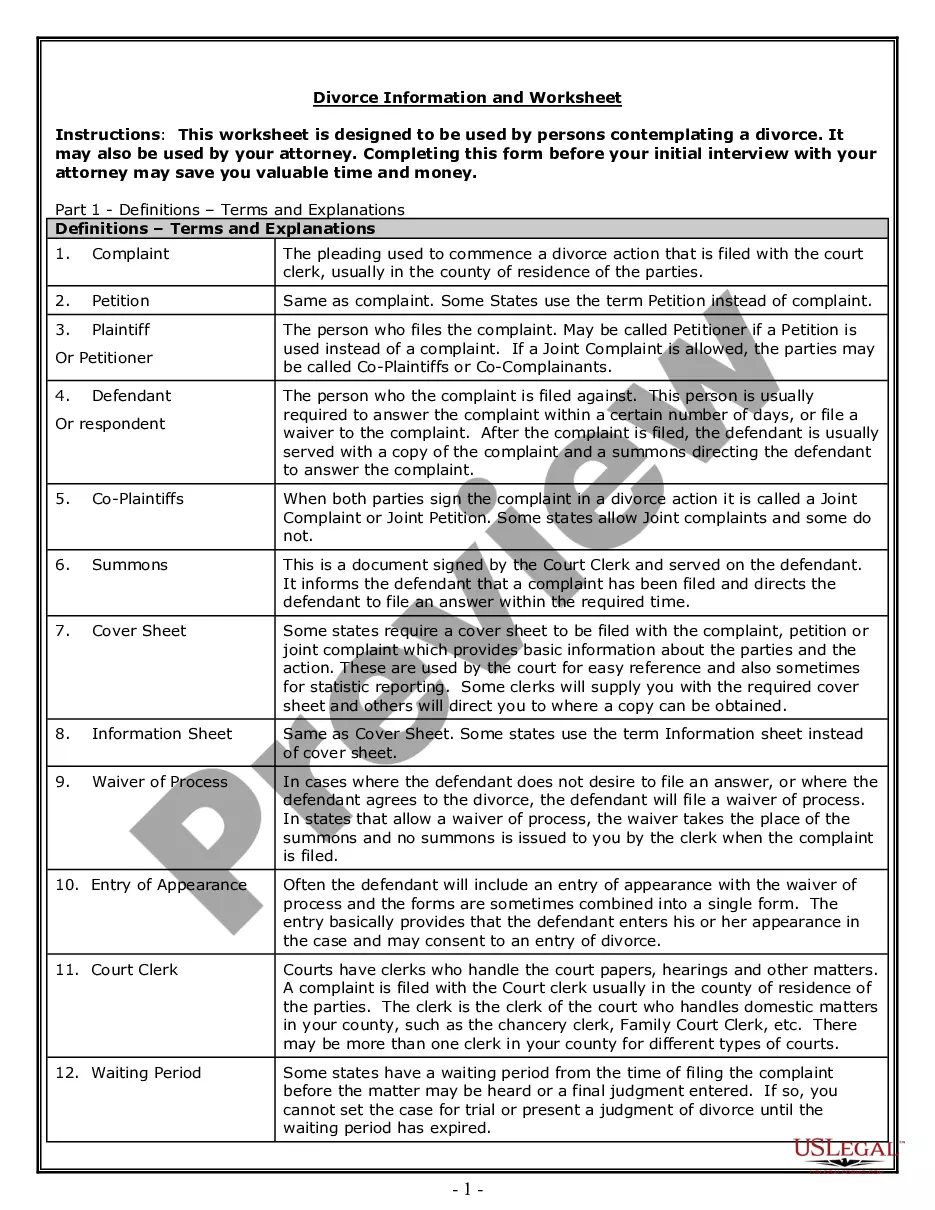
Discrimination Definition By Scholars In Montgomery
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Discrimination is thus the act of treating two – otherwise identical individuals – differently based on any attribute, behaviour, or characteristic that allows one to distinguish them.
Discrimination is the unfair or prejudicial treatment of people and groups based on characteristics such as race, gender, age, or sexual orientation.
Discrimination is the unfair or prejudicial treatment of people and groups based on characteristics such as race, gender, age, or sexual orientation.
A simplified description of the legal definition of discrimination is when a person is treated disfavourably or when a person's dignity is violated.
Direct evidence often involves a statement from a decision-maker that expresses a discriminatory motive. Direct evidence can also include express or admitted classifications, in which a recipient explicitly distributes benefits or burdens based on race, color, or national origin.
To treat a person or particular group of people differently, especially in a worse way from the way in which you treat other people, because of their race, gender, sexuality, etc.: be discriminated against She felt she had been discriminated against because of her age.
Moral philosophers have defined discrimination using a moralized definition. Under this approach, discrimination is defined as acts, practices, or policies that wrongfully impose a relative disadvantage or deprivation on persons based on their membership in a salient social group.