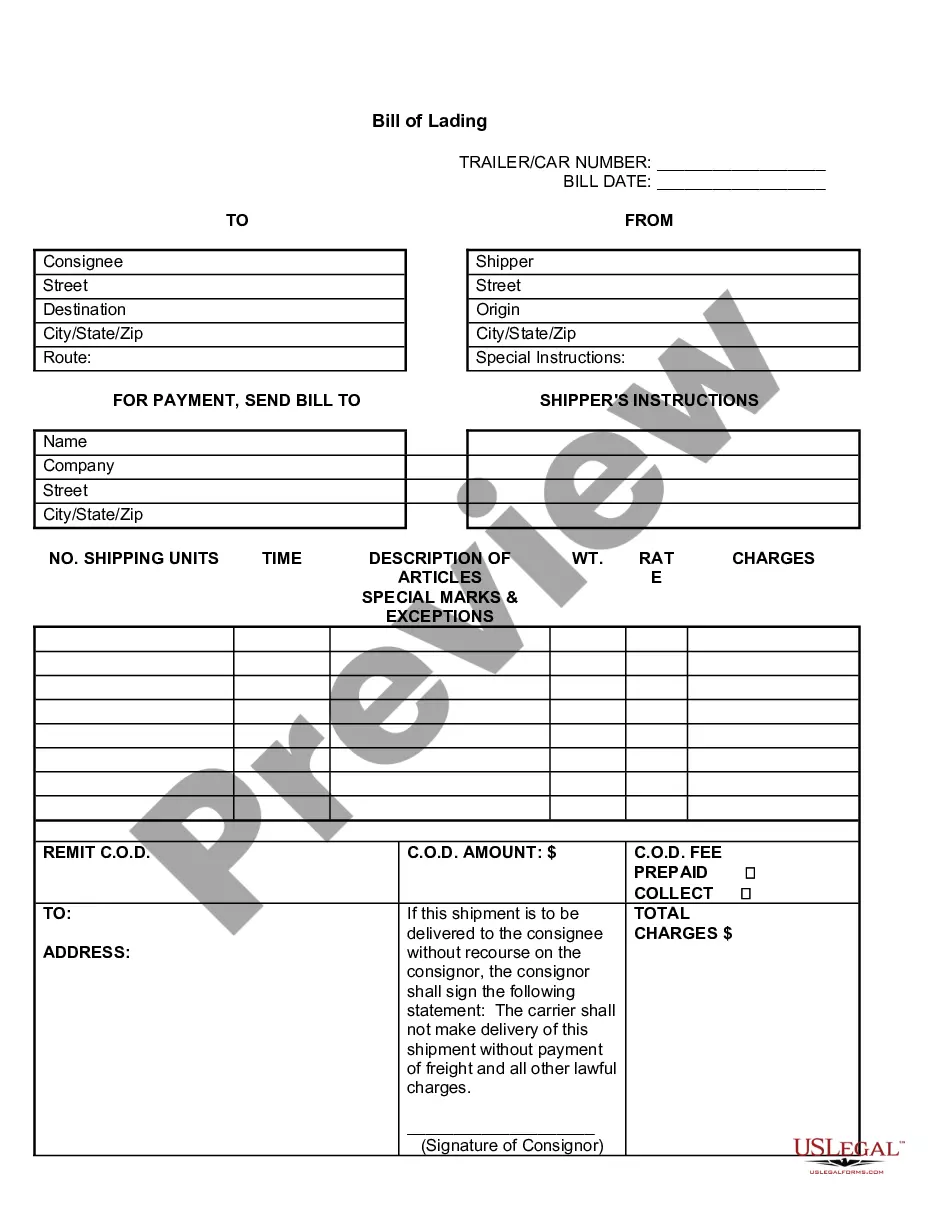
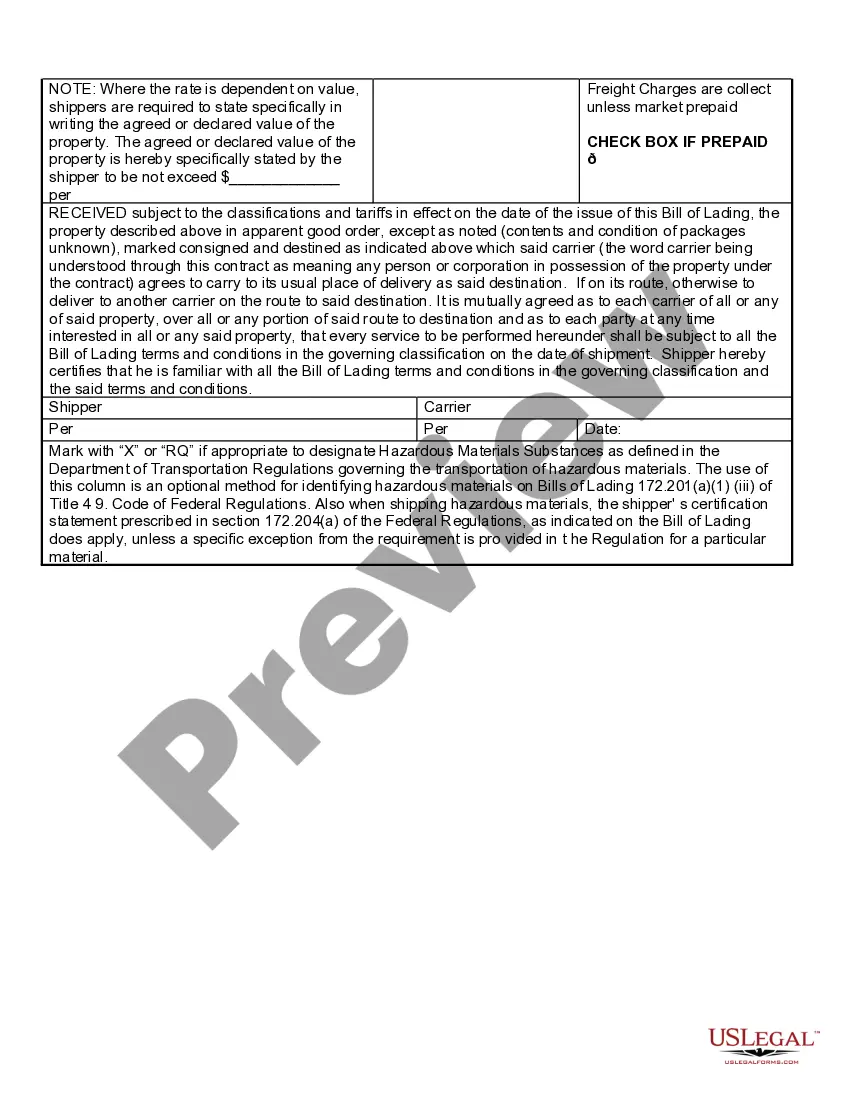
A blank endorsement for a bill of lading refers to an endorsement made without specifying the name of the transferee of the goods. In simple terms, it is an endorsement that makes the bill of lading bearer paper, allowing it to be transferred to anyone who possesses it, just like cash. This type of endorsement is also known as a general endorsement or an open endorsement. Blank endorsement offers great flexibility and convenience in the transfer of ownership of goods. It allows for easy and swift negotiation of the bill as the document becomes freely transferable and can be delivered to subsequent buyers without the need for additional documentation or formalities. The main purpose of a blank endorsement is to facilitate trade and commerce by enabling quick and efficient transfers of goods. It eliminates the need for specific endorsements and simplifies the process of transferring ownership from one party to another. Blank endorsements on bills of lading are commonly used in international trade and shipping. They provide an easy way to transfer the rights to the goods to subsequent parties, such as freight forwarders, consignees, or buyers. The absence of a specified transferee allows for flexibility in the supply chain and can be particularly useful in cases where goods need to change multiple hands before reaching their final destination. It is worth noting that while a blank endorsement provides convenience, it also represents a higher risk compared to more specific endorsements. Since the bill of lading becomes bearer paper, it can be negotiated by anyone possessing it, potentially introducing the risk of unauthorized transfers or fraud. Therefore, it is essential to handle blank-endorsed bills of lading with care and ensure appropriate security measures are in place. In addition to the blank endorsement, there are other types of endorsements for bills of lading that provide more specific instructions for the transfer of goods. These include: 1. Special Endorsement: This type of endorsement specifies the party to whom the bill of lading is to be transferred. It restricts the negotiability of the document to the named party only and ensures a more secure transfer. 