The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLEA) is a federal law that establishes the minimum wage, overtime pay, record keeping, and child labor standards for employers in the United States. It covers both full-time and part-time employees, and applies to most private and public employers. The FLEA sets the federal minimum wage at $7.25 per hour, requires employers to pay time-and-a-half for overtime work, and prohibits employers from employing minors in hazardous occupations. The FLEA also provides protections for workers in the form of minimum wage, overtime pay, and record keeping requirements. The FLEA is divided into two parts: the Wage and Hour Division (WHO) and the Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking (OCT). The WHO is responsible for enforcing the minimum wage, overtime pay, record keeping, and other labor standards. The OCT is responsible for enforcing child labor laws, including prohibiting the employment of minors in hazardous occupations. The FLEA is enforced by the U.S. Department of Labor (DOL). Employers who violate the FLEA may be subject to civil and criminal penalties, including back pay, liquidated damages, and criminal fines.
Fair Labor Standards Act
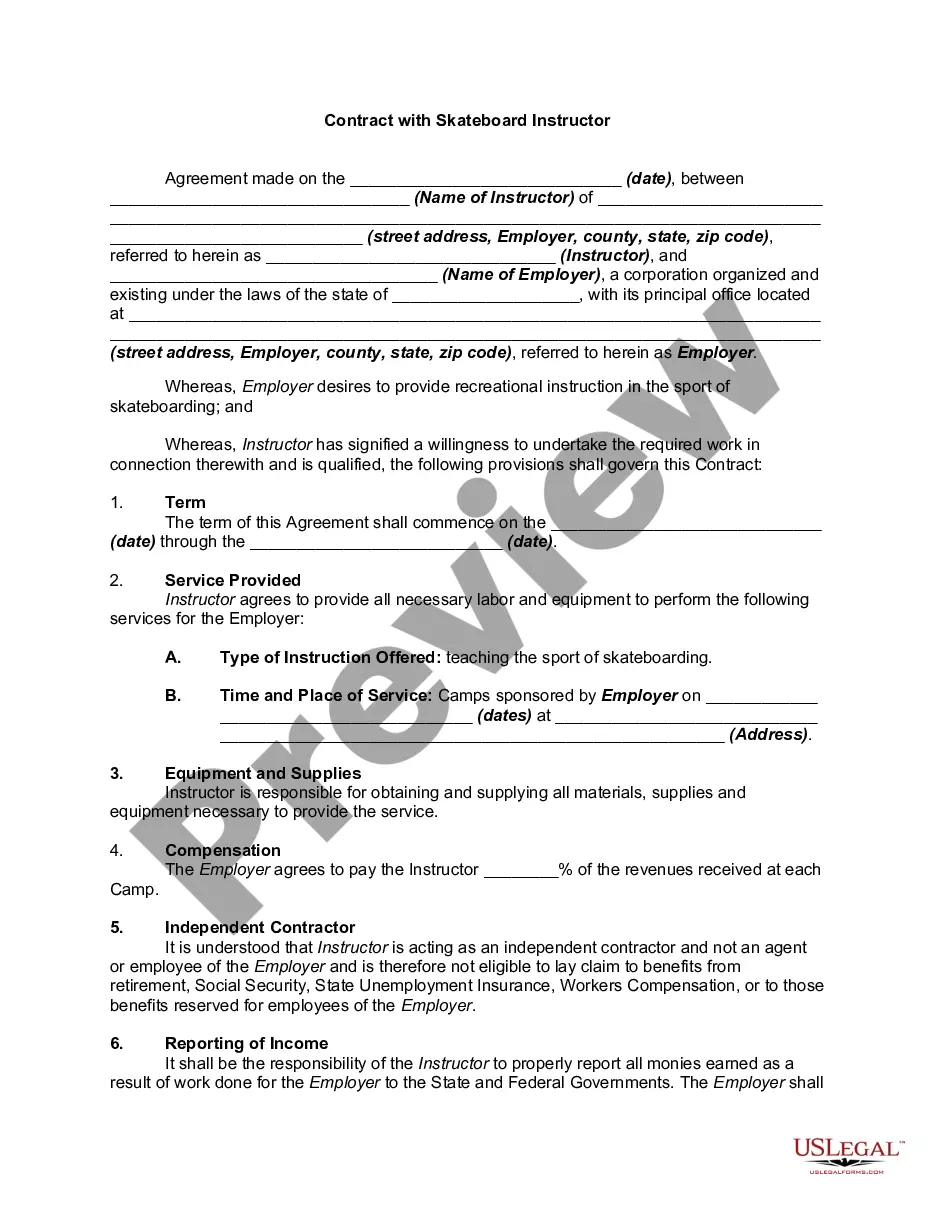
Description
How to fill out Fair Labor Standards Act?
How much time and resources do you typically spend on drafting official paperwork? There’s a better way to get such forms than hiring legal experts or spending hours browsing the web for an appropriate template. US Legal Forms is the premier online library that provides professionally designed and verified state-specific legal documents for any purpose, like the Fair Labor Standards Act.
To obtain and prepare an appropriate Fair Labor Standards Act template, adhere to these simple instructions:
- Examine the form content to ensure it meets your state regulations. To do so, read the form description or use the Preview option.
- If your legal template doesn’t meet your needs, locate a different one using the search bar at the top of the page.
- If you already have an account with us, log in and download the Fair Labor Standards Act. If not, proceed to the next steps.
- Click Buy now once you find the correct blank. Opt for the subscription plan that suits you best to access our library’s full opportunities.
- Register for an account and pay for your subscription. You can make a payment with your credit card or via PayPal - our service is totally safe for that.
- Download your Fair Labor Standards Act on your device and fill it out on a printed-out hard copy or electronically.
Another advantage of our service is that you can access previously downloaded documents that you safely store in your profile in the My Forms tab. Obtain them at any moment and re-complete your paperwork as frequently as you need.
Save time and effort completing legal paperwork with US Legal Forms, one of the most reliable web solutions. Sign up for us today!