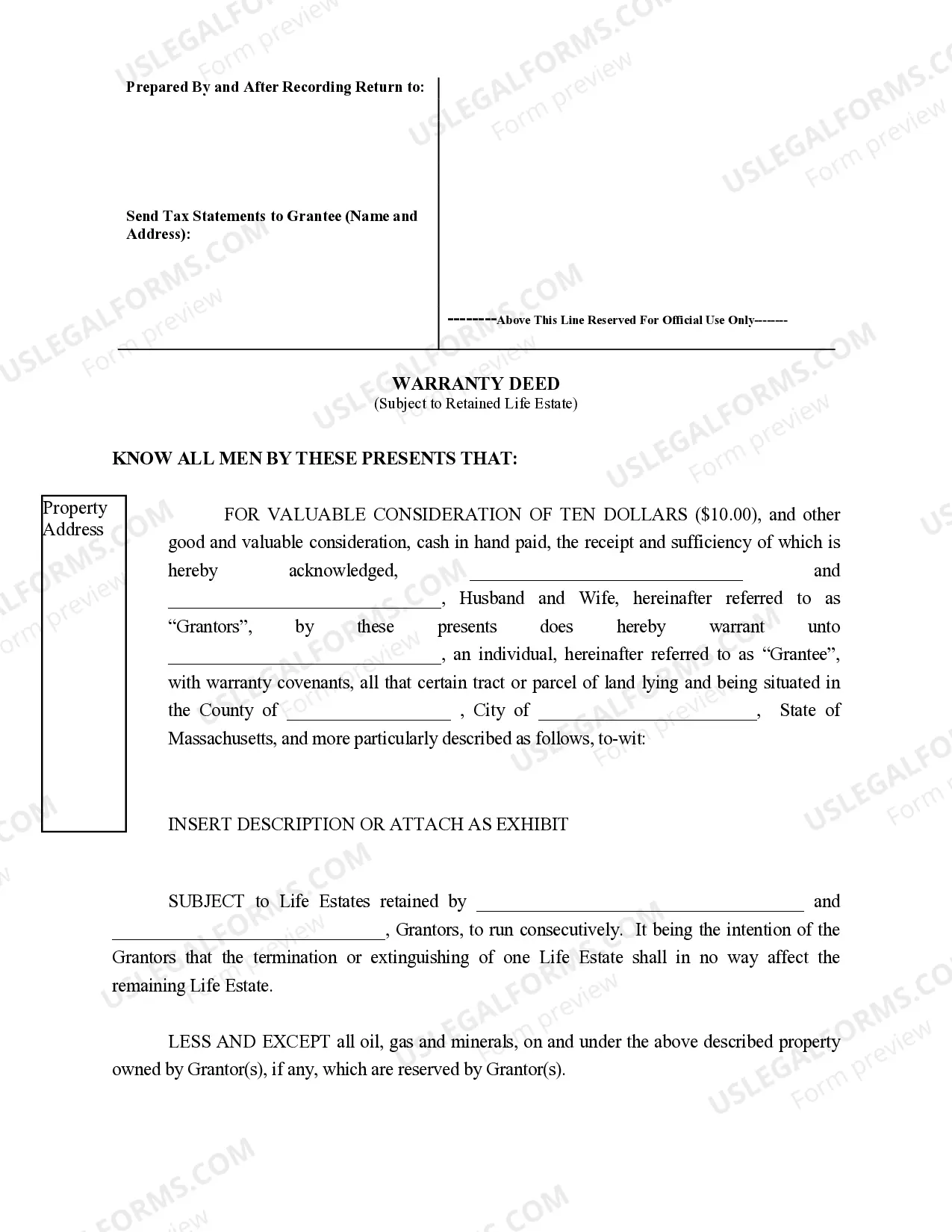
A life estate deed is a legal document that grants an individual, known as the life tenant, the right to own and use a property for their lifetime or for the lifetime of another person, usually referred to as the remainder man. In Massachusetts, the life estate deed follows a specific format, ensuring that the interests of all involved parties are protected. Here is a detailed description of the life estate deed format in Massachusetts, including its key components and any specific types. The life estate deed in Massachusetts is governed by specific laws and regulations under Chapter 184, Section 3 of the Massachusetts General Laws. This format allows a property owner to transfer ownership rights in a manner that ensures the property's continuous use and enjoyment by the life tenant while also securing the rights of the remainder man upon the life tenant's death. The Massachusetts life estate deed format typically consists of the following essential components: 1. Granter and Grantee Details: The deed must clearly identify the parties involved in the transfer. The granter is the property owner who transfers the life estate interest, while the grantee is the life tenant or the remainder man. 2. Property Description: The deed must include a detailed description of the property being transferred, including the property's legal description, address, and any other identifying features that clearly establish its boundaries. 3. Life Estate Language: This section of the deed outlines the specific terms and conditions of the life estate interest, including the duration and limitations. It specifies that the life tenant holds the right to occupy, use, and enjoy the property during their lifetime. 4. Remainder man Designation: The remainder man is the individual or entity who will inherit the property upon the life tenant's death. The deed must clearly identify the remainder man and specify their rights and interests. 5. Rights and Responsibilities of the Parties: The deed may include provisions specifying the responsibilities of the life tenant and the remainder man regarding property maintenance, taxes, insurance, and any other obligations necessary to ensure the property's proper upkeep. 6. Signatures and Notarization: To be legally enforceable, the life estate deed must be signed by both the granter and the grantee in the presence of a notary public. Notarization serves as proof of the deed's authenticity. In Massachusetts, there are no specific variations in the life estate deed format based on different types. However, individuals may choose to incorporate additional provisions to customize the agreement according to their specific needs, such as granting the life tenant the right to lease or sell the property with the remainder man's consent. In conclusion, a life estate deed in Massachusetts is a legally binding document that outlines the transfer of property rights, granting a life tenant the right to own and use the property for life while designating a remainder man to inherit the property upon the life tenant's death. By adhering to the specific format and including key provisions, the life estate deed ensures the smooth transition of ownership while protecting the interests of all parties involved.
