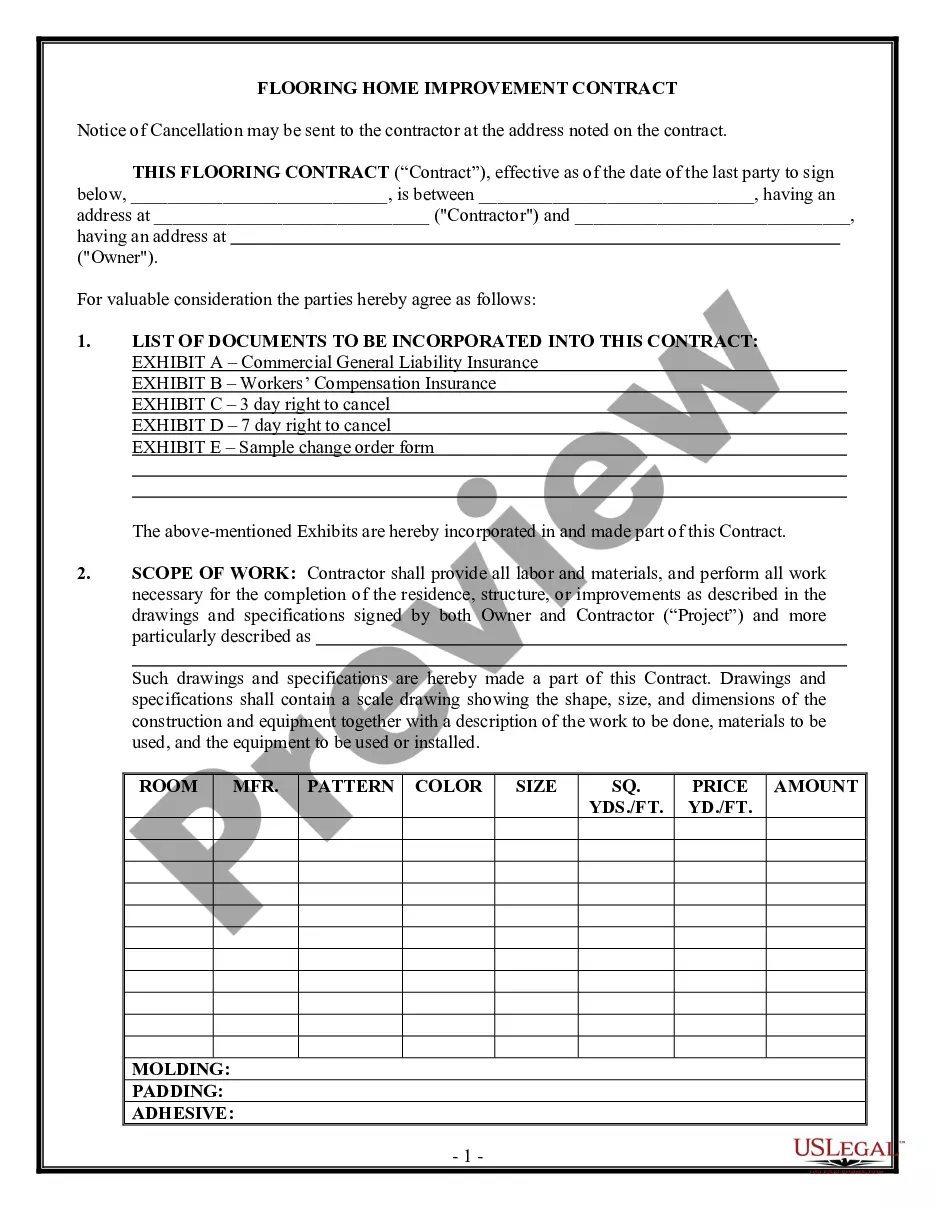
This form is a sample letter in Word format covering the subject matter of the title of the form.
State Bar Fort Wayne Photos In Minnesota
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
In order to be eligible for admission without taking the Minnesota Bar Exam, the applicant must have engaged in the active practice of law for 5 of the 7 years preceding admission or received a scaled score of 145 or above on the MBE within 24 months of application, and be a graduate of an ABA accredited law school.
If you received a scaled score of 145 or higher on the Multistate Bar Examination (MBE) in the past 36 months and you were admitted in another jurisdiction on the basis of the examination in which you obtained that score, you may be eligible. See Rule 7B for additional requirements.
Reciprocity. You may be admitted to the Minnesota Bar without taking the bar exam (admission on motion) if you have graduated with a JD degree from an ABA-approved law school and meet one of the following requirements: You have been practicing law for a minimum of 1,000 hours per year for 36 of the past 60 months.
How can I be admitted to the Minnesota Bar without taking the exam? If your educational requirements qualify under Rule 4A, there are three ways you can be admitted on motion in Minnesota: If you have been practicing law for at least 1000 hours per year for at least 36 of the past 60 months, you may be eligible.
The MSBA is one of the oldest state bar associations in the United States. Membership is not required to practice law in Minnesota.
Minnesota Applicants to the Minnesota bar must have either (1) a degree from a law school that is fully or provisionally approved by the ABA or (2) all of the following: (a) a JD from any US law school, (b) a bachelor's degree accredited by an agency recognized by the US Department of Education, and (c) evidence that ...
The UBE is an exam prepared by the National Conference of Bar Examiners (NCBE). It is comprised of six (6) Multistate Essay Examination (MEE) questions, two (2) Multistate Performance Test questions (MPT), and the Multistate Bar Examination (MBE).
The Minnesota Bar Exam is a twice-yearly exam that tests law students for their ability to practice law in the state. Successful applicants, those who score higher than a 260, pass and enter the bar if they meet the other requirements put forth by the state.
The Minnesota Board of Law Examiners will accept applications for admission by motion, without examination.