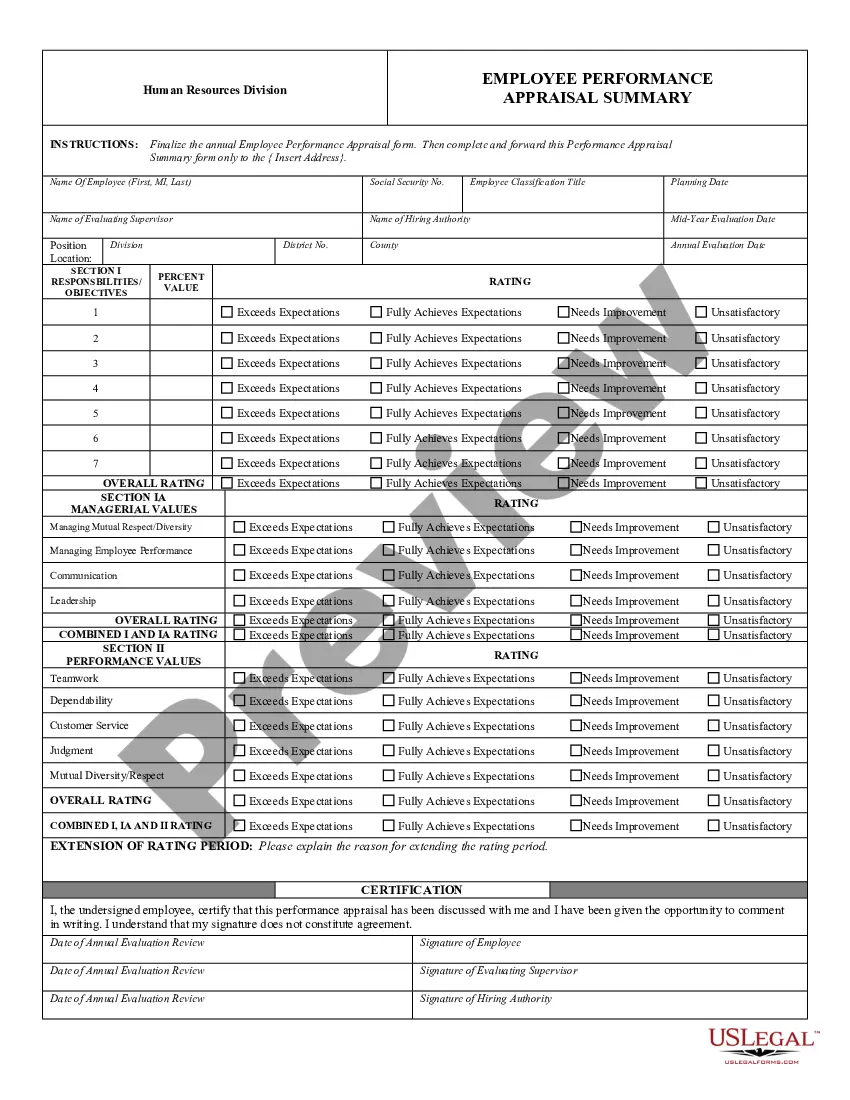
Homestead Act Information Form Massachusetts In Suffolk
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
The Massachusetts Homestead Act is a law under which a homeowner is protected by an Estate of Homestead. A homestead estate provides limited protection of the value of the home, up to $1,000,000, against unsecured creditor claims.
Other differences between the declared and homestead exemptions include: In the event of a voluntary sale, the declared homestead protects the sale proceeds up to the applicable statutory amount. In contrast, the automatic homestead offers no protection from a voluntary sale.
In Massachusetts, the homestead law protects up to $125,000 of your home's value automatically. This means that if you have $125,000 or less in equity, no one can force you to sell your house.
A Declaration of Homestead is a written legal document that allows homeowners to protect their family home from certain creditors, up to a particular amount. An Automatic Homestead exists on all principal residences, protecting the home to the extent of $125,000.
The homestead right might be terminated or extinguished either by abandonment, or by a release in writing properly signed and properly acknowledged, or by surrender of the possession to a grantee in a deed in pursuance of the deedii.
Elderly persons, regardless of marital status, are personally exempt up to one million dollars ($1,000,000) each. If two owners qualify for the elderly or disabled homestead protection, the aggregate protection on the home increases to two million dollars ($2,000,000).
Clauses 41, 41B, 41C or 41C½ provide exemptions to seniors who meet specific ownership, residency, income and asset requirements. Seniors 70 or older may, alternatively, qualify for exemption under Clauses 17, 17C, 17C½ or 17D, which provide a reduced benefit, but have less strict eligibility requirements.