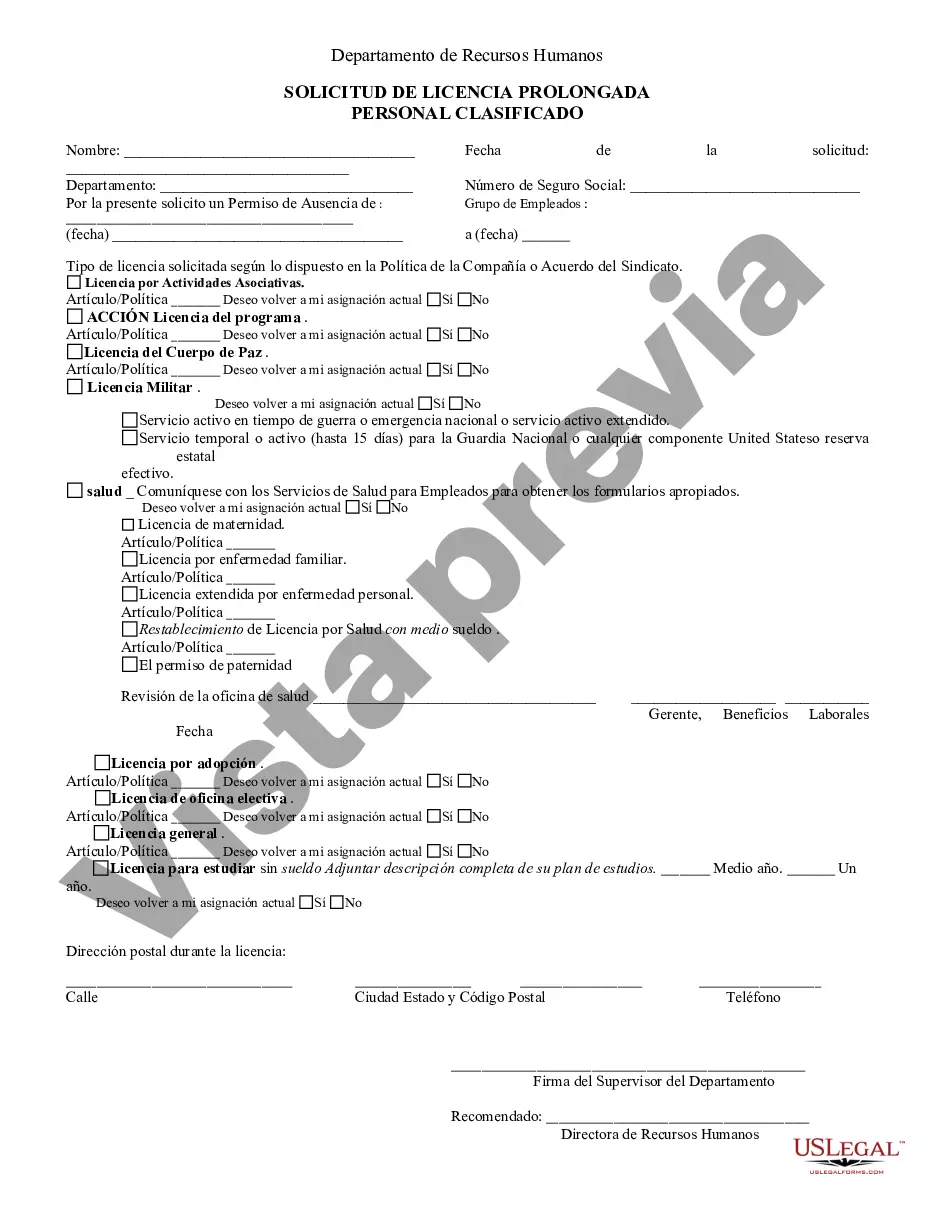
Title: Explore New York Request for Extended Personal Leave: Types, Process, and Employer Obligations Introduction: In the bustling metropolis of New York, taking extended personal leave is a sought-after benefit for employees seeking a well-deserved break, personal development, or to attend to pressing family matters. In this article, we will delve into the details of what a New York Request for Extended Personal Leave entails, including its types and key considerations for employees and employers. Types of New York Request for Extended Personal Leave: 1. Medical Leave: — Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA): Employees can request medical leave under FMLA, which grants up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave in a 12-month period for specified medical and family reasons. — New York State Paid Family Leave (PFL): Starting in 2021, employees are entitled to paid family leave for up to 12 weeks (expanding to 14 weeks in 2022) to bond with a newborn, care for a family member with a serious health condition, or attend to military family obligations. — New York City Earned Safe and Sick Time Act (ENSTA): Offers job-protected paid leave to employees, including those who need time off for health-related issues. 2. Personal or Non-Medical Leave: — Unpaid Leave: Employees may request unpaid leave for personal reasons, such as advancing education, attending to family matters, or pursuing travel opportunities. — Sabbatical Leave: Some organizations offer employees the opportunity to take a sabbatical, usually after a specified period of employment, where they can focus on personal growth, research, writing, or other enrichment activities. Process of Requesting Extended Personal Leave: 1. Early Notification: Employees should inform their employer as early as possible, preferably in writing, outlining the reason for the requested leave, its expected duration, and any relevant supporting documentation. 2. Eligibility Assessment: Employers review employees' eligibility for different types of extended leave, considering regulations like FMLA, PFL, and ENSTA, and provide appropriate guidance accordingly. 3. Documentation: Employees may be required to provide relevant documentation, such as medical certificates, birth/adoption certificates, or other supporting paperwork depending on the type of leave requested. 4. Communication and Approval: Employers and employees engage in open communication to discuss the implications of the requested leave, potential coverage arrangements, and obtain final approval or denial of the leave request. Employer Obligations: 1. Compliance: Employers must adhere to federal and state laws regarding extended leave, including FMLA, PFL, ENSTA, and other applicable regulations. 2. Leave Policies: Employers should establish and communicate clear leave policies, outlining procedures for requesting extended personal leave, documentation requirements, and any additional benefits available during the leave period. 3. Accommodation and Reinstatement: Employers are generally obliged to provide reasonable accommodations for employees' leave requests, and reinstate them to the same or equivalent position upon their return, per legal requirements. 