2. Restrictive Endorsement: A restrictive endorsement imposes certain conditions or limitations on the transfer of the bill of lading. It may require the endorsement to be made for collection, to a specific bank, or for a particular purpose, providing additional control and security. 3. Qualified Endorsement: This endorsement includes additional terms, conditions, or qualifications with the intention of reducing liability or transferring goods subject to specific conditions. In conclusion, a blank endorsement for a bill of lading allows for the free and unrestricted transfer of ownership without specifying the transferee. It offers convenience and flexibility in the transfer of goods, but also carries a higher risk of unauthorized transfers. Other types of endorsements, such as special, restrictive, and qualified endorsements, provide more specific instructions and conditions for the transfer of goods.
Blank Endorsement For Bill Of Lading
Description blank endorsed
How to fill out Blank Bills?
Drafting legal paperwork from scratch can often be intimidating. Certain scenarios might involve hours of research and hundreds of dollars invested. If you’re looking for a an easier and more cost-effective way of creating Blank Endorsement For Bill Of Lading or any other documents without jumping through hoops, US Legal Forms is always at your fingertips.
Our virtual library of over 85,000 up-to-date legal forms covers almost every element of your financial, legal, and personal matters. With just a few clicks, you can quickly access state- and county-compliant templates diligently prepared for you by our legal specialists.
Use our platform whenever you need a trusted and reliable services through which you can quickly find and download the Blank Endorsement For Bill Of Lading. If you’re not new to our services and have previously created an account with us, simply log in to your account, locate the template and download it away or re-download it at any time in the My Forms tab.
