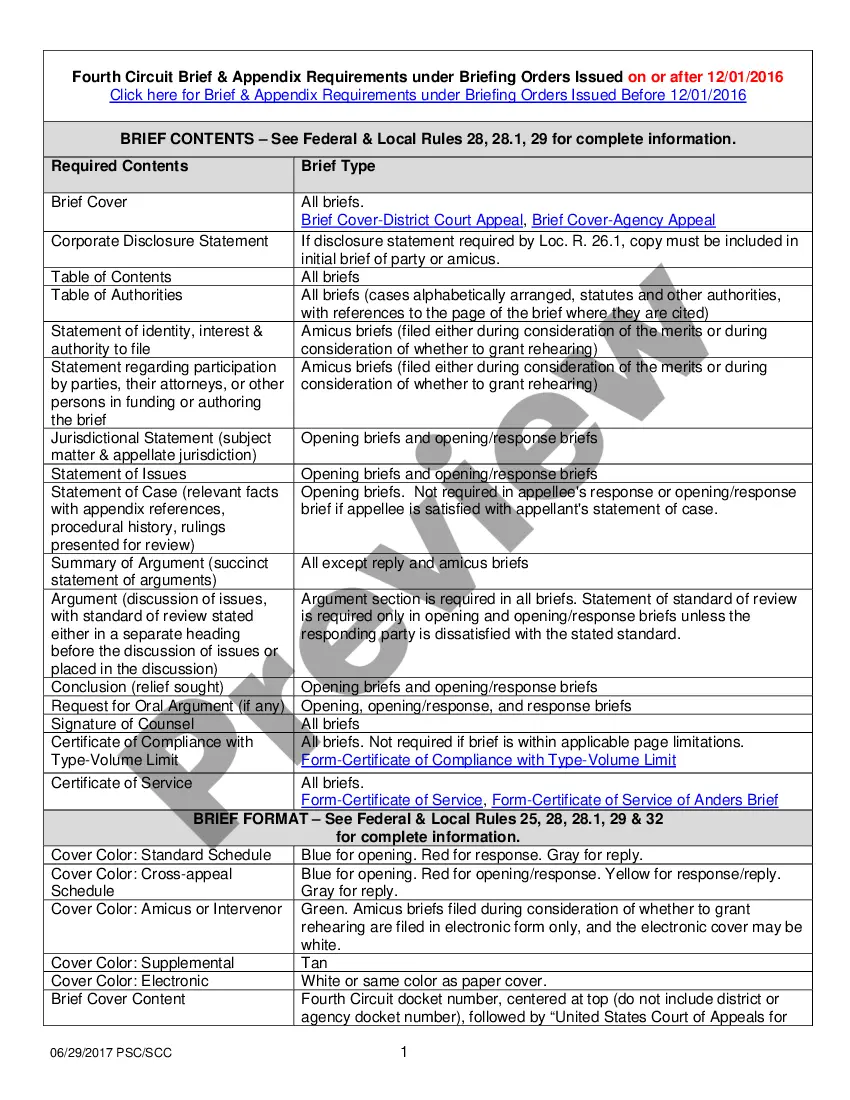
Chattel Form Paper With Code In North Carolina
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Chattel paper refers to a document used in secured transactions to sell property on credit while retaining some interest in the property.
The se- curity or lease interest is embodied in a writing which evidences the debt. This writing constitutes the "chattel paper," which may consist of a conditional sales contract, a chattel mortgage, a security agreement or a chattel lease,2 with or without an accompanying negotiable instru- ment.
Chattel paper is an asset type over which an entity can grant a security interest under Article 9 of the UCC. For more information on security interests in chattel paper, see Practice Note, UCC Creation, Perfection, and Priority of Security Interests.
Chattel property law is defined as any property that is not land or physical items that belong to the land. Chattel is movable goods and land cannot be moved. A house would not be considered chattel property because it is attached to the land.
Chattel is personal property that is movable between locations, as opposed to real property, which has a fixed location. Common examples include mobile homes, furniture, and automobiles. This article explains what chattel is and how it is used as security in chattel mortgages.
Chattel paper refers to a document used in secured transactions to sell property on credit while retaining some interest in the property.
Upon the issuance of a complaint and notice of hearing or order pursuant thereto, a notice of lis pendens, with a copy of the complaint and notice of hearing or order attached thereto, may be filed by the Officer in the Office of the Clerk of Superior Court for the county, as provided in G.S. § 1-120.2.
A basic case citation contains the following elements: (1) the case name, (2) the reporter volume number, (3) the abbreviation for the reporter, (4) the page number in the reporter on which the case begins, and (5) the date of the decision. North Carolina Supreme Court: King v. Town of Chapel Hill, 367 N.C. 400 (2014).