Form X201 is not a recognized form or designation within the sole proprietorship or IRS context. However, there are relevant forms and considerations for sole proprietorship that one can describe. A sole proprietorship is a common business structure where a single individual owns and operates a business and is personally liable for its debts. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires sole proprietors to report their business income and expenses on their personal tax return using specific forms. One of the key forms utilized by sole proprietors for reporting business income and expenses is Schedule C (Form 1040). Schedule C is an attachment to the individual's personal tax return (Form 1040) and is used to report the net profit or loss of the sole proprietorship. In Schedule C, the sole proprietor details the revenue, deductible expenses, and calculates the resulting net profit or loss for their business. Additionally, sole proprietors may need to consider filing Form 8829, which is used to claim deductions for the business use of their home (home office expenses). This form can be relevant for sole proprietors who operate their business from their residence. Another important form that may be relevant for sole proprietors is Form 1099-MISC. This form is used to report income earned from clients or customers who have paid $600 or more to the sole proprietor during the tax year. It is essential for sole proprietors to keep track of their income received from various sources to ensure accurate reporting on this form. It's important to note that while there are various schedules and forms that sole proprietors commonly use, there is no specific Form X201 associated with sole proprietorship or the IRS. Sole proprietors should refer to the official IRS resources, such as the IRS website or consult a tax professional for accurate information and guidance on the appropriate forms and reporting requirements for their specific situation.
Form X201 Sole Proprietorship With Irs
Description
How to fill out Form X201 Sole Proprietorship With Irs?
Obtaining legal document samples that comply with federal and local laws is a matter of necessity, and the internet offers many options to choose from. But what’s the point in wasting time searching for the appropriate Form X201 Sole Proprietorship With Irs sample on the web if the US Legal Forms online library already has such templates collected in one place?
US Legal Forms is the largest online legal library with over 85,000 fillable templates drafted by lawyers for any professional and personal situation. They are easy to browse with all files arranged by state and purpose of use. Our experts stay up with legislative changes, so you can always be confident your paperwork is up to date and compliant when acquiring a Form X201 Sole Proprietorship With Irs from our website.
Obtaining a Form X201 Sole Proprietorship With Irs is fast and simple for both current and new users. If you already have an account with a valid subscription, log in and download the document sample you need in the right format. If you are new to our website, adhere to the instructions below:
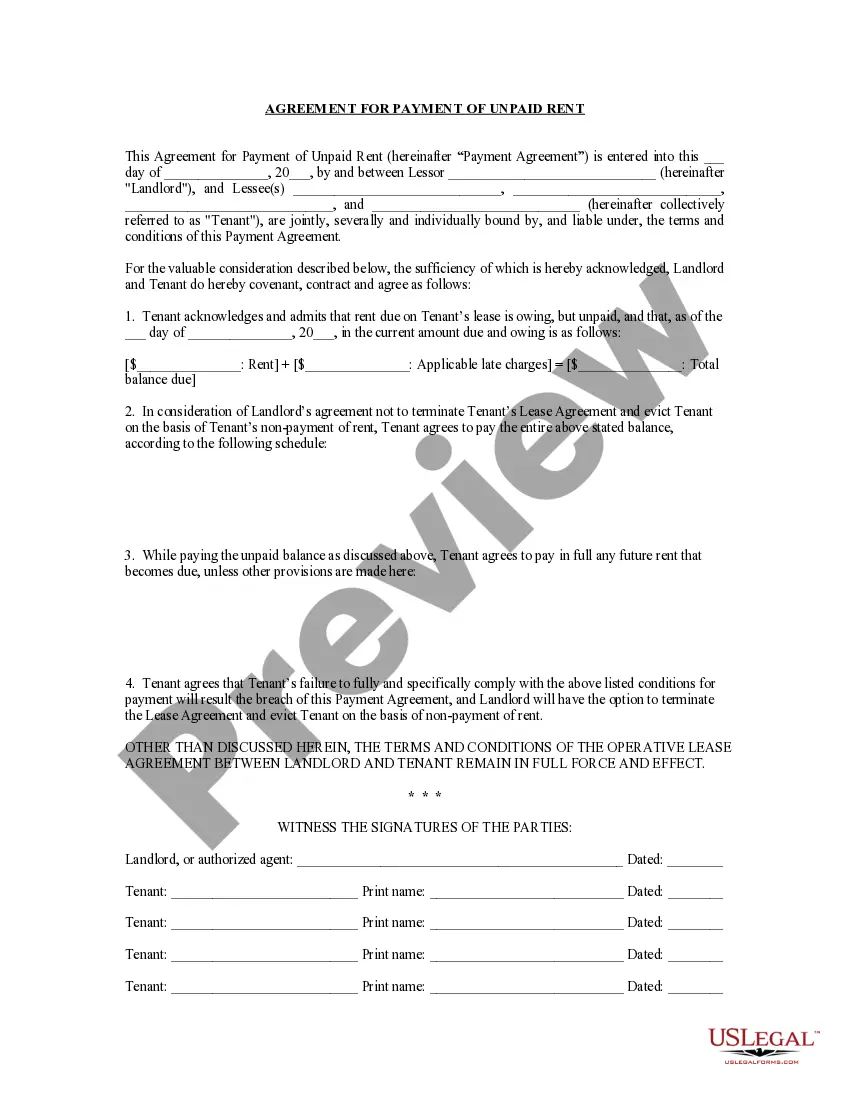
- Take a look at the template using the Preview option or via the text outline to make certain it meets your needs.
- Look for another sample using the search tool at the top of the page if necessary.
- Click Buy Now when you’ve located the correct form and select a subscription plan.
- Create an account or log in and make a payment with PayPal or a credit card.
- Choose the right format for your Form X201 Sole Proprietorship With Irs and download it.
All documents you locate through US Legal Forms are reusable. To re-download and fill out earlier purchased forms, open the My Forms tab in your profile. Enjoy the most extensive and straightforward-to-use legal paperwork service!
Form popularity
FAQ
And, as is the case with other types of business entities, sole proprietors are also subject to self-employment taxes. As a sole proprietor, instead of filing a separate tax return for your business, you report your business income on IRS Form 1040, using Schedule C to report your business profit or loss.
A sole proprietor files Schedule C (Form 1040), Profit or Loss from Business (Sole Proprietorship) to report the income and expenses of the business and reports the net business earnings on Form 1040 series.
What tax forms to use as a sole proprietorship? The main form is Schedule C, on IRS Form 1040. You can find Form 1040 instructions here and the instructions for Schedule C here.
As a sole proprietor, instead of filing a separate tax return for your business, you report your business income on IRS Form 1040, using Schedule C to report your business profit or loss.
As a sole proprietor, you must report all business income or losses on your personal income tax return; the business itself isn't taxed separately. (The IRS calls this type of reporting "pass-through" taxation because business profits pass through the business to be taxed on your personal tax return.)