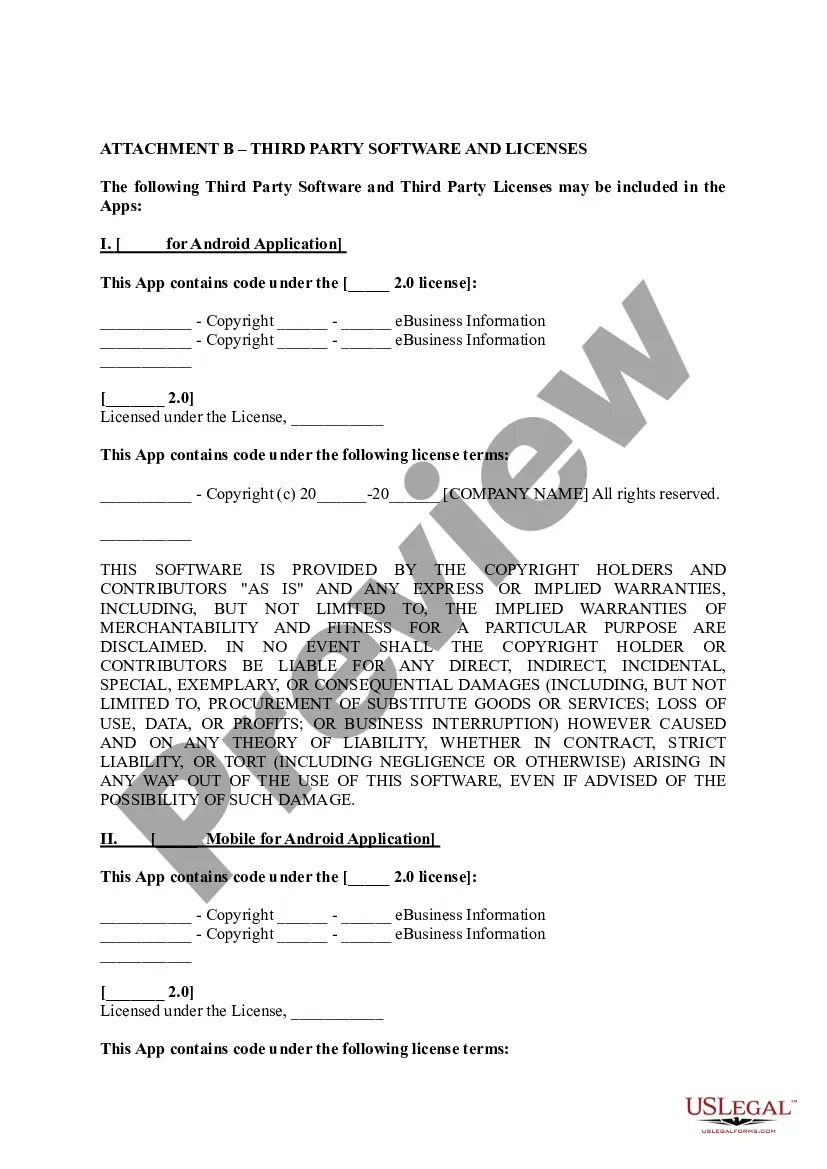
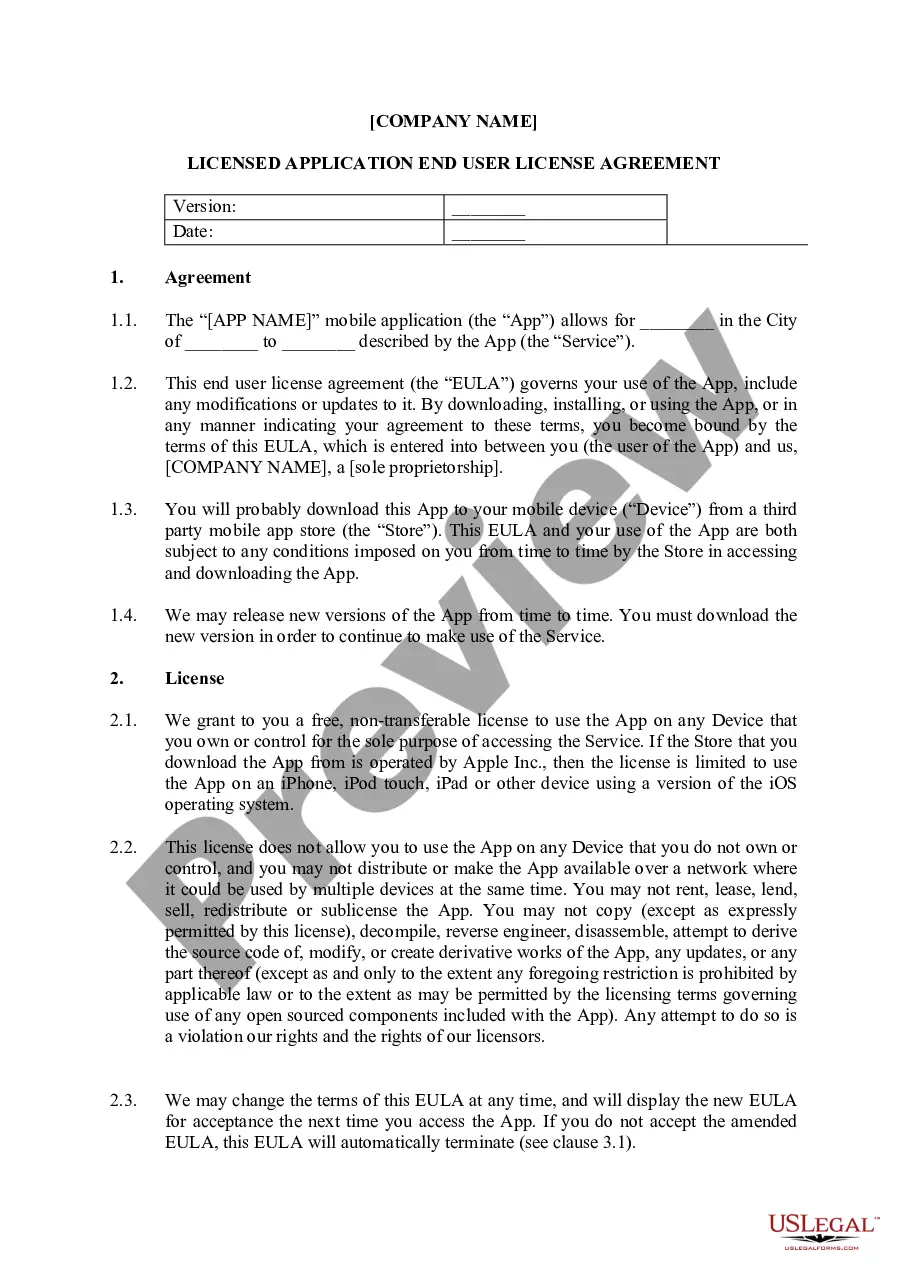
Vermont End User License Agreement for Mobile Applications
Description
How to fill out End User License Agreement For Mobile Applications?
US Legal Forms - among the most significant libraries of lawful forms in America - offers a variety of lawful document layouts you may obtain or produce. Using the web site, you can get 1000s of forms for organization and person purposes, sorted by classes, suggests, or key phrases.You will discover the most up-to-date models of forms much like the Vermont End User License Agreement for Mobile Applications in seconds.
If you already possess a registration, log in and obtain Vermont End User License Agreement for Mobile Applications from the US Legal Forms catalogue. The Obtain switch will show up on each and every type you see. You have access to all formerly acquired forms in the My Forms tab of your account.
In order to use US Legal Forms initially, allow me to share straightforward guidelines to help you started out:
- Make sure you have selected the correct type for the city/region. Click the Review switch to examine the form`s content material. See the type explanation to ensure that you have chosen the proper type.
- In the event the type doesn`t fit your specifications, make use of the Search industry towards the top of the monitor to find the one which does.
- Should you be pleased with the form, confirm your option by clicking the Purchase now switch. Then, choose the rates plan you like and supply your references to sign up for the account.
- Process the financial transaction. Use your bank card or PayPal account to perform the financial transaction.
- Select the formatting and obtain the form on your device.
- Make changes. Fill up, revise and produce and indicator the acquired Vermont End User License Agreement for Mobile Applications.
Every single format you included with your account does not have an expiration particular date and is yours forever. So, in order to obtain or produce another duplicate, just proceed to the My Forms portion and click on about the type you want.
Get access to the Vermont End User License Agreement for Mobile Applications with US Legal Forms, one of the most comprehensive catalogue of lawful document layouts. Use 1000s of skilled and state-particular layouts that meet up with your small business or person requirements and specifications.
