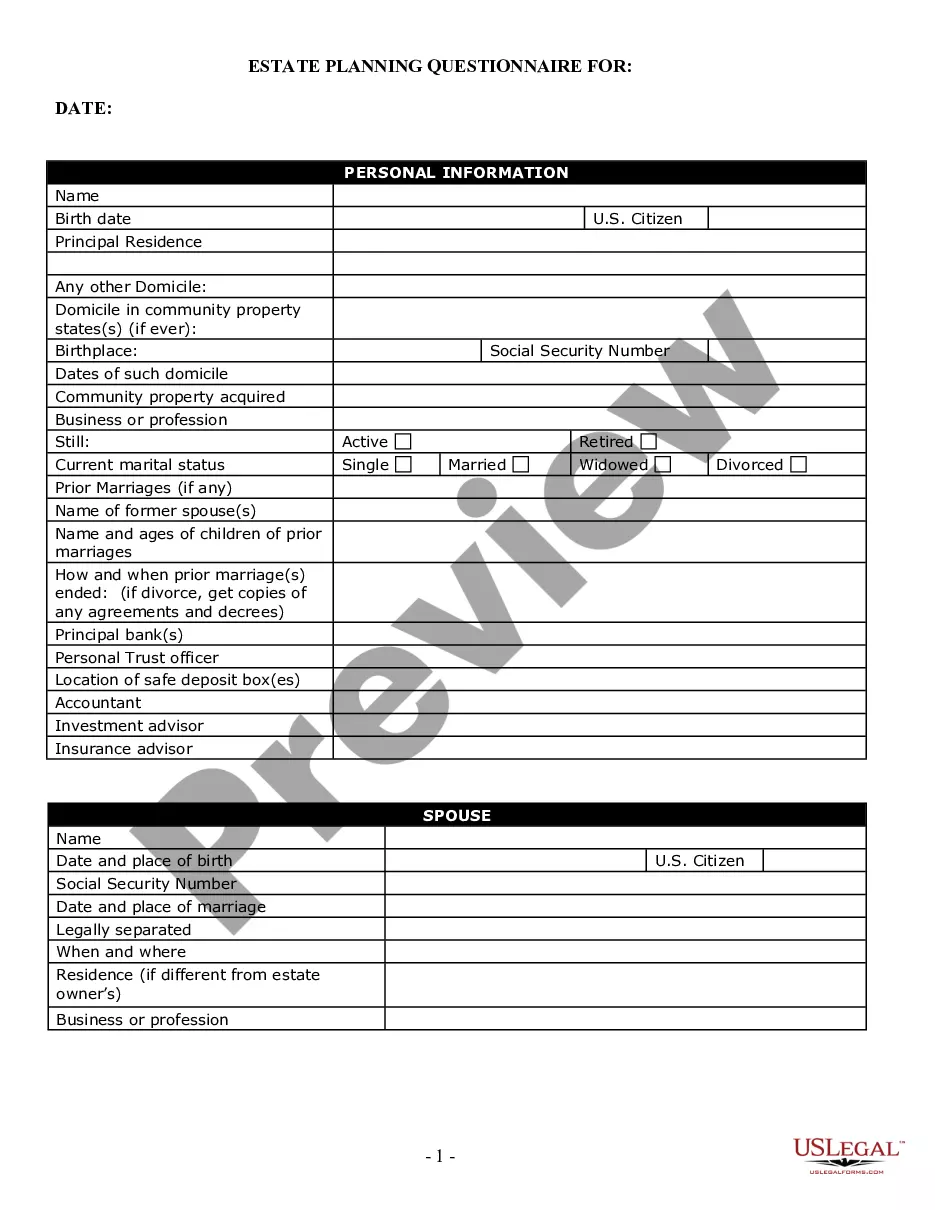
Contract For International Sale Of Goods Template In Salt Lake
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Top ten tips in drafting and negotiating an international contract Avoiding retaliation claims. The language of the contract. Clear contract prose. Common law versus civil law. Jurisdictional issues. Terms of art. Personnel. In negotiations, expect the unexpected.
Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (Vienna, 1980) The United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) drafted the CISG. Currently the CISG has seventy-six parties. The CISG aims to provide an internationally recognizable body of law governing the sale of goods across international borders.
In an international business contract, it's essential to define the jurisdiction that will govern the contract and the laws that will apply in the event of a dispute. Your dispute resolution section should also detail the agreed-upon dispute resolution mechanism.
Some common types of international contracts include sales agreements, distribution agreements, licensing agreements, joint venture agreements, and employment contracts.
An example of a treaty that does have provisions for further binding agreements is the UN Charter. By signing and ratifying the Charter, countries agreed to be legally bound by resolutions passed by UN bodies such as the General Assembly and the Security Council.
Top ten tips in drafting and negotiating an international contract Avoiding retaliation claims. The language of the contract. Clear contract prose. Common law versus civil law. Jurisdictional issues. Terms of art. Personnel. In negotiations, expect the unexpected.
Establish the rights and obligations of each party Identify the rights and obligations of each party under the agreement. Take into account any applicable laws or regulations that will apply. Consider what type of remedies or sanctions the parties may be entitled to in the event of a breach of the agreement.
The CISG governs international sales contracts if (1) both parties are located in Contracting States, or (2) private international law leads to the application of the law of a Contracting State (although, as permitted by the CISG (article 95), several Contracting States have declared that they are not bound by the ...
The CISG governs contracts for the international sales of goods between private businesses, excluding sales to consumers and sales of services, as well as sales of certain specified types of goods.
The United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CISG) entered into force on January 1, 1988 for the 11 contracting parties, including the United States. The United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) drafted the CISG.