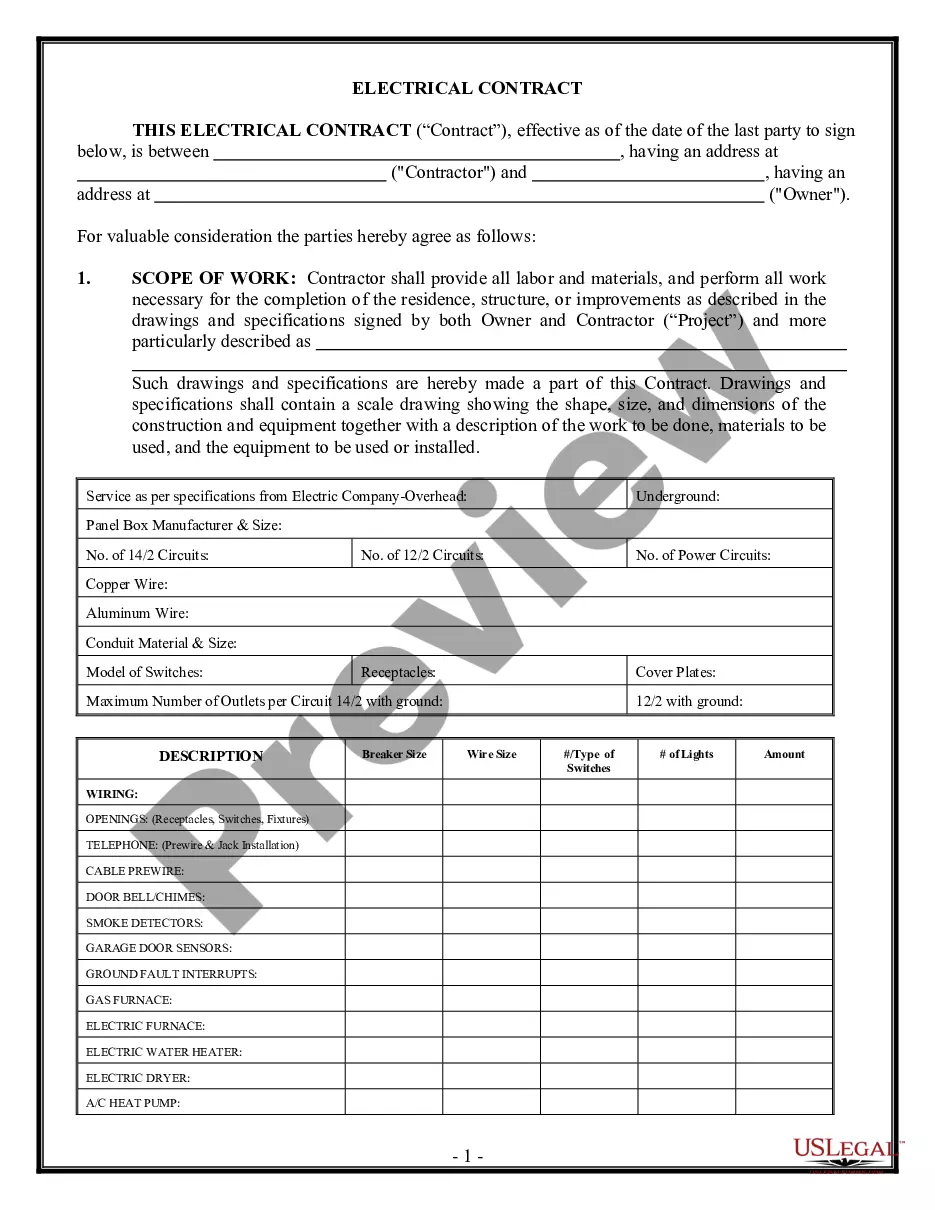
This Handbook provides an overview of federal laws addressing employer-employee rights and obligations. Information discussed includes wages & hours, discrimination, termination of employment, pension plans and retirement benefits, workplace safety, workers' compensation, unions, the Family and Medical Leave Act, and much more in 25 pages of materials.
Labour Law Act In Sri Lanka In Clark
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
With the recent passing of the National Minimum Wage of Workers (Amendment) Act No. 48 of 2024, the national minimum monthly wage payable to a worker increased from Rs. 12,500 to Rs. 17,500/- and the national minimum daily wage payable increased from Rs.
As of January 1, 2024, Sri Lanka's minimum wage rates are: 97.22 LKR p/h LKR per month. Applies nationwide across all sectors. Adjustments typically occur annually.
Minimum Wage – National Minimum Wage The current minimum wage in Sri Lanka is LKR21,000.00 per month in 2025. It became valid on March 1, 2024. Minimum wage with effect from March 1, 2024.
The Act provides that the Minimum Retirement Age in Sri Lanka is 60 years of age.
Today, we're going to be talking about the Shop and Office Employees (Regulation of Employment and Remuneration) Act No 19 of 1954. This act was written about the labour laws in Sri Lanka. The laws in this act apply to every employee working in Shops and Offices in Sri Lanka.
Amendments. Section 2 of the Termination of Employment Act either the prior written consent of the employee or the prior written approval of the Commissioner of Labour is required to terminate the services of an employee.
Wages in Sri Lanka decreased to 1135 LKR/Day in February from 1147.20 LKR/Day in January of 2018. Wages in Sri Lanka averaged 1101.91 LKR/Day from 1997 until 2018, reaching an all time high of 7556.25 LKR/Day in December of 2007 and a record low of 427.00 LKR/Day in January of 2008. source: Central Bank of Sri Lanka.
(2) Where a worker is employed on a piece-rate basis, or a daily-rate basis, the budgetary relief allowance payable under this Law shall be a sum not less than six per centum of the wages payable to him on a piece-rate basis or a daily-rate basis, as the case may be, so however, that the amount payable under this ...
(2) Where a worker is employed on a piece-rate basis, or a daily-rate basis, the budgetary relief allowance payable under this Law shall be a sum not less than six per centum of the wages payable to him on a piece-rate basis or a daily-rate basis, as the case may be, so however, that the amount payable under this ...