Form popularity
FAQ
Hear this out loud PauseSoftware publishers employ them to enforce their copyright rights, which provide them exclusive rights to distribute, reproduce, and change the program under copyright laws. By accepting the terms of the EULA, the end user acknowledges these rights and agrees not to participate in acts that violate them.
Hear this out loud PauseIf the app or software has to be purchased by the user, they are typically required to agree to the EULA before paying, which means that there is no harm done if the user doesn't agree to the licensing agreement. Some companies include licensing agreements to maintain control of their image.
Although EULAs vary, every EULA should include clauses explaining: The enactment date. The binding nature of the agreement. Your contact details and full business name designation. The governing laws. Permitted and restricted uses. Termination conditions. Warranties and limitation of liability. Related agreements.
An end-user license agreement grants a person or organization the right to use a software application. Typically, EULAs set forth other terms and conditions, but their primary purpose is to protect the software developer's intellectual property rights.
Hear this out loud PauseIn brief, an EULA is the contract between the mobile app user and the software developer who provides the app. It works to distribute a license to the user of the app and lays out the terms of the use of that license.
Both parties must act within their rights based on applicable laws. Writing a EULA yourself gives you more control over the document, but it can also be time-consuming and complicated.
How do you write EULA? clearly identify yourself/your business; clear state the rules for user behaviour and access to your product/software; disclose the copyright/intellectual property license that applies (e.g. open source); include other details of the software license including conditions for termination;
Hear this out loud PauseThe EULA protects the ownership of your software or app, specifying that the end-users only obtain a license to use your product, not any ownership rights. It also provides disclaimers and limits your liability to any injury or damage that may occur when the consumer uses your product.