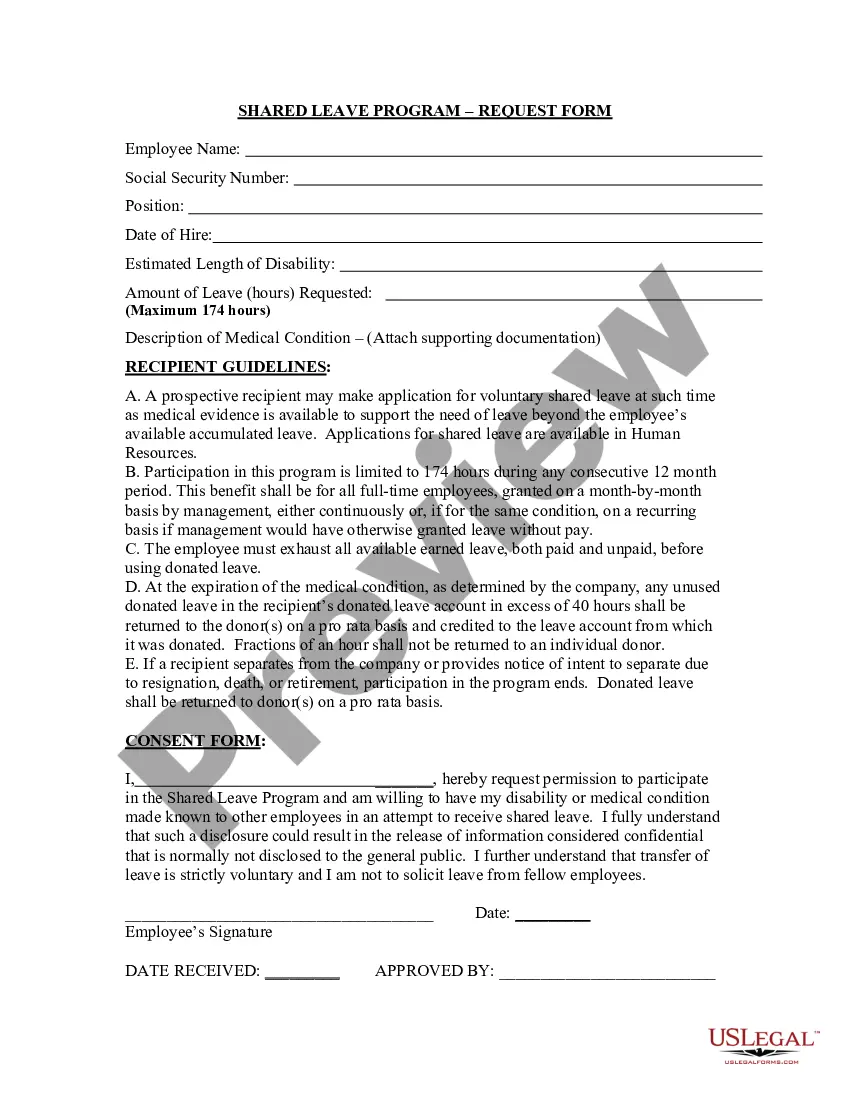
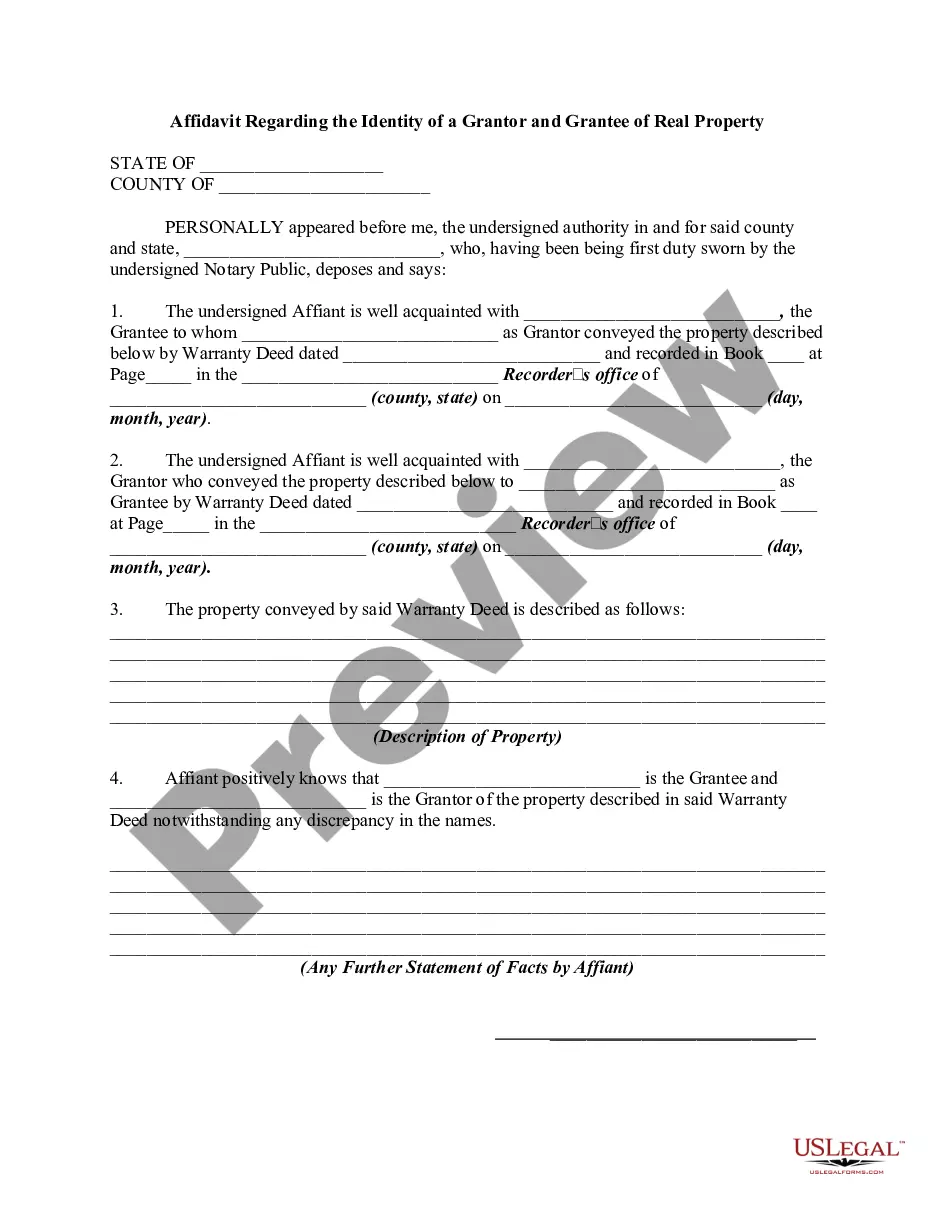
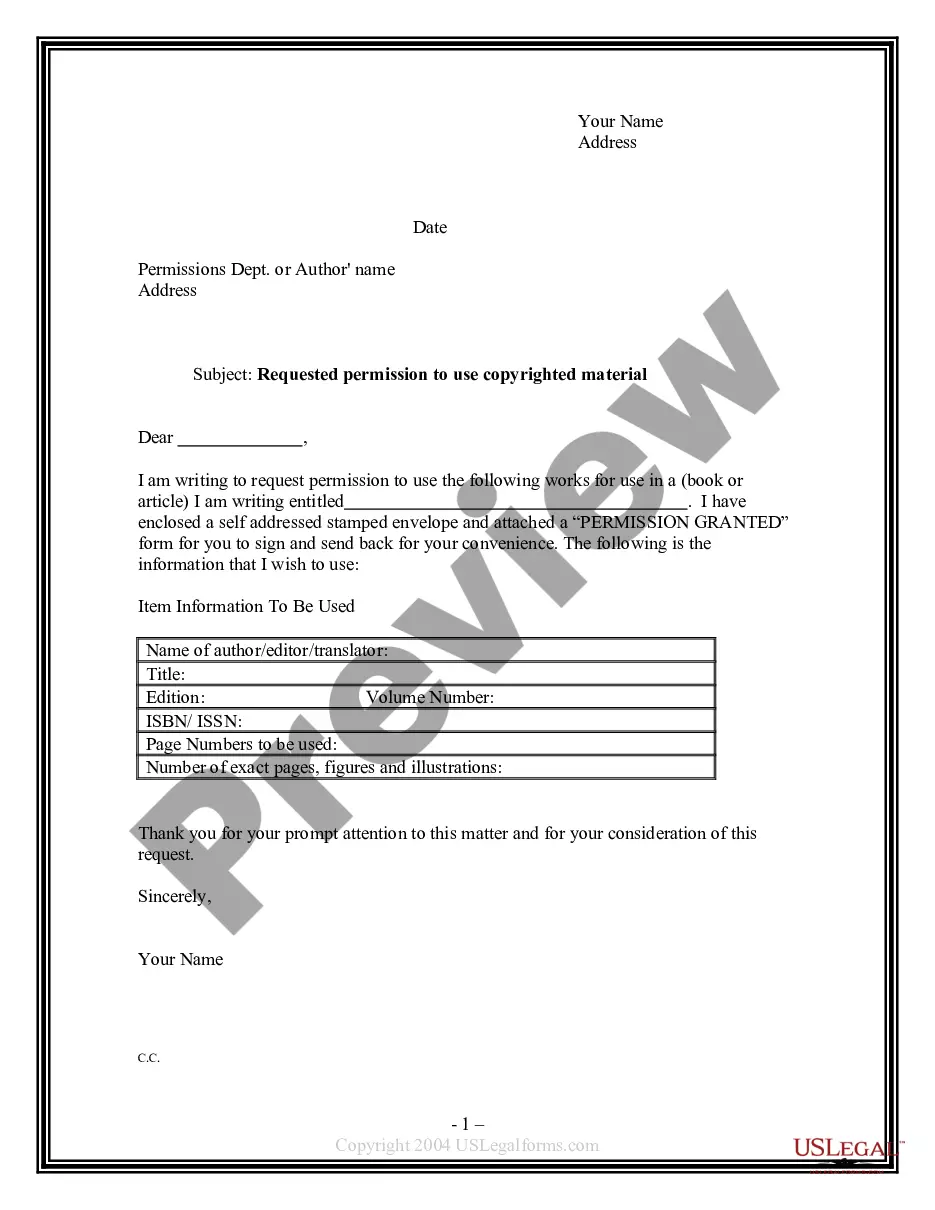
A Notary signature is a prominent feature of any official document or agreement that has been notarized. It serves as proof that the notary public, a designated state official, has verified the identities of the signatories and witnessed the signing of the document. This signature also confirms that the document is authentic, legitimate, and binding in a court of law. One example of a Notary signature entails the notary signing the document with their full name, followed by their official title, such as "John Doe, Notary Public." This conventional format provides a clear indication of the notary's identity and professional role. Another type of Notary signature is known as an inked stamp or seal. In this case, the notary would apply their unique official seal, typically embossed or stamped onto the document. The seal contains vital information, including the notary's name, commission number, state of commission, and expiration date. This method adds an extra layer of authenticity to the notarized document as it prevents tampering or alteration. It is worth noting that in some jurisdictions, notaries may also use an electronic signature. Electronic notarization involves the use of digital platforms or software that allows parties to sign documents electronically, with the notary electronically attaching their signature and seal. Although the format may differ, the purpose of the notary's signature remains the same: to authenticate the document and ensure its legality. In conclusion, a Notary signature is a crucial element in notarized documents, providing credibility and legal validity. Whether in the form of a handwritten signature, an inked stamp, or an electronic signature, it serves as a tangible proof that the notary public has performed their duties in accordance with the law.
