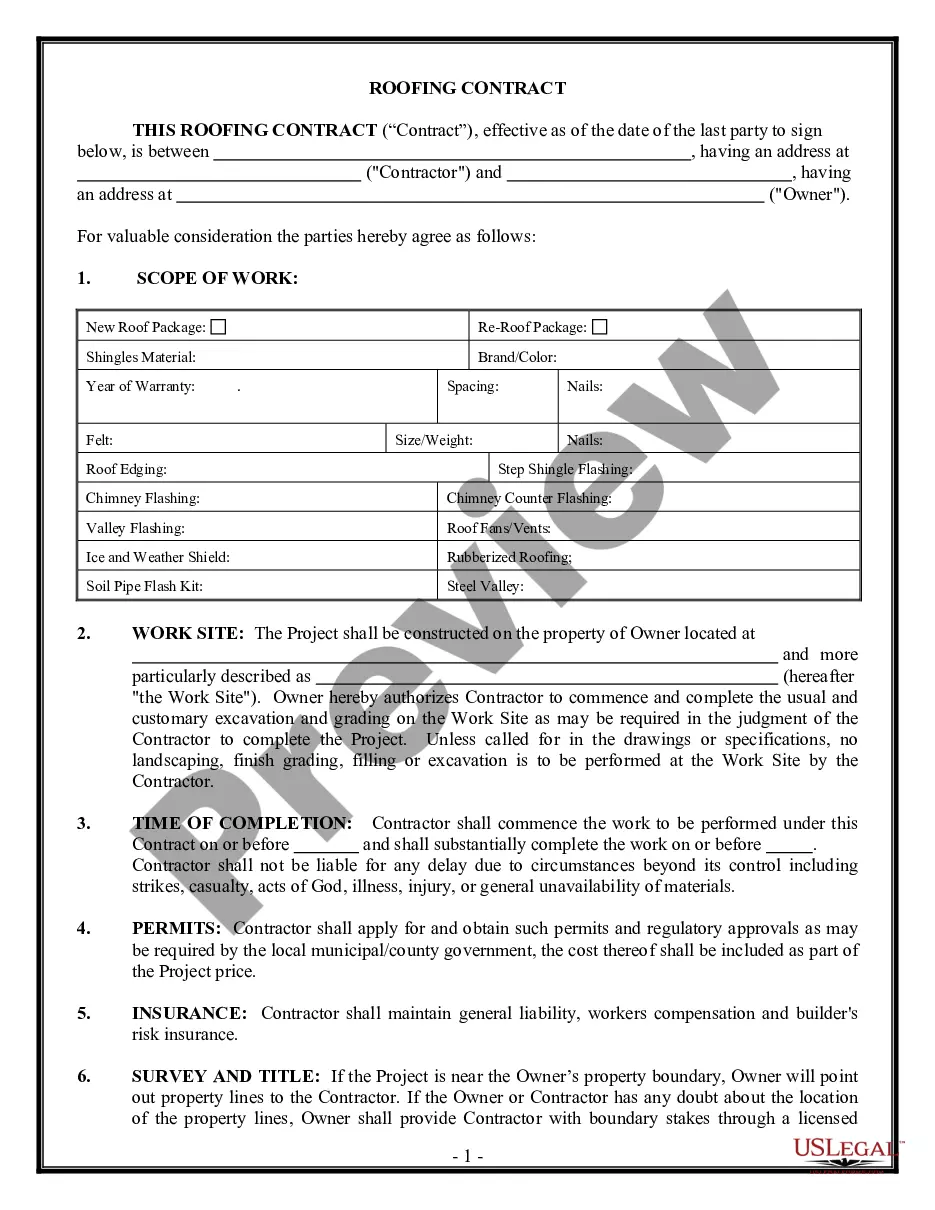
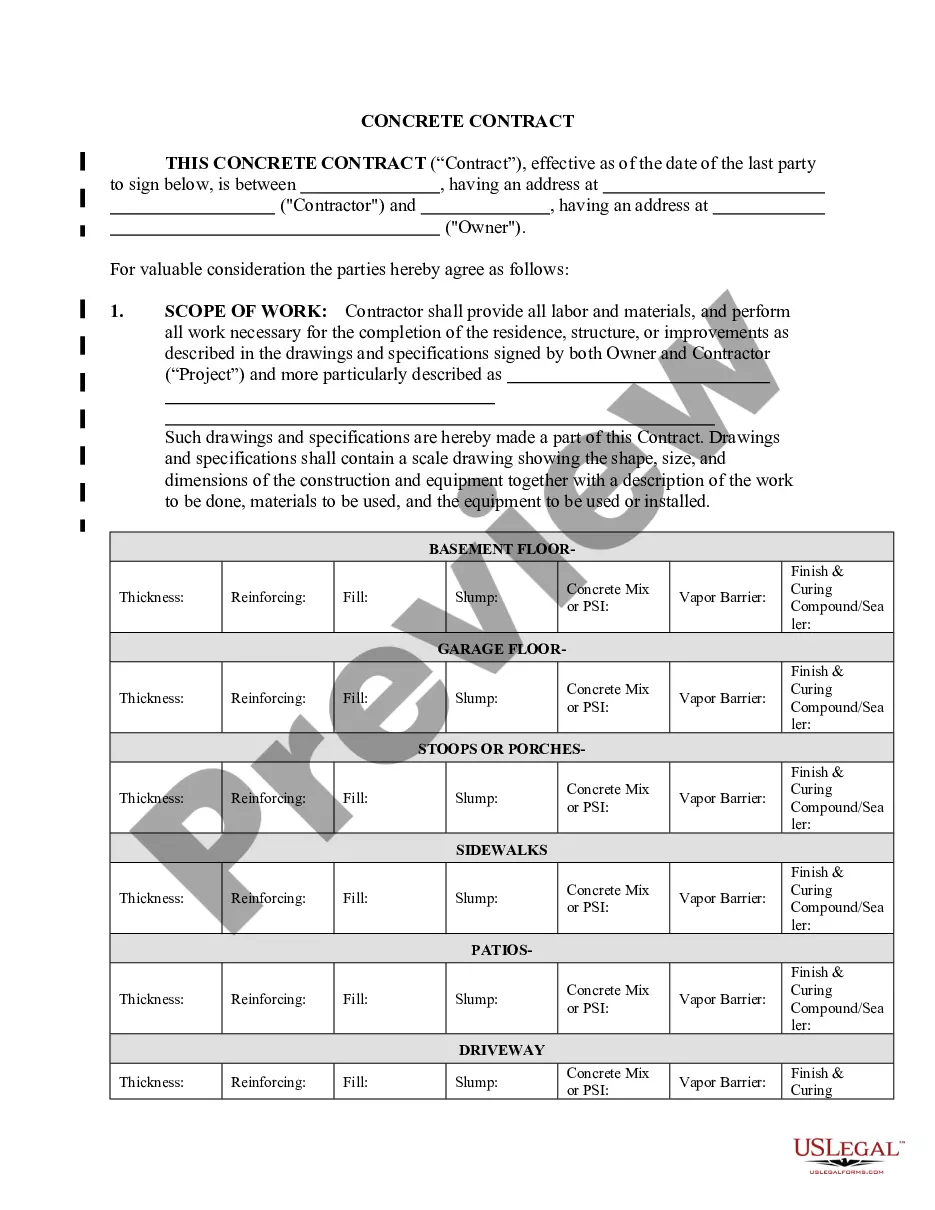
This is a comparison of China's contract law with the U.S. contract law. It discusses the restrictions placed upon military members and commanders in the conduct of operations in both international and non-international armed conflicts.
Principles Law Of Armed Conflict In San Diego
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
An armed conflict is said to exist when there is an armed confrontation between the. armed forces of States (international armed conflict), or between governmental authorities and. organised armed groups or between such groups within a State (non-international armed conflict).
LOAC demands proportionality, ensuring any harm inflicted on civilians is incidental and minimal compared to the anticipated military advantage. Necessity: Every bullet fired, every bomb dropped, should serve a specific military objective. Indiscriminate attacks or excessive force are strictly prohibited by LOAC.
Three interdependent principles—military necessity, humanity, and honor—provide the foundation for other law of war principles—such as, distinction and proportionality—and most of the treaty and customary rules of the law of war.
All personnel must be aware of the basic rules of the law of armed conflict, including the practical application of the principles of military necessity, proportionality, distinction and humanity.
This historical precedent has inspired the military manuals of other countries and the subsequent codification of IHL. The principle of military necessity requires that a party to an armed conflict may resort only to the means and methods that are necessary to achieve the legitimate aims of the armed conflict.
International Humanitarian Law, also known as the law of armed conflict, is the body of wartime rules that protect people who are not or are no longer participating in hostilities. IHL also restricts the means and methods of war. Its central purpose is to limit and prevent human suffering in times of armed conflict.
This historical precedent has inspired the military manuals of other countries and the subsequent codification of IHL. The principle of military necessity requires that a party to an armed conflict may resort only to the means and methods that are necessary to achieve the legitimate aims of the armed conflict.
For example, the core of the law of armed conflict, the 1949 Geneva Conventions, has been accepted by almost every member State of the United Nations. The law is therefore quite simply your State's law. It is binding on you as a member of the armed forces of your State.
Paragraphs 1-23 through 1-48 explain the principles of military necessity, humanity, honor, distinction, and proportionality. See table 1-1. required to defeat the enemy as quickly and efficiently as possible that are not prohibited by the law of armed conflict.
All personnel must be aware of the basic rules of the law of armed conflict, including the practical application of the principles of military necessity, proportionality, distinction and humanity.