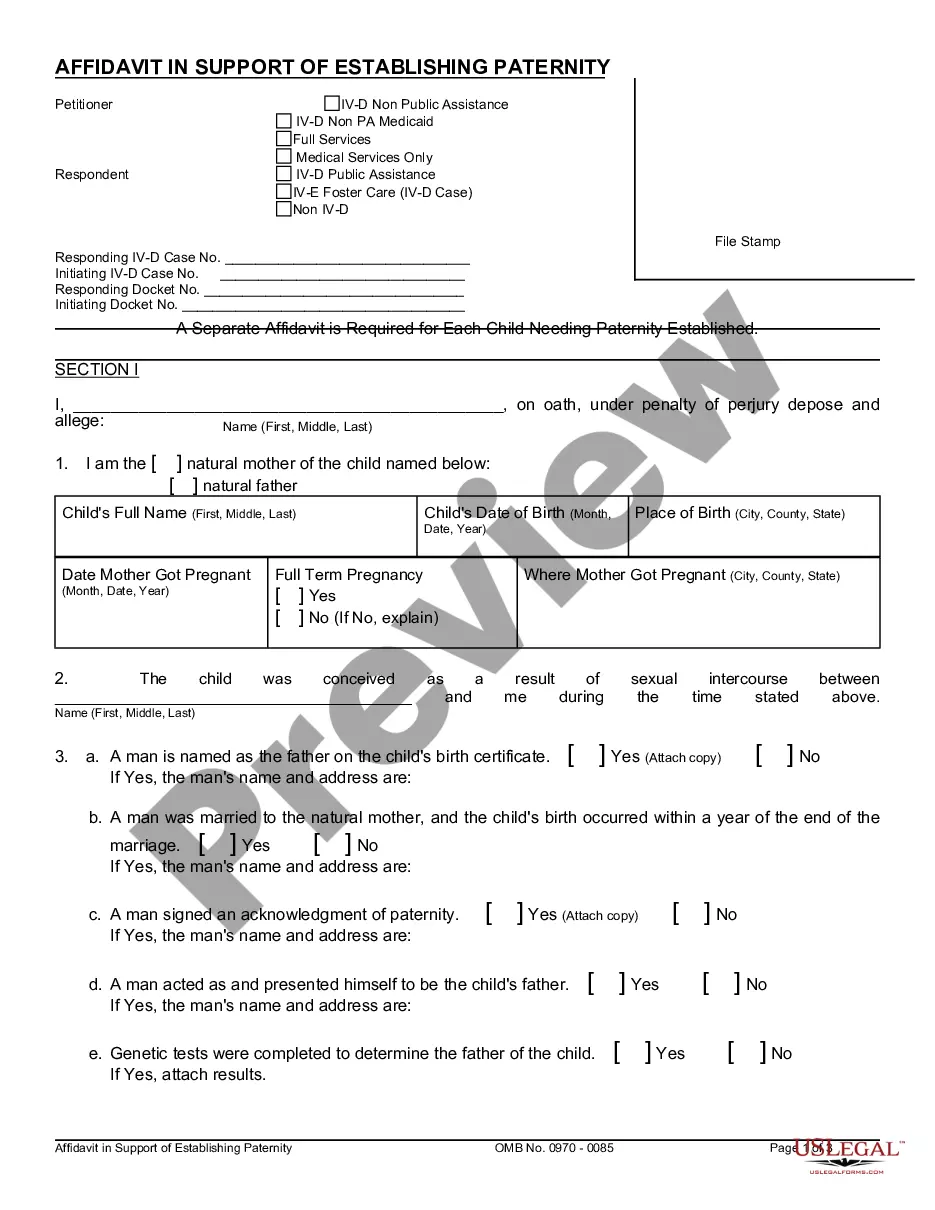
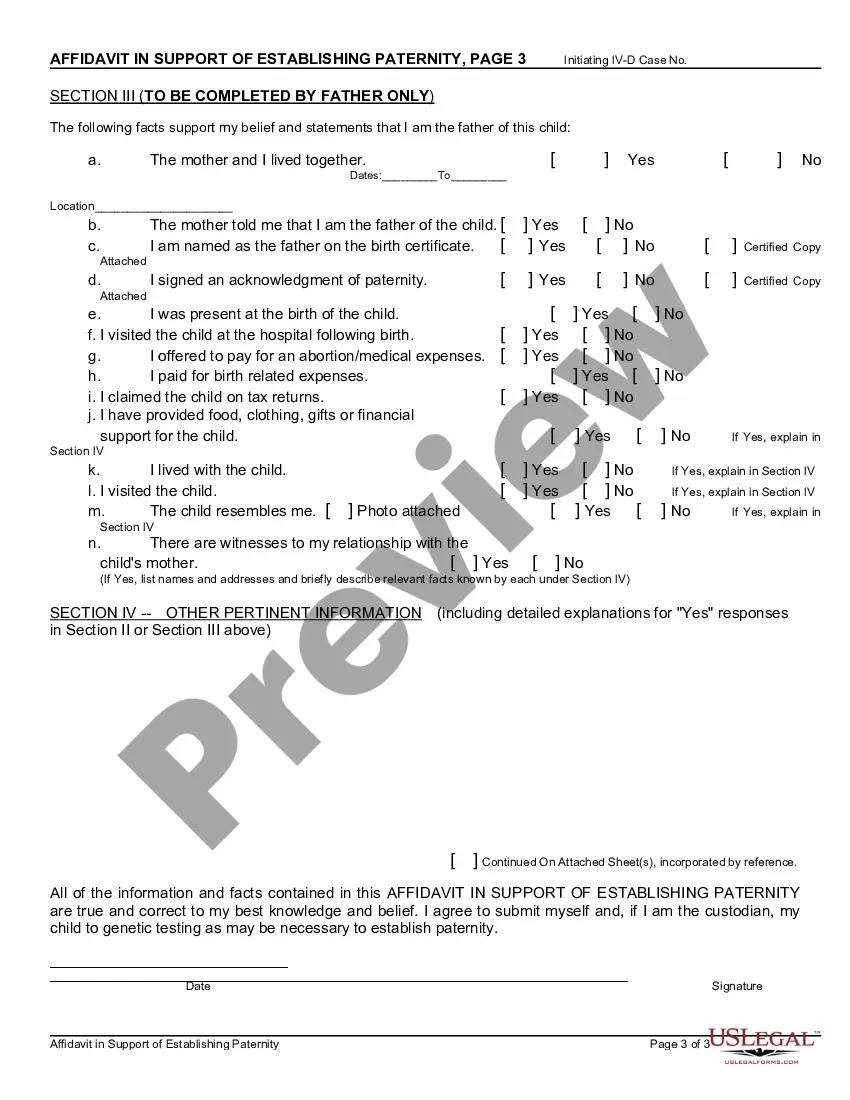
The Declaration of Paternity form (CS 909) is a legally binding document that establishes the legal father of a child. This form is designed to be used when the biological parents of a child are not married or in a registered domestic partnership at the time of the child's birth. By completing this form, both the mother and alleged father acknowledge the biological relationship between the alleged father and the child. The Declaration of Paternity form is a critical tool in ensuring that children have legal rights, including financial support, inheritance, and access to medical history. It provides a legal framework for unmarried parents to establish paternity without having to go through a court process. The CS 909 form is typically provided by the hospital or birthing center where the child is born. Both parents must sign the form voluntarily and in the presence of a witness, such as a notary public or hospital representative. The completed form is then filed with the appropriate state agency, usually the State Department of Child Support Services or the Vital Records Office. Some variations of the Declaration of Paternity form (CS 909) include: 1. Voluntary Declaration of Paternity: This is the most common type of form used to establish paternity. It is filed voluntarily by both parents and is legally binding once properly executed. 2. Rescission of Voluntary Declaration of Paternity: This form is used when a person wishes to revoke or cancel a previously signed Declaration of Paternity. It must be filed within a specific time frame, usually within 60 days, after signing the initial declaration. 3. Contested Declaration of Paternity: In cases where there is disagreement or dispute about the paternity of a child, a contested declaration may be filed. This type of form initiates a legal process to determine paternity through DNA testing and court proceedings. It is essential to obtain and complete the appropriate Declaration of Paternity form (CS 909) to establish legal paternity accurately. This process ensures that both parents' rights and responsibilities are protected, and the child's legal rights are secured.
Declaration Of Paternity Form (cs 909)
Description declaration of paternity form
How to fill out Declaration Of Paternity Form (cs 909)?
The Declaration Of Paternity Form (cs 909) you see on this page is a reusable legal template drafted by professional lawyers in accordance with federal and regional laws. For more than 25 years, US Legal Forms has provided people, companies, and legal professionals with more than 85,000 verified, state-specific forms for any business and personal situation. It’s the fastest, easiest and most trustworthy way to obtain the documents you need, as the service guarantees bank-level data security and anti-malware protection.
