This Handbook provides an overview of federal laws addressing employer-employee rights and obligations. Information discussed includes wages & hours, discrimination, termination of employment, pension plans and retirement benefits, workplace safety, workers' compensation, unions, the Family and Medical Leave Act, and much more in 25 pages of materials.
Employment Law Policy In Minnesota
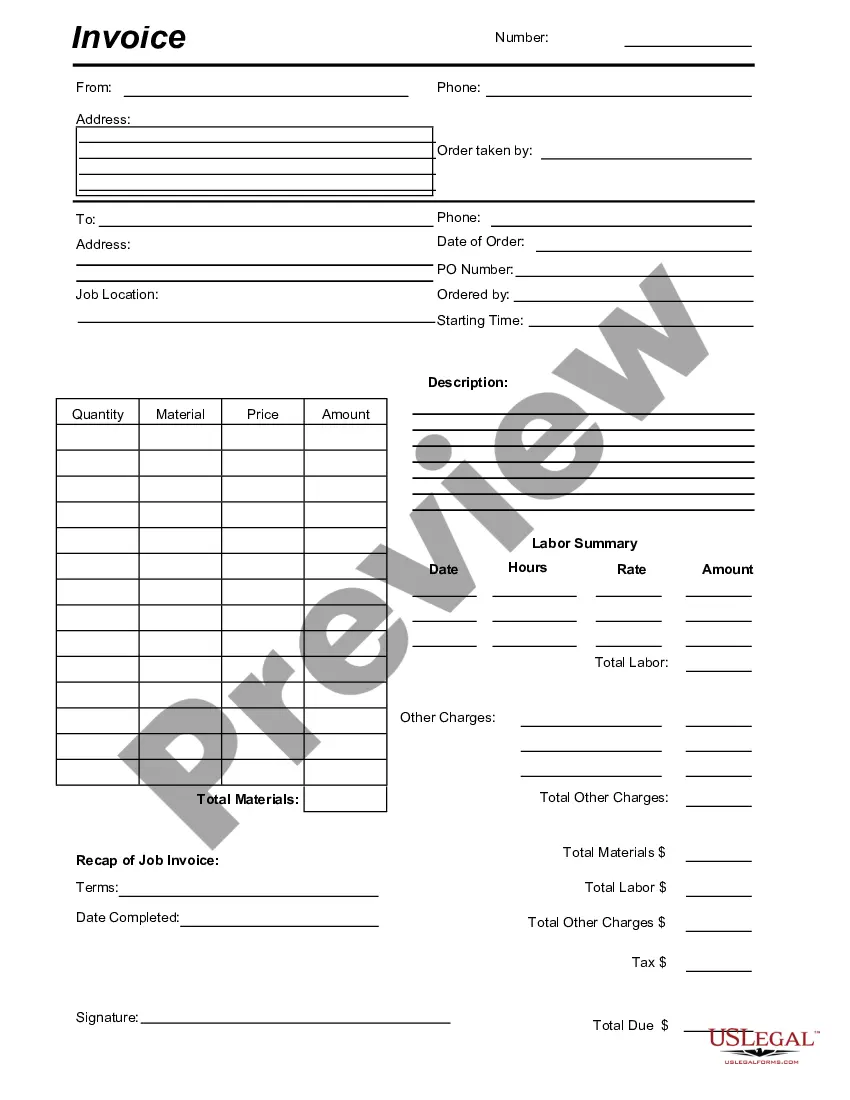
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
(a) No employer shall make any deduction, directly or indirectly, from the wages due or earned by any employee, who is not an independent contractor, for lost or stolen property, damage to property, or to recover any other claimed indebtedness running from employee to employer, unless the employee, after the loss has ...
No notice of separation is required by law, by either party, upon separation of an employee for any reason. Courtesy and time to collect accrued benefits are reasons why notice is given.
Employment First is based on the idea that all people with disabilities who want to have a job in their community should have one. Ultimately, it is the person's choice where they will work if at all.
Minnesota has laws that provide greater protections to employees than federal law, including pregnancy accommodation rights, a higher minimum wage, health care continuation coverage obligations for smaller employers and bone marrow donation leave, but generally follows federal law with respect to topics such as ...
Employment laws in Minnesota provide essential protections for workers, including minimum wage and overtime regulations, discrimination and harassment protections, breaks and rest periods, and leaves of absence.
An employer can give out the following information only with a Release signed by you: written employee evaluations and your response to them, written disciplinary warnings and actions in the last 5 years, and. written reasons for why you left the job.
Summary. Minnesota law prohibits an employer from discriminating and retaliating against employees in a variety of protected classes. Employers must also provide pregnancy accommodations, protect whistleblowers and allow employees to access their personnel files and to discuss their wages.
Employers aren't obligated to respond to calls to verify an individual's employment for a third party unless the requests are made by federal entities.
All employers must complete a Form I-9, Employment Eligibility Verification, to verify an employee's identity and employment authorization. Federal law also protects employees from discrimination based on national origin or citizenship status.
The Immigration Reform and Control Act, enacted on November 6, 1986, requires employers to verify the identity and employment eligibility of their employees and sets forth criminal and civil sanctions for employment-related violations.