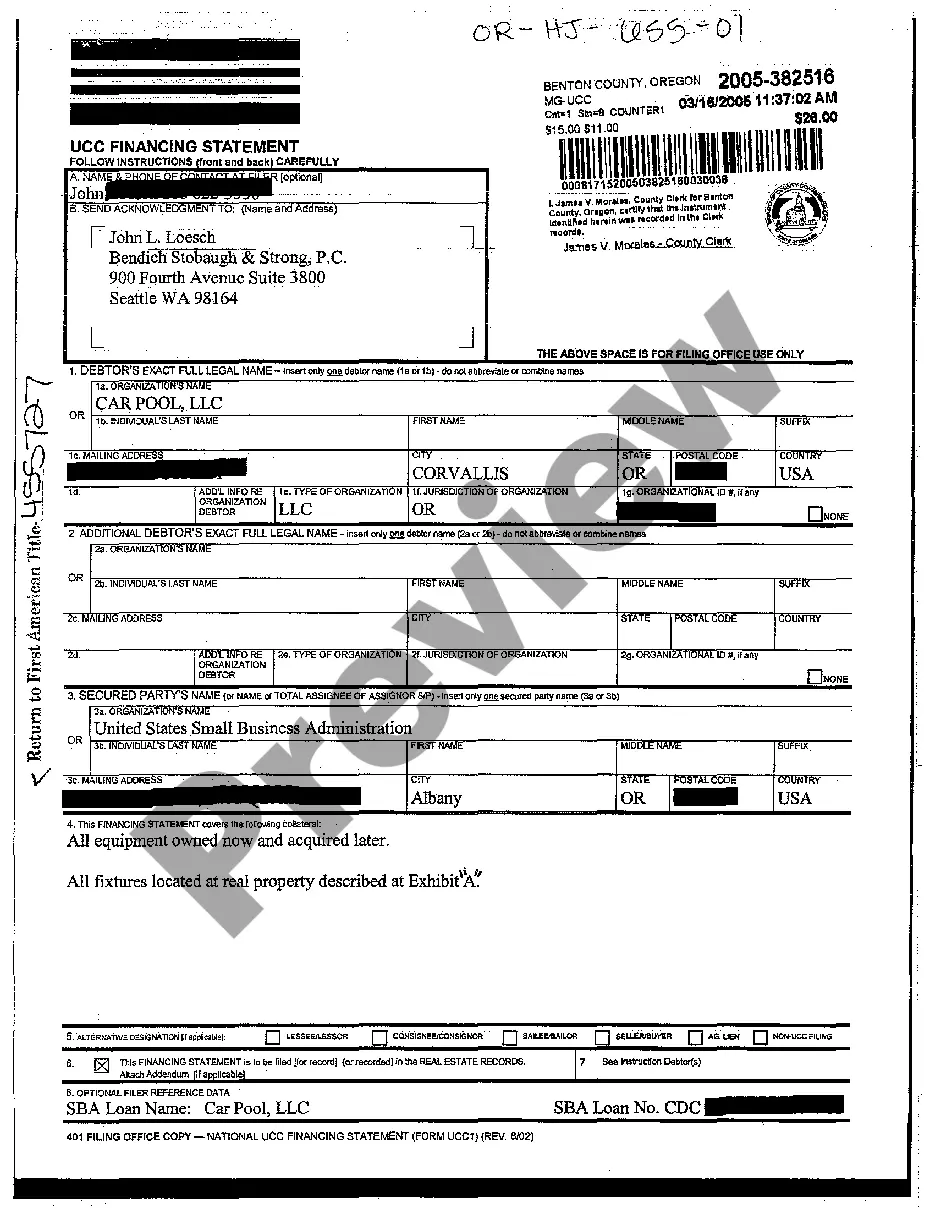
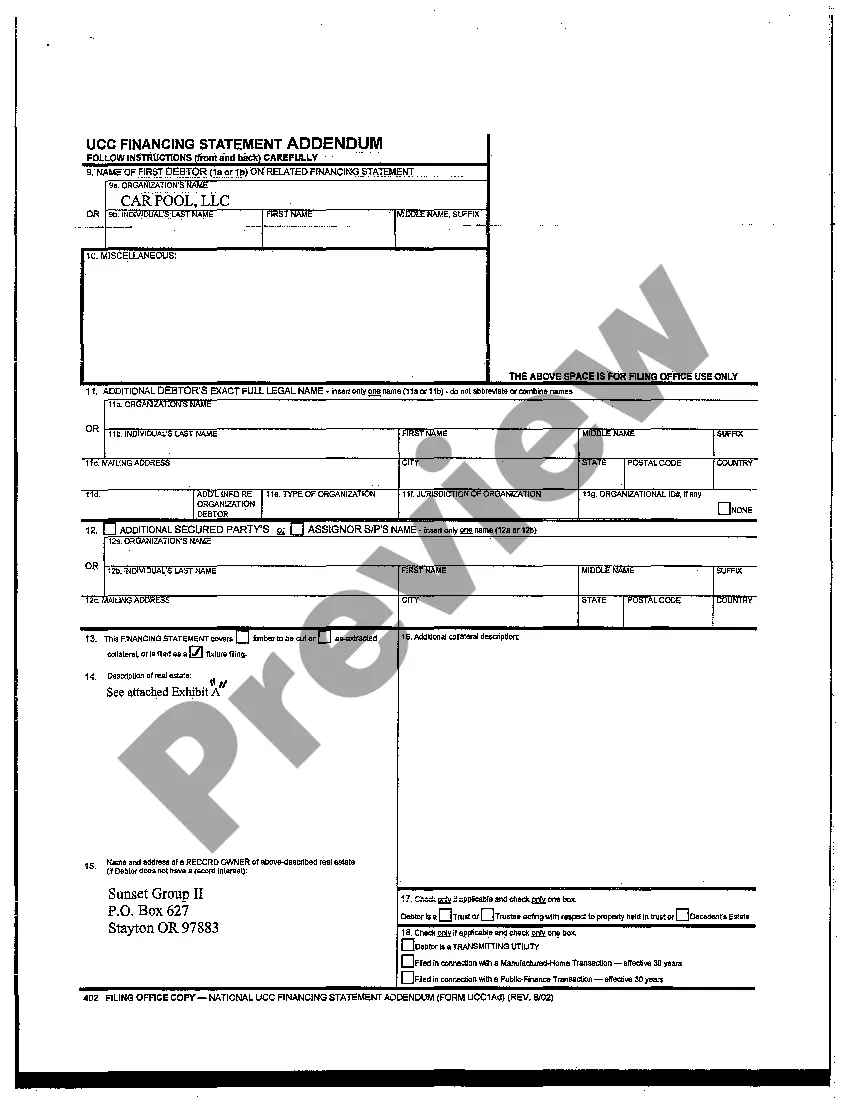
Title: UCC Filing Explained: Understanding the Basics and Types of UCC Filings Introduction: In the realm of business and commercial transactions, UCC filing plays a pivotal role in establishing and protecting secured interests. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of UCC filing, explaining its significance, process, and different types that exist. Key Terms/Keywords: UCC filing, Uniform Commercial Code, secured interests, collateral, debtor, creditor, financing statement, UCC-1, UCC-3, perfection, priority, public record, personal property, real property, tangible assets, intangible assets. 1. What is UCC Filing? UCC filing refers to the process of creating a public record to establish and enforce a secured interest in certain types of property. The Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) is a set of laws enacted in the United States to standardize commercial transactions across different states. UCC filing helps parties involved in such transactions by providing notice of a creditor's financial interest in a debtor's property. 2. Importance of UCC Filing: UCC filing is crucial for creditors as it allows them to secure their investments against default or bankruptcy. It offers a legal framework to establish priority rights in case multiple creditors claim the same collateral. Additionally, UCC filing helps potential buyers and lenders assess the financial status and risks associated with a debtor. For debtors, UCC filing may enhance their credibility by showcasing their existing creditor relationships. 3. Types of UCC Filings: a. Initial UCC-1 Filing: The UCC-1 financing statement is the most common filing used to establish a creditor's interest in personal property collateral. It records essential details such as debtor and creditor names, description of collateral, and the nature of the secured transaction. b. Amendments and Continuations (UCC-3): UCC-3 filings are utilized to modify, amend, or extend the original UCC-1 filing. Common reasons for UCC-3 filings include updating debtor information, adding or removing collateral, and extending the duration of the lien. c. UCC-1 Fixture Filing: A UCC-1 fixture filing is a unique type of filing used to create a security interest in goods that have become fixtures, i.e., personal property that is attached to real property. This filing ensures