Obtaining this Declaration Of Paternity Form (cs 909) will take you just a few simple steps:
- Look for the document you need and review it. Look through the file you searched and preview it or review the form description to ensure it suits your requirements. If it does not, make use of the search bar to find the appropriate one. Click Buy Now once you have found the template you need.
- Sign up and log in. Choose the pricing plan that suits you and create an account. Use PayPal or a credit card to make a prompt payment. If you already have an account, log in and check your subscription to proceed.
- Get the fillable template. Pick the format you want for your Declaration Of Paternity Form (cs 909) (PDF, DOCX, RTF) and save the sample on your device.
- Complete and sign the paperwork. Print out the template to complete it manually. Alternatively, use an online multi-functional PDF editor to rapidly and precisely fill out and sign your form with a legally-binding] {electronic signature.
- Download your paperwork again. Utilize the same document once again anytime needed. Open the My Forms tab in your profile to redownload any previously downloaded forms.
Sign up for US Legal Forms to have verified legal templates for all of life’s scenarios at your disposal.
Form popularity
FAQ
The Declaration of Paternity (CS 909) form is only to be used by unmarried couples to establish the paternal relationship with the child. You must use the official triplicate form (photocopies are not acceptable) that is available through local child support agencies.
You can ask for the form to be sent to you by mail by e-mailing askpop@dcss.ca.gov, or you can get it at any of the above government locations. You and the other parent can then sign it in front of a notary public. There's usually a fee to use a notary.
You can open a parentage case with the Court. Once the legal parents are established by the Court, follow the procedure on the State Dept. of Public Health website to request that the birth certificate be amended to include the father's name. You and the other parent can sign a Voluntary Declaration of Parentage .
The Declaration of Paternity form can be obtained from the State of California Department of Child Support Services by sending your mailing address to askpop@dcss.ca.gov or by obtaining a copy from one of the following locations: County Department of Child Support Services. Local Registrars of Births and Deaths.
The Declaration of Paternity form can be obtained from the State of California Department of Child Support Services by sending your mailing address to askpop@dcss.ca.gov or by obtaining a copy from one of the following locations: County Department of Child Support Services. Local Registrars of Births and Deaths.