4. Confidentiality: Employers must maintain the confidentiality of employees' personal or medical information shared during the leave request process. Conclusion: New York offers various types of extended personal leave, allowing employees to address medical, family, or personal needs. Understanding these different types, following the appropriate process, and being aware of employer obligations are crucial for employees seeking to make use of these benefits. By fostering a harmonious work-life balance, extended personal leave contributes to the well-being and satisfaction of individuals in the bustling city of New York.
Para su conveniencia, debajo del texto en español le brindamos la versión completa de este formulario en inglés. For your convenience, the complete English version of this form is attached below the Spanish version.New York Solicitud de licencia personal extendida - Request for Extended Personal Leave
Description
How to fill out New York Solicitud De Licencia Personal Extendida?
US Legal Forms - one of several greatest libraries of legitimate types in America - gives a wide range of legitimate papers web templates you may obtain or print. While using web site, you may get thousands of types for company and personal functions, categorized by classes, claims, or keywords.You will discover the latest variations of types such as the New York Request for Extended Personal Leave in seconds.
If you have a monthly subscription, log in and obtain New York Request for Extended Personal Leave from your US Legal Forms collection. The Obtain switch can look on every single type you look at. You gain access to all in the past delivered electronically types in the My Forms tab of your own profile.
If you would like use US Legal Forms the very first time, listed below are simple directions to help you started:
- Make sure you have picked the correct type to your town/county. Click the Preview switch to analyze the form`s information. Look at the type information to actually have chosen the right type.
- In the event the type does not match your requirements, make use of the Search area at the top of the monitor to discover the the one that does.
- When you are content with the form, affirm your choice by clicking the Purchase now switch. Then, opt for the pricing plan you prefer and offer your references to sign up for an profile.
- Procedure the financial transaction. Use your bank card or PayPal profile to finish the financial transaction.
- Pick the format and obtain the form on your own system.
- Make changes. Complete, change and print and indicator the delivered electronically New York Request for Extended Personal Leave.
Each and every template you included with your bank account lacks an expiry day and is the one you have permanently. So, if you would like obtain or print another duplicate, just visit the My Forms area and click on around the type you need.
Obtain access to the New York Request for Extended Personal Leave with US Legal Forms, probably the most considerable collection of legitimate papers web templates. Use thousands of expert and status-distinct web templates that meet up with your company or personal requirements and requirements.