Installment Contract For Deed In San Antonio
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Liquidity risk Structured installment sales can tie up a significant amount of capital, which could limit the seller's ability to invest in other opportunities or meet their financial obligations.
The document must be notarized any time a deed is required as part of a real estate transaction. This is the case for all deeds, regardless of the situation.
Is a contract for deed a good idea? The seller retains the title. This can extend through the completion of your payment plan, which can complicate things like ownership and taxes, as well as personal security and rights. Maintenance gets confusing. There's little regulation. Sellers don't have it easy.
Yes, but Texas law requires sellers to comply with strict disclosure and filing regulations to protect buyers. 5. How long do contract for deed agreements usually last? The terms vary but typically range from 3 to 10 years, with many requiring a balloon payment at the end.
The bottom line is that lawyers can help draft contract for deed language that protects both parties in case a buyer can no longer make payments.
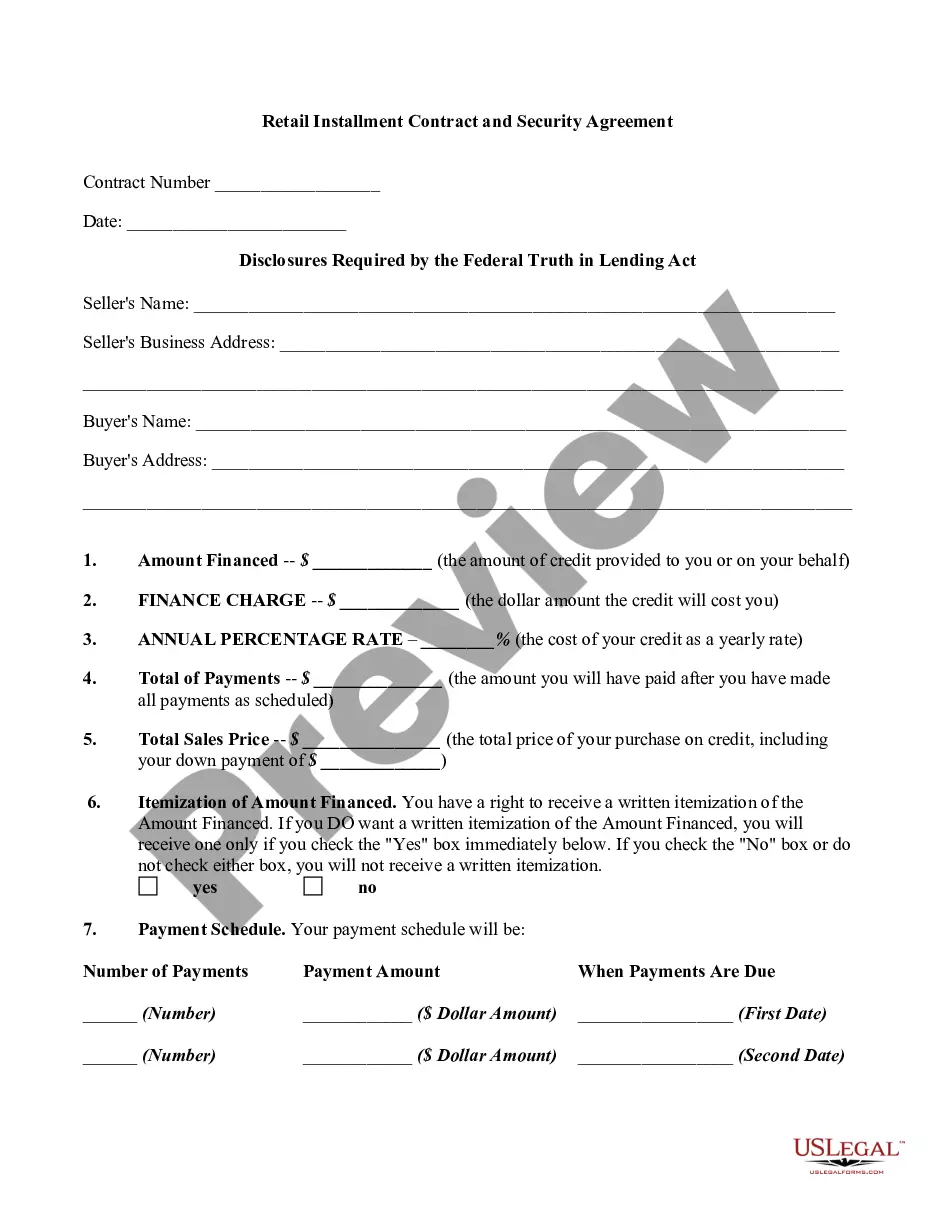
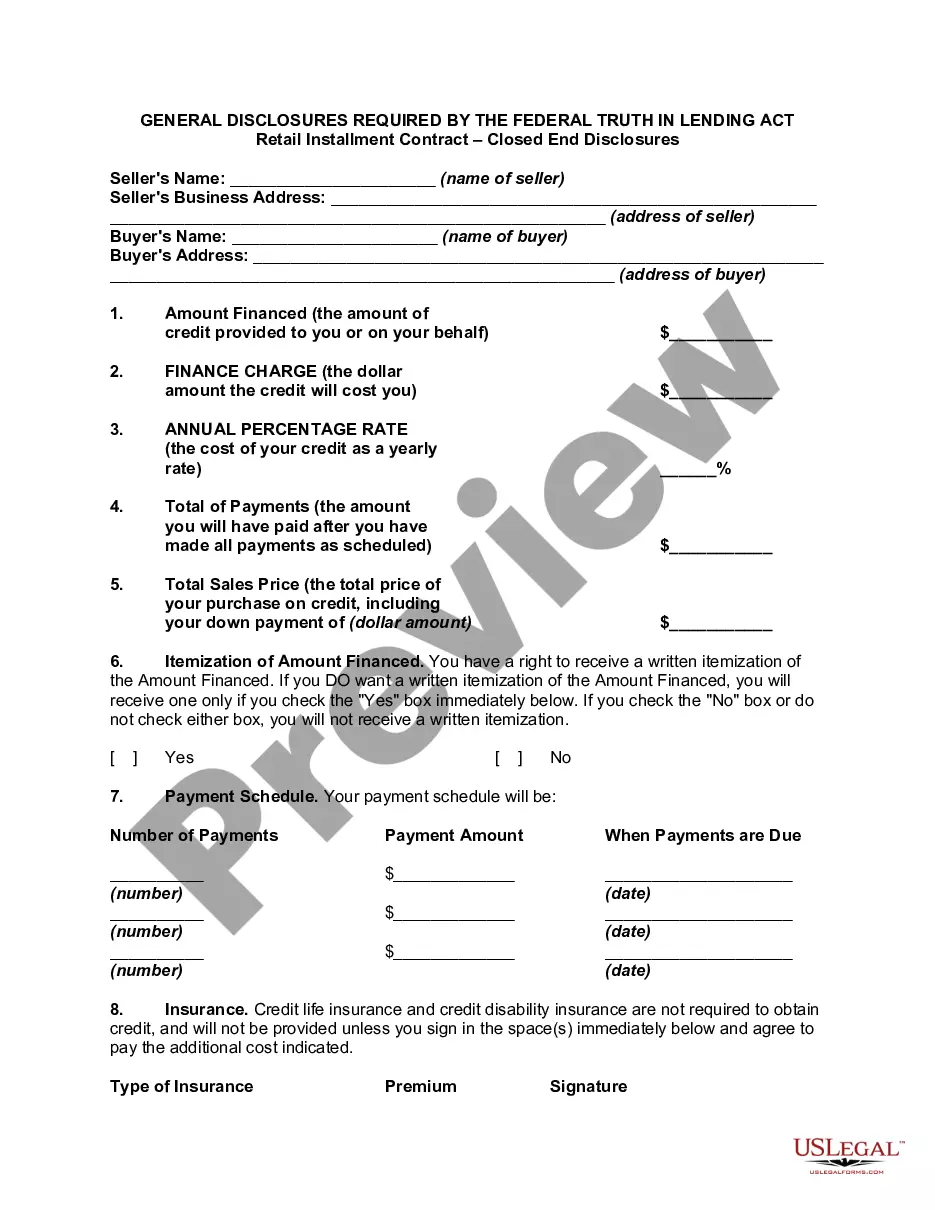
This is because the buyer is considered the owner of the property even though they have not yetMoreThis is because the buyer is considered the owner of the property even though they have not yet obtained a traditional mortgage. The seller may require the buyer to provide proof of insurance.
Risks of a Contract for Deed Additionally, balloon payments may be required after a certain amount of time has passed, which can also lead to financial hardship if not planned for. If disputes arise between the buyer and seller of a contract for deed property, legal recourse is limited for the party living in the home.
"Contracts for Deed" - Contracts for deed, sometimes referred to as "rent to own" financing arrangements, are legal in Texas.
“Executory Contracts” include contract for deed, lease-purchases, and lease-options. Texas law did not outlaw these methods: contract for deed, lease-purchases, or lease-options, but it has made them perilous for those still interested in trying to use them.
With only extremely narrow exceptions relating to certain regulated industries or collective bargaining agreements, adults, as well as youths ages 16 or 17, may work, and/or may be required to work, unlimited hours each day (the only limits are employee morale, practical realities, and common sense in general).