that the creditor's interest is recognized and protected in case of real estate transactions or foreclosure proceedings. d. UCC-1 Farm Products Filing: Farm products, including crops, livestock, and certain supplies, require a specific UCC-1 farm products filing. This filing creates a public record of the creditor's security interest in farm-related collateral. It is important when multiple creditors claim the same agricultural assets. e. UCC-1 Public Finance Filing: UCC-1 public finance filing deals with the unique requirements of government financing. It allows lenders to establish priority rights in collateral related to public debt transactions, including tax-exempt securities, bond issuance, and public infrastructure projects. Conclusion: UCC filing is a vital tool for creditors and debtors involved in commercial transactions. By understanding the basics of UCC filing and the various types available, parties can ensure proper execution, protection of interests, and compliance with the UCC. It is always recommended consulting legal professionals to navigate the complexity of UCC filing and guarantee the desired outcomes in securing collateral or conducting business transactions.
Ucc Filing Explained
Description filing a ucc 1 on yourself template
How to fill out Fixture Filing Meaning?
It’s obvious that you can’t become a legal expert overnight, nor can you grasp how to quickly draft Ucc Filing Explained without having a specialized background. Creating legal forms is a time-consuming process requiring a specific education and skills. So why not leave the creation of the Ucc Filing Explained to the pros?
With US Legal Forms, one of the most comprehensive legal template libraries, you can access anything from court papers to templates for internal corporate communication. We know how important compliance and adherence to federal and state laws and regulations are. That’s why, on our website, all templates are location specific and up to date.
Here’s start off with our platform and obtain the document you require in mere minutes:
- Discover the document you need by using the search bar at the top of the page.
- Preview it (if this option available) and check the supporting description to figure out whether Ucc Filing Explained is what you’re searching for.
- Begin your search again if you need a different form.
- Set up a free account and select a subscription plan to purchase the form.
