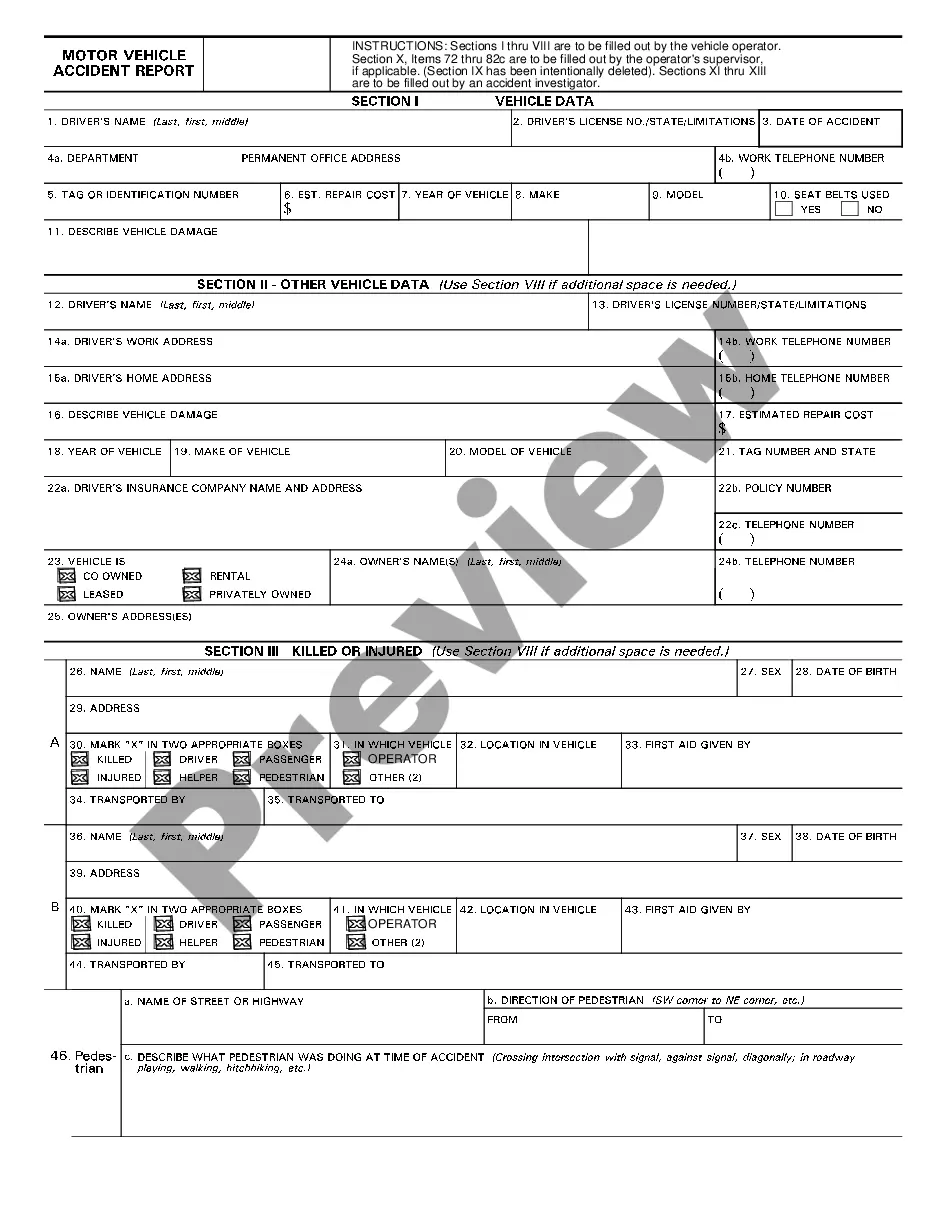
Work Labor Law For Salaried Employees In Texas
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
First, effective July 1, 2024, the 2024 rule raised the standard minimum salary level to the 20th percentile of weekly earnings of full-time salaried workers in the lowest-wage census region—from $684 per week to $844 per week (or from $35,568 annually to $43,888 annually).
The DOL issued its Final Rule on April 26, 2024. The Rule imposed a 65 percent increase to the minimum salary requirements for the EAP exemptions to take effect in two phases. The minimum salary threshold first rose from $684 per week ($35,568 per year) to $844 per week ($43,888 annually) on July 1, 2024.
The 2024 rule implemented three changes to the EAP salary-level test: An increase in the minimum salary level from $684 per week, or $35,568 annually, to $844 per week, or $43,888 annually, starting on July 1, 2024. A second increase to $1,128 a week, or $58,656 annually, starting on January 1, 2025.
(1) An employer must not request or require an employee to work more than the following number of hours in a week unless the additional hours are reasonable: (a) for a full-time employee—38 hours; or (b) for an employee who is not a full-time employee—the lesser of: (i) 38 hours; and (ii) the employee's ordinary hours ...
Most full-time salaried employees work 40-hour weeks. Salaried employees might occasionally work between 45 and 50 hours, depending on the company's needs. Other weeks, they might put in less than 40 hours.
Maximum hours an exempt employee can be required to work The law does not provide a maximum number of hours that an exempt worker can be required to work during a week. This means that an employer could require an exempt employee to work well beyond 40 hours a week without overtime compensation.
Minimum Salary Threshold: The new rule raises the standard salary level from $35,568 per year ($684 per week) to $58,656 annually ($1,128 per week).
Under the 2024 Rule, the salary threshold for professional, administrative, and executive exemptions was set to increase from $684 per week ($35,568 annually) to $844 per week ($43,888 annually) on July 1, 2024.
As a refresher, the Final Rule featured three components: (1) an increase to $844 per week (or $43,888 per year) for the EAP exemptions and to $132,964 for the HCE exemption that took effect on July 1, 2024; (2) a further increase to $1,128 per week (or $58,656 per year) for the EAP exemptions and to $151,164 for the ...
5. What is the current minimum wage in Texas? As of 2024, the Texas minimum wage is $7.25 per hour for non-exempt employees, matching the federal minimum wage.