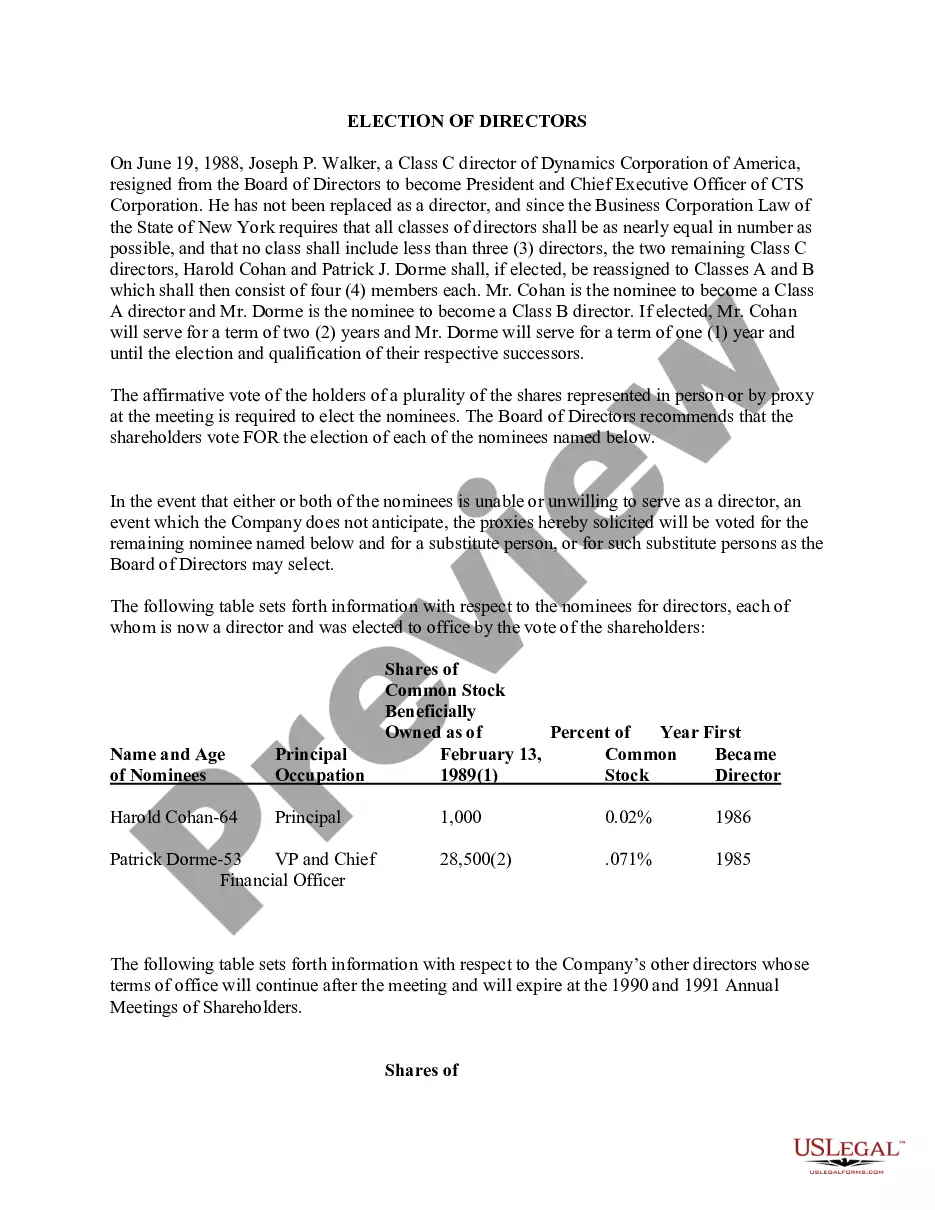
Tort Negligence Liability For Dummies In Clark
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Any one of the four Cs of medical malpractice (compassion, communication, competence, and charting), which are outlined below, violates a doctor's fiduciary duty of care.
To succeed in a negligence case in California, you must establish four key elements: duty, breach of duty, causation, and damages.
Legally speaking, negligence is a failure to use reasonable care under the circumstances. In order to establish negligence, you must be able to prove four “elements”: a duty, a breach of that duty, causation and damages.
Under California law, there are four legal principles of negligence required for a claim include duty of care, breach of duty of care, causation, and damages.
So you should say something like: “In order to sue B in negligence for compensation for injury to his leg, A will have to show that: (1) B owed him a duty of care; (2) B breached that duty of care; (3) B's breach caused A to suffer the leg injury for which he wants compensation; and (4) that loss is actionable (that is ...
In order to win your negligence claim, and obtain one or more of the types of damages available to you as an injured victim, your personal injury lawyer will have to prove four things: (1) duty; (2) breach; (3) causation; and (4) damages. More specifically, your attorney will have to prove the following: Duty.
For information regarding a specific legal issue affecting you, please contact an attorney in your area. The elements of a negligence claim include duty, breach, causation, and damages. Negligence occurs when one person fails to exercise the care we expect of an ordinary or reasonable person in that situation.
To recover on a negligence claim, the plaintiff must establish the existence of a legal duty on the part of the defendant, a breach of that duty, causation, and damages. United Blood Servs. v. Quintana, 827 P.
Some common negligence case examples under this category include, but are not limited to, the following scenarios: A driver runs a stop sign and slams into another car. A driver operates illegally in the bicycle lane and hits a bicyclist. A driver runs a red light and hits a pedestrian in a crosswalk.
These legal elements include a professional duty owed to a patient, breach of duty, proximate cause or causal con- nection elicited by a breach of duty, and resulting in- juries or damages suffered. 1 These 4 elements apply to all cases of negligence regardless of specialty or clin- ician level.