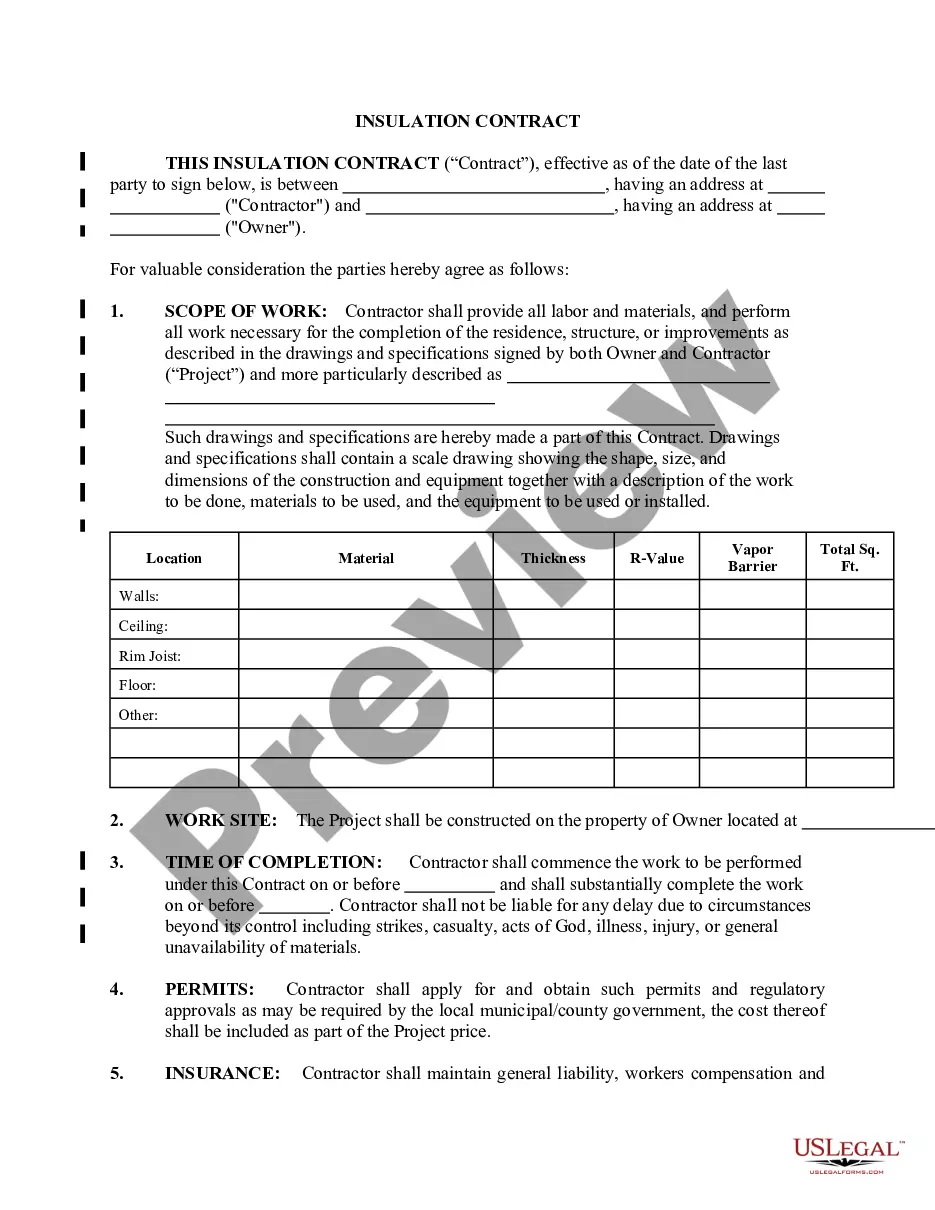
Torts For Dummies In Travis
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
From this perspective, to make a claim in tort a claimant must show that they have (or had) a right, exercisable against the defendant, that has been infringed. However, the claimant's right is not a right exercisable against the defendant as it is not a property right (which is exercisable against the world).
Explanation: In an intentional tort case, the plaintiff must establish four fundamental elements to prove the defendant's liability. The four elements are: intention, act, causation, and harm or damage.
To file a claim, complete these steps: Complete Standard Form 95. Explain in detail what happened, using additional pages if necessary. Attach all documents that support your claim, which may include the following. Submit the completed Standard Form 95 and supporting documents to the OPM Office of the General Counsel.
Intentional torts involve deliberate actions that cause harm, such as assault or battery. To win an intentional tort case, you must prove that the defendant intended to cause harm, and that harm resulted from their actions.
Simply put, a tort is an action by one party which results in loss or harm to another party and is governed by civil, not criminal, law. There are three main categories of torts: intentional, negligent, and strict liability. Assault, battery, and fraud are common examples of intentional torts.
To win a tort case, three elements that must be established in a claim include: That the defendant had a legal duty to act in a certain way. That the defendant breached this duty by failing to act appropriately. That the plaintiff suffered injury or loss as a direct result of the defendant's breach.
The existence of a legal duty to the plaintiff; The defendant breached that duty; The plaintiff was injured; and, The defendant's breach of duty caused the injury.
Negligence Torts This usually involves car accidents, slip and fall accidents, or medical malpractice. To succeed in a negligence claim, you must prove duty, breach, causation, and damages.
Analyzing Tort Essay Exam Problems List the people in the problem. Identify the injured people. Identify the relationships between the injured persons and all other persons, injured or uninjured. Identify unnamed persons or legal entities who breached a duty to the plaintiff.
Under California law, there are four legal principles of negligence required for a claim include duty of care, breach of duty of care, causation, and damages.