Notary Signature Example With Explanation
Description
How to fill out Notary Signature Example With Explanation?
Whether for business purposes or for personal matters, everybody has to deal with legal situations at some point in their life. Filling out legal paperwork demands careful attention, starting with picking the right form template. For example, when you choose a wrong edition of a Notary Signature Example With Explanation, it will be rejected once you send it. It is therefore crucial to get a trustworthy source of legal documents like US Legal Forms.
If you have to obtain a Notary Signature Example With Explanation template, stick to these simple steps:
- Find the sample you need by utilizing the search field or catalog navigation.
- Check out the form’s information to make sure it fits your situation, state, and county.
- Click on the form’s preview to view it.
- If it is the incorrect form, return to the search function to locate the Notary Signature Example With Explanation sample you need.
- Download the file if it matches your requirements.
- If you already have a US Legal Forms profile, just click Log in to gain access to previously saved documents in My Forms.
- If you do not have an account yet, you may obtain the form by clicking Buy now.
- Select the correct pricing option.
- Complete the profile registration form.
- Choose your payment method: use a bank card or PayPal account.
- Select the file format you want and download the Notary Signature Example With Explanation.
- Once it is downloaded, you can complete the form by using editing software or print it and finish it manually.
With a vast US Legal Forms catalog at hand, you never need to spend time searching for the right sample across the internet. Make use of the library’s straightforward navigation to find the correct template for any occasion.