Not registered yet? No worries. It takes little to no time to set it up and navigate the catalog. But before jumping straight to downloading Blank Endorsement For Bill Of Lading, follow these tips:
- Review the form preview and descriptions to make sure you have found the form you are searching for.
- Make sure the template you select complies with the regulations and laws of your state and county.
- Pick the best-suited subscription option to get the Blank Endorsement For Bill Of Lading.
- Download the form. Then fill out, certify, and print it out.
US Legal Forms has a spotless reputation and over 25 years of experience. Join us today and transform form completion into something easy and streamlined!
blank endorsment Form popularity
endorsement in blank Other Form Names
made out to order and blank endorsed FAQ
Endorsing the bill simply means the Shipper of the named consignee signs the back of the bill and adds the name of the party to whom it is transferring the bill.
Blank Endorsement ? Where the endorser signs his name only, and it becomes payable to bearer. Special Endorsement ? Where the endorser puts his sign and writes the name of the person who will receive the payment. Restrictive Endorsement ? Which restricts further negotiation.
13[(1) If the endorser signs his name only, the endorsement is said to be "in blank", and if he adds a direction to pay the amount mentioned in the instrument to, or to the order of, a specified person, the endorsement is said to be "in full", and the person so specified is called the "endorsee" of the instrument.
Blank endorsement is one of the most typical endorsements, and it consists of a person signing the back of a check that does not indicate a payee. The payee endorses the check and then goes to cash or deposit it after being properly verified by the bank official.
Blank endorsement is a kind of signature on a financial instrument. It has no designated payee, so the person who possesses it can demand payment, for example, a check made payable to cash and endorsed on the back with the signature of the account held.