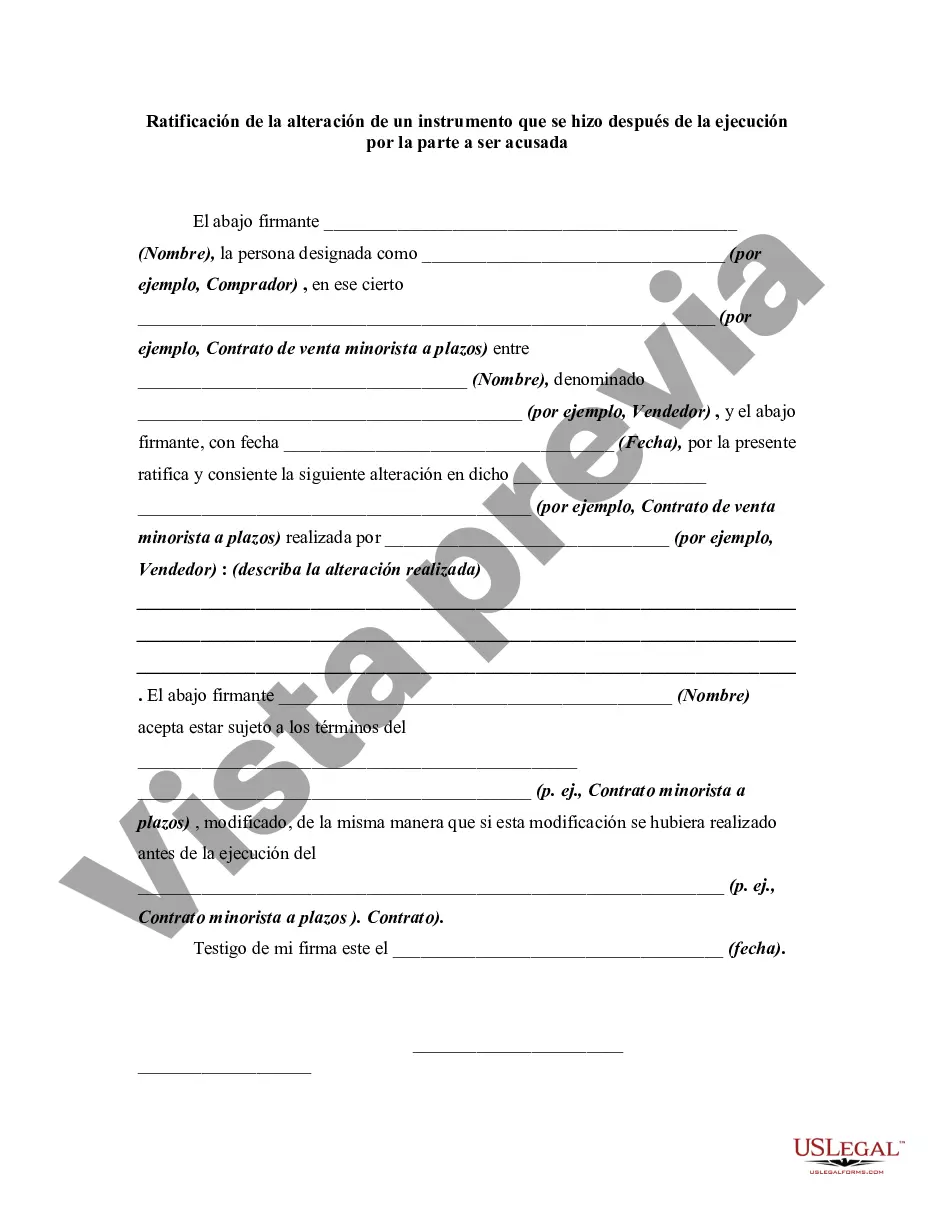
An alteration of a written instrument is a change in language of the instrument that is made by one of the parties to the instrument who is entitled to make the change. Any material alteration of a written instrument, after its execution, made by the owner or holder of the instrument, without the consent of the party to be charged, renders the instrument void as to the nonconsenting party. The party to be charged refers to that party or parties against whom enforcement of a contract or instrument is sought. If a party consents to the alteration, the instrument will not be rendered invalid as to that party.
Hennepin County is located in the state of Minnesota and is one of the most populous counties in the state. Within this county, there is a legal concept known as "Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged." This term refers to a legal process by which a party acknowledges and approves changes or modifications made to a document after it has been executed. In Hennepin County, there are two main types of ratification for alterations of instruments which were made after execution by the party to be charged: express ratification and implied ratification. 1. Express Ratification: This type of ratification occurs when the party to be charged explicitly acknowledges and approves the alterations made to the instrument. It can be done through a written statement, recorded audio, or even in-person communication. 2. Implied Ratification: Implied ratification is a bit more complex and refers to situations where the party to be charged's actions or behavior indicate approval or acceptance of the altered instrument. This can be demonstrated through actions such as continuing to carry out the terms of the modified instrument without objection. The Hennepin Minnesota Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged is a crucial legal concept that ensures transparency and accountability when changes are made to legally binding documents. It is important to consult with an experienced attorney in Hennepin County to understand the specific procedures and requirements for ratifying altered instruments in this jurisdiction.Hennepin County is located in the state of Minnesota and is one of the most populous counties in the state. Within this county, there is a legal concept known as "Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged." This term refers to a legal process by which a party acknowledges and approves changes or modifications made to a document after it has been executed. In Hennepin County, there are two main types of ratification for alterations of instruments which were made after execution by the party to be charged: express ratification and implied ratification. 1. Express Ratification: This type of ratification occurs when the party to be charged explicitly acknowledges and approves the alterations made to the instrument. It can be done through a written statement, recorded audio, or even in-person communication. 2. Implied Ratification: Implied ratification is a bit more complex and refers to situations where the party to be charged's actions or behavior indicate approval or acceptance of the altered instrument. This can be demonstrated through actions such as continuing to carry out the terms of the modified instrument without objection. The Hennepin Minnesota Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged is a crucial legal concept that ensures transparency and accountability when changes are made to legally binding documents. It is important to consult with an experienced attorney in Hennepin County to understand the specific procedures and requirements for ratifying altered instruments in this jurisdiction.
Para su conveniencia, debajo del texto en español le brindamos la versión completa de este formulario en inglés. For your convenience, the complete English version of this form is attached below the Spanish version.