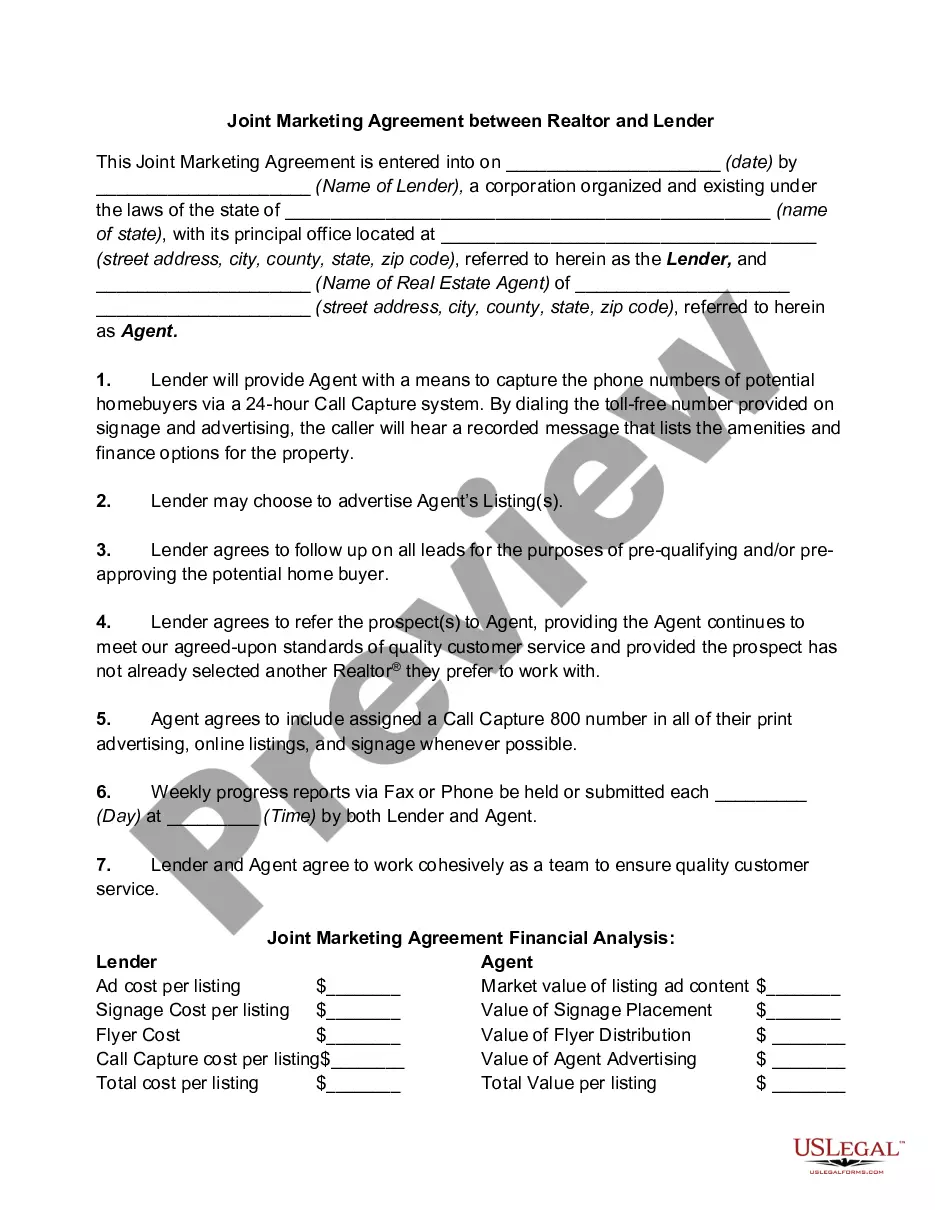
Arbitration Agreement With Employer In California
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Arbitration agreements are subject to certain rules in order to have enforceability under California and federal law. If an arbitration agreement fails to meet these requirements, it can be held unenforceable.
Under the Armendariz standards, an arbitration agreement will not be enforced in California if it is both “procedurally unconscionable” and “substantively unconscionable.” Any arbitration agreement required as a condition of employment (i.e., any mandatory arbitration agreement) is automatically considered procedurally ...
Background. AB 51 was intended to prohibit employers from requiring individuals to sign, as a condition of employment or employment-related benefits, arbitration agreements concerning disputes arising under the California Fair Employment and Housing Act or Labor Code.
To further complicate matters, new laws set to take effect in 2025 will reshape arbitration in California. SB 365 will allow cases to proceed through the trial process even where a party appeals an order denying a petition to compel arbitration.
The court said the state law is preempted by the Federal Arbitration Act (FAA). As a result, Assembly Bill 51 no longer stands as an obstacle to employers that wish to require arbitration agreements as a condition of employment in California, so long as the FAA applies and governs the agreement.
Under California law, an employer can require its employees to agree to arbitration as a term of employment. However, if the agreement has too many unfair or biased conditions, courts may refuse to enforce the arbitration agreement or chop off the unfair terms.
Under California law, you cannot be fired solely for refusing to sign an arbitration agreement. The California Labor Code provides strong protections for employees, ensuring that refusal to sign an arbitration agreement cannot be used as grounds for termination.
The arbitrator will explain the process. Each side may present an uninterrupted opening statement setting forth its position as to the facts and the law. After opening statements, the parties present their evidence and witnesses. The arbitrator swears in the witnesses and makes rulings on the admissibility of evidence.
Some contracts give you the right to opt out of the forced arbitration clause within a certain period of time, often 30 to 60 days, after signing the agreement by notifying the company that you wish to opt out. Check your contract for the deadline and for specific instructions for opting out.
Under California law, an employer can require its employees to agree to arbitration as a term of employment.