Us Amendments For Dummies In Montgomery
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
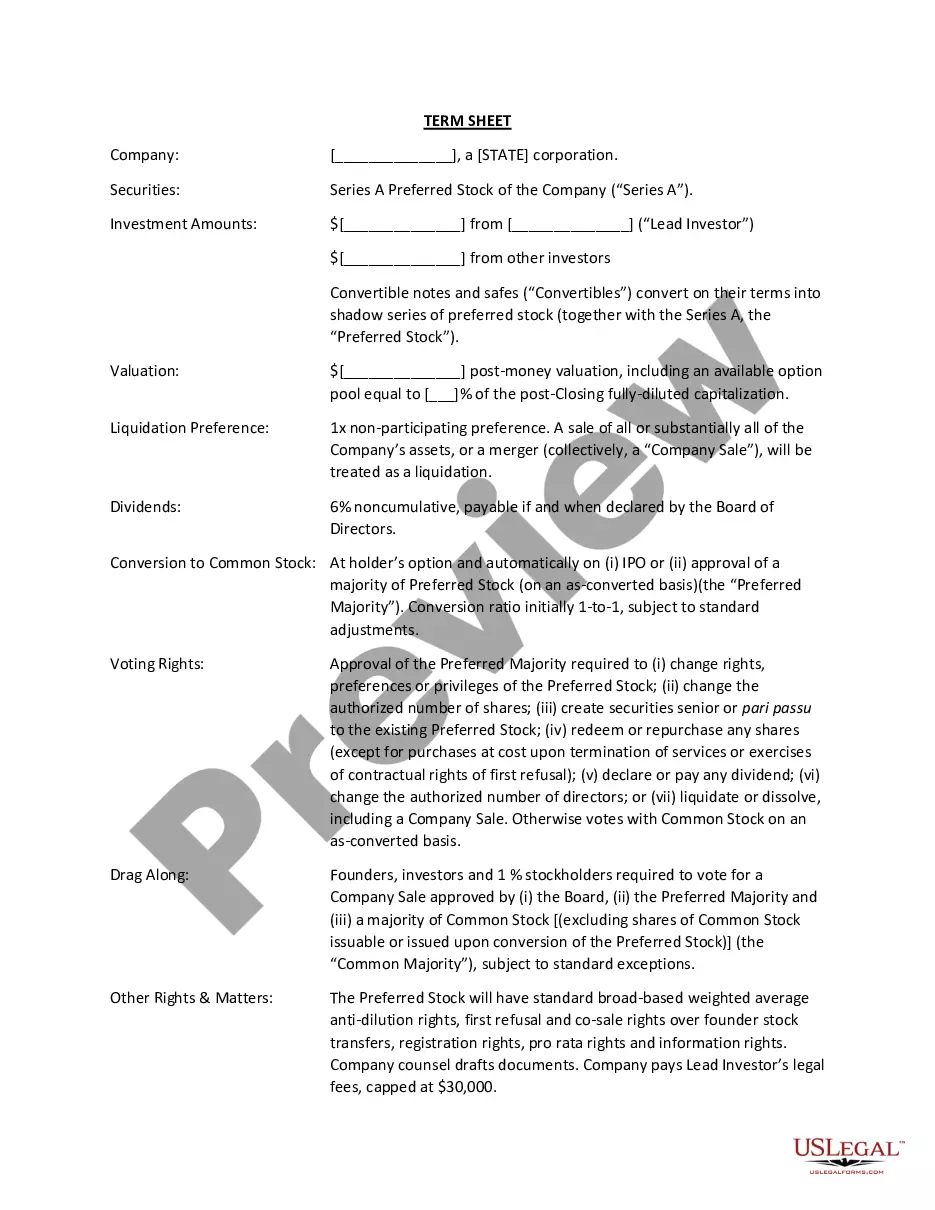
Congress must call a convention for proposing amendments upon application of the legislatures of two-thirds of the states (i.e., 34 of 50 states). Amendments proposed by Congress or convention become valid only when ratified by the legislatures of, or conventions in, three-fourths of the states (i.e., 38 of 50 states).
The Constitution provides that an amendment may be proposed either by the Congress with a two-thirds majority vote in both the House of Representatives and the Senate or by a constitutional convention called for by two-thirds of the State legislatures.
Amendment Ten to the Constitution was ratified on December 15, 1791. It makes clear that any powers that are not specifically given to the federal government, nor withheld from the states, are reserved to those respective states, or to the people at large.
An amendment may be proposed by a two-thirds vote of both Houses of Congress, or, if two-thirds of the States request one, by a convention called for that purpose. The amendment must then be ratified by three-fourths of the State legislatures, or three-fourths of conventions called in each State for ratification.
The U.S. Constitution is difficult to change and has only been amended 27 times. State constitutions, on the other hand, are much easier to modify, and state constitutional amendments are adopted on a regular basis. The current constitutions of the 50 states have been amended around 7,000 times.
Under Article V of the Constitution, there are two ways to propose and ratify amendments to the Constitution. To propose amendments, two-thirds of both houses of Congress can vote to propose an amendment, or two-thirds of the state legislatures can ask Congress to call a national convention to propose amendments.
Change or addition to a law is called an amendment. The word usually refers to a change to the constitution of a government. In the United States there have been 27 amendments to the Constitution.
How to create a contract amendment Pinpoint what you want to change or add. Look at your contract and write down the parts you need to change. Date and title the new amendment. Next, add the current date and the title and date of the original agreement to the document. Draft and describe the changes. Finalize the changes.
Bill of Rights - The Really Brief Version 1Freedom of religion, speech, press, assembly, and petition. 7 Right of trial by jury in civil cases. 8 Freedom from excessive bail, cruel and unusual punishments. 9 Other rights of the people. 10 Powers reserved to the states.5 more rows
U.S. Constitutional Amendments Second Amendment - Bearing Arms. Third Amendment - Quartering Soldiers. Fourth Amendment - Search and Seizure. Fifth Amendment - Rights of Persons. Sixth Amendment - Rights of Accused in Criminal Prosecutions. Seventh Amendment - Civil Trials. Eighth Amendment - Cruel and Unusual Punishment.