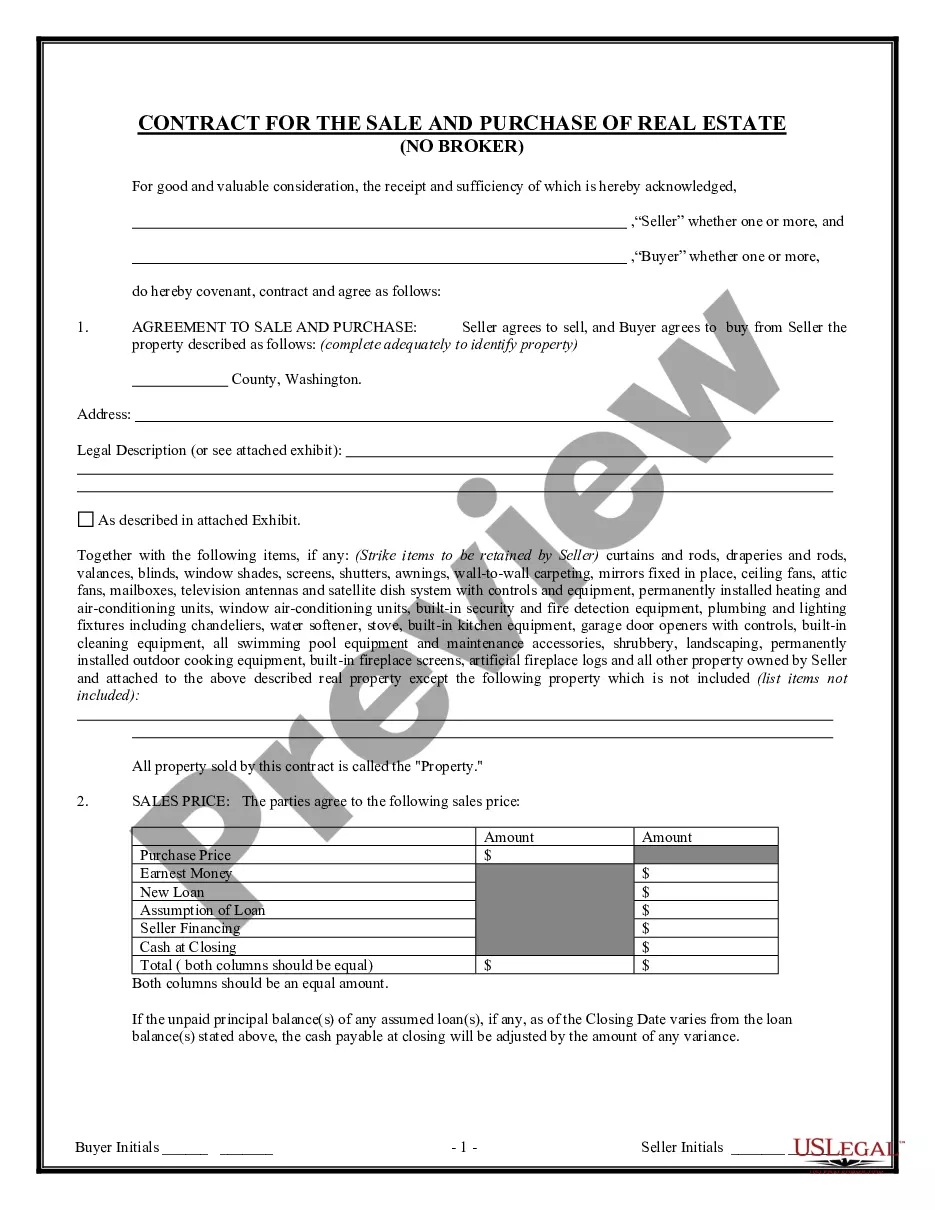
This is a multi-state form covering the subject matter of the title.
Title Vii Of The Civil Rights Act Of 1964 Originally Provided For Protection Against In Allegheny
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
In 1965, King helped to organize the Selma to Montgomery marches. He worked tirelessly to assure the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and was in attendance when President Johnson signed both that Act and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 into law.
The Civil Rights Movement was a social movement in the United States that tried to gain equal rights for African Americans that European Americans had. The movement is famous for using non-violent protests and civil disobedience (peacefully refusing to follow unfair laws).
This act, signed into law by President Lyndon Johnson on July 2, 1964, prohibited discrimination in public places, provided for the integration of schools and other public facilities, and made employment discrimination illegal. It was the most sweeping civil rights legislation since Reconstruction.
This act, signed into law by President Lyndon Johnson on July 2, 1964, prohibited discrimination in public places, provided for the integration of schools and other public facilities, and made employment discrimination illegal. It was the most sweeping civil rights legislation since Reconstruction.
The biggest failure of the Civil Rights Movement was in the related areas of poverty and economic discrimination. Despite the laws we got passed, there is still widespread discrimination in employment and housing. Businesses owned by people of color are still denied equal access to markets, financing, and capital.
This act, signed into law by President Lyndon Johnson on July 2, 1964, prohibited discrimination in public places, provided for the integration of schools and other public facilities, and made employment discrimination illegal. It was the most sweeping civil rights legislation since Reconstruction.