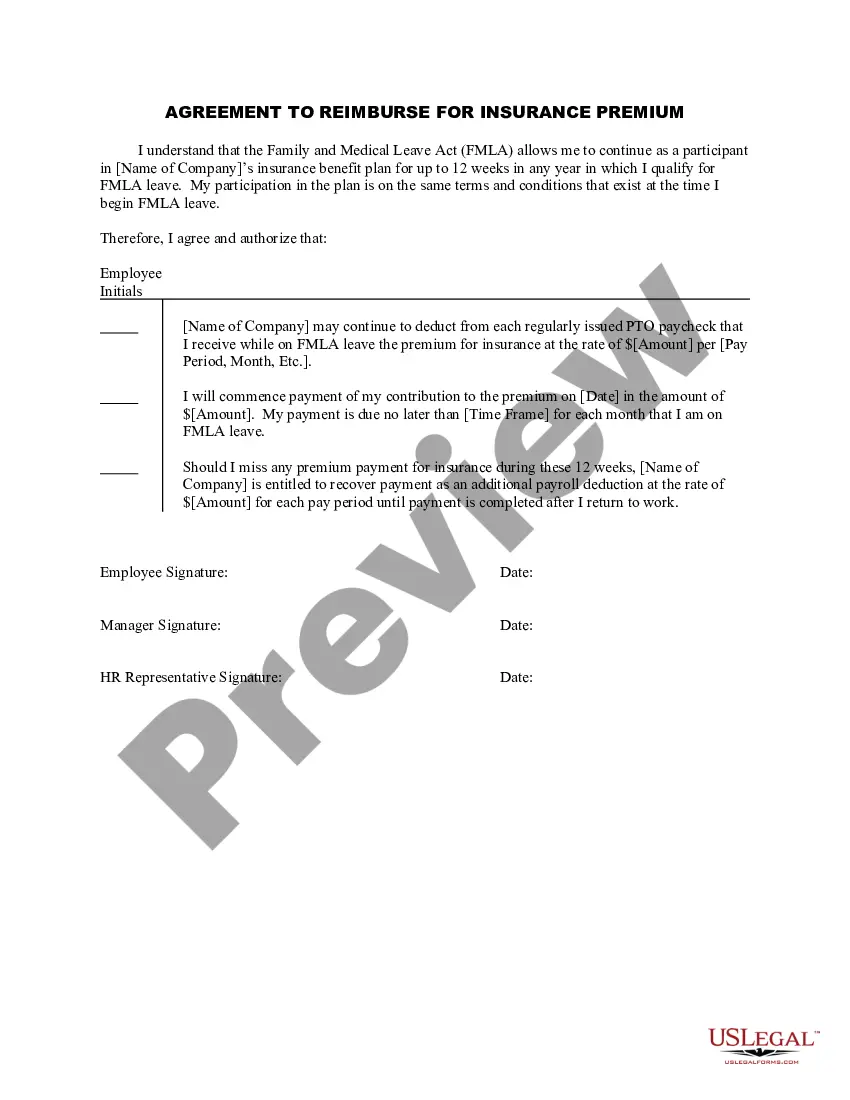
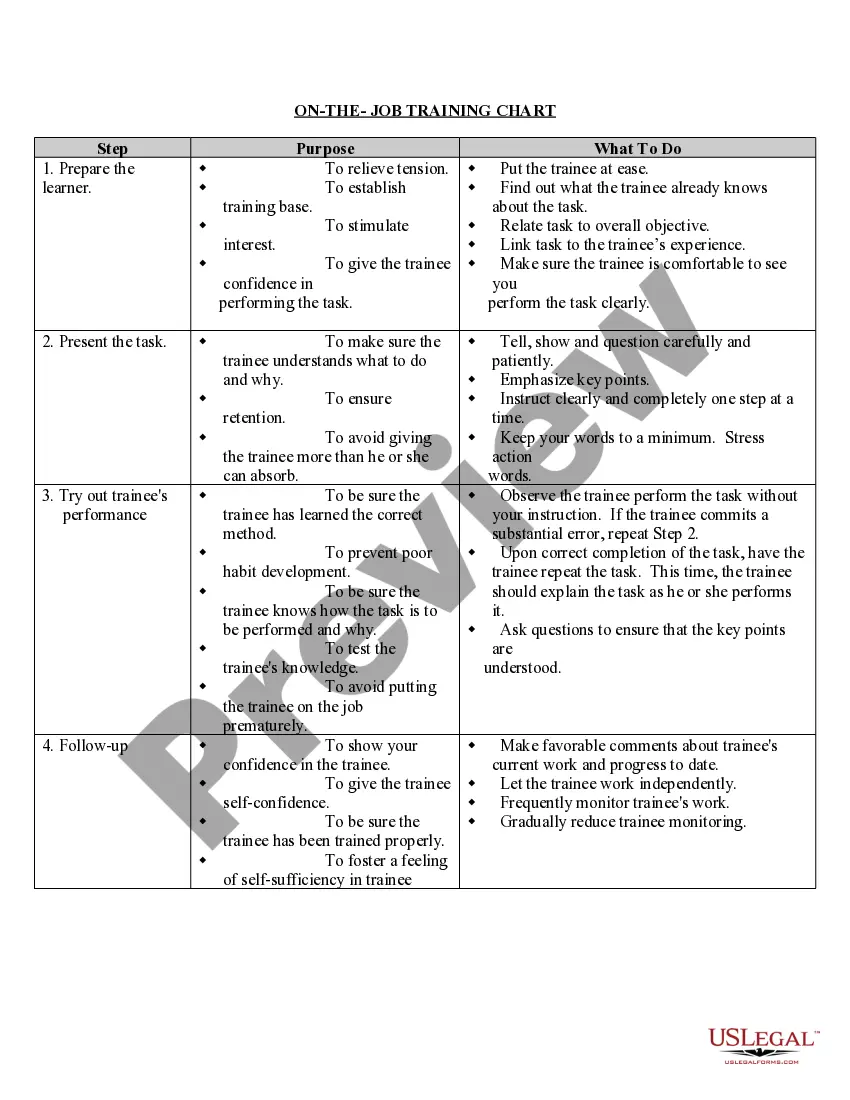
This is a multi-state form covering the subject matter of the title.
Title Vii Of The Civil Rights Act Of 1964 Forbids Employer Discrimination Brainly In Washington
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Simply put, Title VII does not apply to every employer. In fact, as a general rule, it typically only covers private and public sector employers with 15 or more employees. These employees may include: Part-time employees.
Examples of Employment Discrimination Failure to hire. Harassment. Quid pro quo: Conditioning employment or promotion on sexual favors. Hostile Work Environment: Continuous actions and comments based on protected characteristics that create an uncomfortable and hostile workplace.
Employers of five or more are subject to the FEHA's prohibition against employment discrimination. Harassment is prohibited in all workplaces, even those with only one employee or independent contractor on staff. “Employer” does not include the federal government or a non-profit religious association or corporation.
Passed by Congress in 1964 in honor of the late President Kennedy. This act banned racial discrimination in places such as hospitals and restaurants. This act also gave the government the power to desegregate schools. It led to the creation of the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission.
This act, signed into law by President Lyndon Johnson on July 2, 1964, prohibited discrimination in public places, provided for the integration of schools and other public facilities, and made employment discrimination illegal. It was the most sweeping civil rights legislation since Reconstruction.
Examples of Title VII violations include: Making sexist comments that a woman belongs in the kitchen as opposed to an office. Denying a job offer to an African American job applicant who is as qualified as the Caucasian applicant you hired. Refusing to allow Muslims prayer time throughout the day.
The employee must first present evidence that he is a member of a protected class, he was qualified for the position he held, he suffered an adverse employment action such as being fired, and that he was replaced with another worker who is not a member of that protected class.
1 Title VII and the ADA apply to employers (including employment agencies and unions) with 15 or more employees, and to federal, state, and local governments.