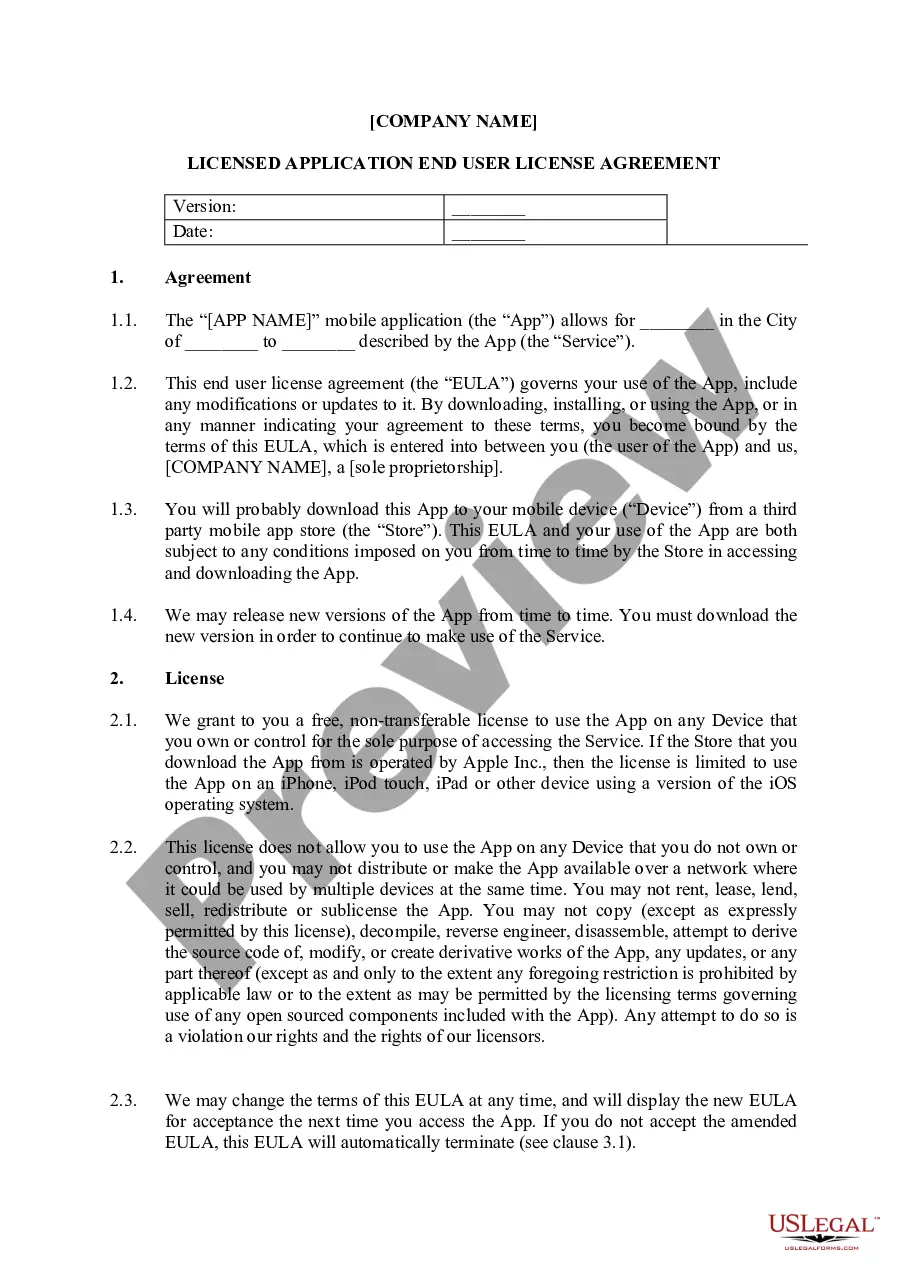
New Hampshire End User License Agreement for Mobile Applications
Description
How to fill out End User License Agreement For Mobile Applications?
If you wish to complete, obtain, or print out authorized record templates, use US Legal Forms, the biggest selection of authorized forms, which can be found online. Take advantage of the site`s easy and practical research to get the documents you require. A variety of templates for enterprise and individual uses are sorted by types and says, or search phrases. Use US Legal Forms to get the New Hampshire End User License Agreement for Mobile Applications with a couple of mouse clicks.
In case you are previously a US Legal Forms client, log in to your bank account and click on the Obtain switch to have the New Hampshire End User License Agreement for Mobile Applications. You can also entry forms you earlier acquired from the My Forms tab of your respective bank account.
If you work with US Legal Forms the first time, follow the instructions under:
- Step 1. Be sure you have selected the form for the right city/nation.
- Step 2. Make use of the Review solution to examine the form`s articles. Never forget to learn the explanation.
- Step 3. In case you are unsatisfied with the type, utilize the Lookup industry near the top of the display to locate other types in the authorized type design.
- Step 4. After you have identified the form you require, click the Acquire now switch. Choose the prices strategy you favor and add your references to register on an bank account.
- Step 5. Method the financial transaction. You may use your credit card or PayPal bank account to complete the financial transaction.
- Step 6. Pick the format in the authorized type and obtain it in your device.
- Step 7. Complete, modify and print out or signal the New Hampshire End User License Agreement for Mobile Applications.
Every single authorized record design you get is yours forever. You might have acces to each and every type you acquired with your acccount. Click on the My Forms portion and decide on a type to print out or obtain once again.
Contend and obtain, and print out the New Hampshire End User License Agreement for Mobile Applications with US Legal Forms. There are millions of skilled and status-distinct forms you can use for your enterprise or individual requires.
Form popularity
FAQ
An End-User License Agreement (EULA) is important to have when you let users download and your mobile apps. That's because you're giving users a license to use the app, and you'll want to maintain control over the use of these licenses. Remember: An EULA is NOT a Terms and Conditions agreement.
How do you write EULA? clearly identify yourself/your business; clear state the rules for user behaviour and access to your product/software; disclose the copyright/intellectual property license that applies (e.g. open source); include other details of the software license including conditions for termination;
Both parties must act within their rights based on applicable laws. Writing a EULA yourself gives you more control over the document, but it can also be time-consuming and complicated.
Some common clauses found in a standard EULA are: Introduction. Licensing of Use. Restrictions of Use. Termination of Use. Limitation of Liability. Disclaimers of Warranties. Copyright Infringement. Contact Information.
Mobile App Terms and Conditions Template Limit your liabilities. Answer common questions about your protocols, guidelines, and user expectations. Protect your intellectual property. Minimize legal disputes. Establish rules that users must follow while accessing your services. Post necessary disclaimers and warranties.
Although EULAs vary, every EULA should include clauses explaining: The enactment date. The binding nature of the agreement. Your contact details and full business name designation. The governing laws. Permitted and restricted uses. Termination conditions. Warranties and limitation of liability. Related agreements.
In brief, an EULA is the contract between the mobile app user and the software developer who provides the app. It works to distribute a license to the user of the app and lays out the terms of the use of that license.
For example, if a user installs a mobile app and agrees to an EULA with this clause in it, then the user's phone malfunctions and breaks, the user cannot seek liability against the provider of the mobile app for reparations for the damaged phone, even if the damage was a result of the mobile app.