Form popularity
FAQ
Feb. 22, 2023, at p.m. COLUMBIA, S.C. (AP) ? The Republican-controlled South Carolina House voted overwhelmingly Wednesday to allow lawful firearm owners to carry handguns openly or concealed without a state permit.
A South Carolina firearm bill of sale is a legal document in the State of South Carolina that formalizes the sale and purchase of a firearm of any kind. The document will provide identifying information with regard to the firearm, change of ownership, the seller, and the buyer.
South Carolina Firearms Laws Firearm laws in South Carolina make it illegal to own an unregistered handgun, shotgun, or rifle, purchase or sell ammunition unless licensed to do so, and manufacture, transport, or possess certain short-barreled rifles and certain firearms with silencers.
South Carolina is rather easy as far as the process is concerned. To purchase a handgun or long gun in SC you are required to have either a Concealed carry permit, or have an instant background check done. If you do not have a concealed carry permit, The firearms dealer will have you fill out an ATF form 4473.
A South Carolina firearm bill of sale is a legal document in the State of South Carolina that formalizes the sale and purchase of a firearm of any kind. The document will provide identifying information with regard to the firearm, change of ownership, the seller, and the buyer.
South Carolina is a "shall issue" state for citizens and lawful permanent residents who are 21 years or older. Permit required for open carry? Open carry of long guns is allowed without a permit. Open carry of a handgun is allowed by individuals with a concealed weapon permit.
Do You Have to Register a Gun in South Carolina? No. South Carolina has no law requiring residents to register firearms.
South Carolina has no law requiring firearms to be registered.