- Pick Buy now. Once the transaction is complete, you can download the Ucc Filing Explained, fill it out, print it, and send or send it by post to the designated people or organizations.
You can re-gain access to your documents from the My Forms tab at any time. If you’re an existing customer, you can simply log in, and find and download the template from the same tab.
No matter the purpose of your forms-whether it’s financial and legal, or personal-our platform has you covered. Try US Legal Forms now!
is a ucc filing bad Form popularity
ucc filing on personal property Other Form Names
oregon ucc FAQ
If none of the persons listed under Paragraphs (A)(1) through (10) of this Section are reasonably available, then the patient's attending physician shall have the discretion to provide or perform any surgical or medical treatment or procedures, including but not limited to an autopsy, and may also make decisions ...
The two most common advance directives for health care are the living will and the durable power of attorney for health care. Living will: A living will is a legal document that tells doctors how you want to be treated if you cannot make your own decisions about emergency treatment.
Unlike medical power of attorney documents, Five Wishes goes beyond just medical and healthcare topics to express spiritual, emotional and personal wishes. It aims to be a more holistic way of planning for the end of life.
A Do Not Resuscitate (DNR) order is another kind of advance directive. A DNR is a request not to have cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) if your heart stops or if you stop breathing. (Unless given other instructions, hospital staff will try to help all patients whose heart has stopped or who have stopped breathing.)
The most common types of advance directives are the living will and the durable power of attorney for health care (sometimes known as the medical power of attorney). There are many advance directive formats.
Louisiana Advance Directive Forms. An advance directive is a legally binding document that gives instructions for your healthcare in the event that you are no longer able to make or communicate those decisions yourself.
Louisiana law recognizes two types of advance directives: 1) A living will (also known as a declaration); and 2) A health care power of attorney. For your convenience, we have included a living will that is compliant with Louisiana law in this booklet.