Life Estate Deed Massachusetts Sample Format
Description
How to fill out Life Estate Deed Massachusetts Sample Format?
The Life Estate Deed Massachusetts Sample Format you see on this page is a multi-usable formal template drafted by professional lawyers in compliance with federal and state regulations. For more than 25 years, US Legal Forms has provided individuals, organizations, and legal professionals with more than 85,000 verified, state-specific forms for any business and personal scenario. It’s the fastest, simplest and most reliable way to obtain the documents you need, as the service guarantees bank-level data security and anti-malware protection.
Acquiring this Life Estate Deed Massachusetts Sample Format will take you only a few simple steps:
- Search for the document you need and review it. Look through the sample you searched and preview it or check the form description to ensure it satisfies your needs. If it does not, utilize the search bar to get the appropriate one. Click Buy Now once you have located the template you need.
- Subscribe and log in. Opt for the pricing plan that suits you and register for an account. Use PayPal or a credit card to make a prompt payment. If you already have an account, log in and check your subscription to continue.
- Acquire the fillable template. Select the format you want for your Life Estate Deed Massachusetts Sample Format (PDF, DOCX, RTF) and download the sample on your device.
- Fill out and sign the paperwork. Print out the template to complete it by hand. Alternatively, use an online multi-functional PDF editor to rapidly and precisely fill out and sign your form with a legally-binding] {electronic signature.
- Download your papers again. Utilize the same document again anytime needed. Open the My Forms tab in your profile to redownload any earlier purchased forms.
Sign up for US Legal Forms to have verified legal templates for all of life’s situations at your disposal.
Form popularity
FAQ
There is no simple way to reverse a life estate because a life estate deed is a legal transfer of the title of a property. This is legally binding and the transaction is complete when the life estate is executed. Essentially, in order to reverse a life estate both parties would need to agree to make it happen.
The life estate ends at the death of the life tenant (or at the death of the last survivor of the life tenants if there is more than one). At that point, the so-called ?remaindermen? take over both full ownership and the right to occupy and control the property.
The life tenant or tenants have the full right of possession, or right to occupy, the premises during their lives. In addition, they have the right to rent out the property and receive the income. They also have the obligation to maintain the property and to pay its expenses, including real estate taxes.
There are three types of real estate deeds in Massachusetts: release deeds, quitclaim deeds, and warranty deeds. Each of these deeds gives a buyer different degrees of protection and guarantees against defects.
Within a life estate, the life estate deed is a document that grants the owner the ability to pass on ownership of a property without including it in a will as part of a person's assets.