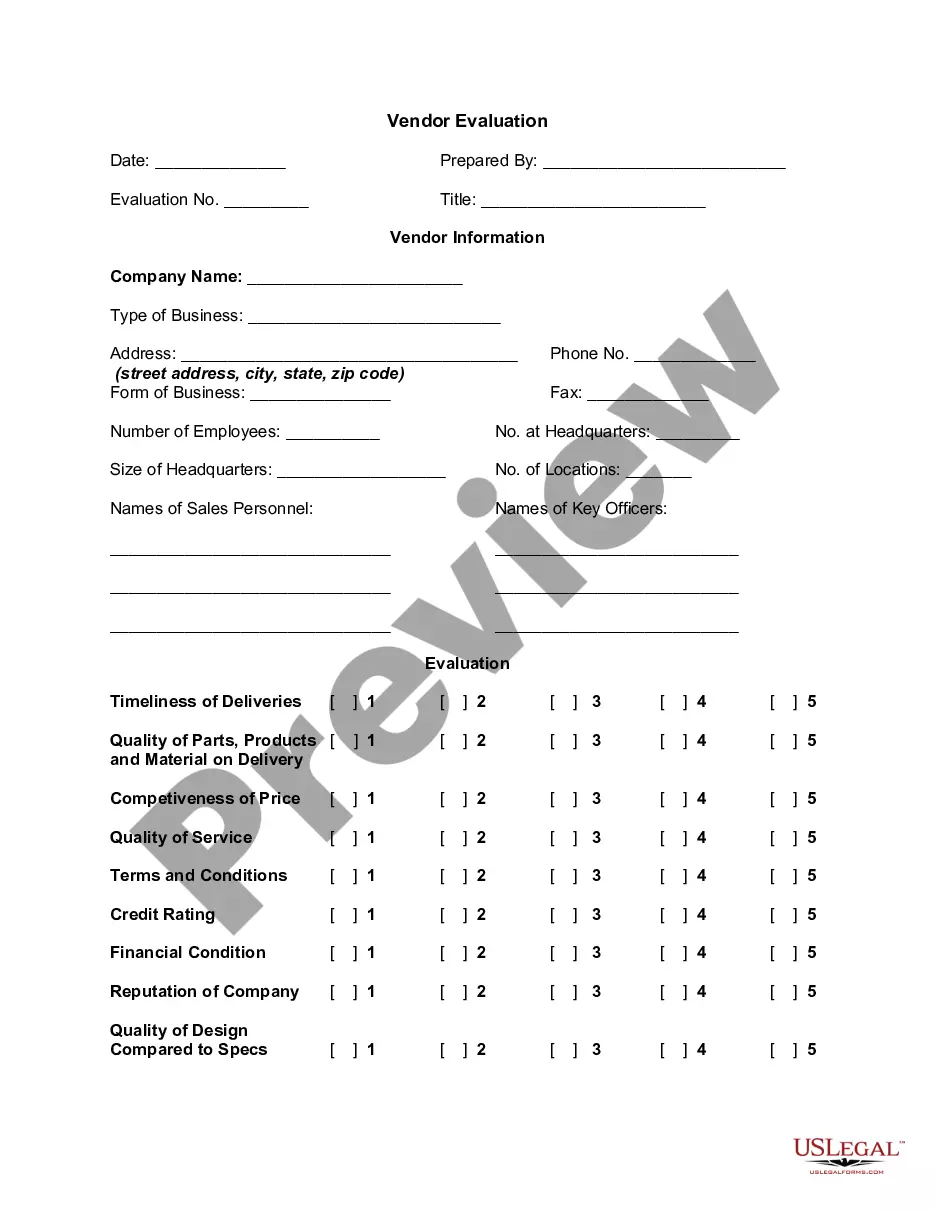
Evaluation criteria for software vendor selection are the parameters or factors that organizations consider when assessing and choosing a vendor for their software needs. These criteria help organizations make informed decisions and select the most suitable vendor based on their specific requirements. The evaluation criteria vary from organization to organization and are based on the unique needs, budget, and long-term goals of the organization. 1. Functional Fit: This criterion assesses how well the software vendor's offerings meet the organization's functional requirements. It examines whether the software's features and capabilities align with the organization's needs and objectives. 2. Scalability: Organizations should consider the ability of the software to accommodate their current and future growth. Scalability evaluation criteria assess whether the software vendor's solution can handle increasing volumes or additional users without compromising performance or requiring significant upgrades. 3. Integration capabilities: The evaluation must include an assessment of how well the software can integrate with the existing systems, databases, and applications in the organization's IT infrastructure. This criterion helps ensure smooth data flow and avoids duplication or disjointed processes. 4. Vendor experience and reputation: Evaluating the vendor's experience in the industry is crucial. Organizations should consider the vendor's track record, customer references, and reputation in terms of reliability, quality of support, and commitment to customer satisfaction. This criterion helps minimize risks associated with working with inexperienced or unreliable vendors. 5. Technical support and maintenance: Organizations should assess the vendor's technical support and maintenance services. This includes availability of support channels, response times, emergency assistance, software updates, and bug fixes. Robust support and maintenance ensure smooth operations in case of issues or upgrades. 6. Cost considerations: Evaluating the cost includes both the software itself and the associated expenses such as implementation, customization, training, and ongoing support. Organizations need to consider their budget and determine whether the vendor's pricing aligns with the expected return on investment (ROI) and overall affordability. 7. Security and data protection: Organizations should evaluate the software vendor's security measures, data protection protocols, and alignment with industry standards and regulations. This criterion ensures that the software and associated data remain secure, protecting the organization's sensitive information. 8. Vendor's financial stability: Assessing the vendor's financial stability and long-term viability is important to minimize risks associated with the vendor going out of business or discontinuing support. Organizations should consider the vendor's financials, growth patterns, and market position. Different types of evaluation criteria may exist based on the industry, organization size, or specific software needs. For example, if the organization operates in a highly regulated sector, compliance with industry-specific regulations may be an important criterion. If the software requires specific integrations with legacy systems, integration capabilities become a primary evaluation factor. Additionally, some organizations may prioritize ease of use, user interface, or customization options as critical criteria.
Evaluation Criteria For Software Vendor Selection
Description software vendor selection criteria template
How to fill out Evaluation Criteria For Software Vendor Selection?
Handling legal documents and procedures might be a time-consuming addition to the day. Evaluation Criteria For Software Vendor Selection and forms like it usually require you to search for them and navigate how you can complete them appropriately. As a result, regardless if you are taking care of economic, legal, or individual matters, having a comprehensive and convenient online catalogue of forms on hand will go a long way.
US Legal Forms is the best online platform of legal templates, boasting more than 85,000 state-specific forms and numerous resources that will help you complete your documents quickly. Discover the catalogue of pertinent papers available to you with just one click.
US Legal Forms provides you with state- and county-specific forms offered at any time for downloading. Protect your document administration processes having a top-notch support that lets you put together any form in minutes with no additional or hidden charges. Just log in in your account, identify Evaluation Criteria For Software Vendor Selection and acquire it right away from the My Forms tab. You may also gain access to previously saved forms.
Is it your first time utilizing US Legal Forms? Sign up and set up an account in a few minutes and you’ll gain access to the form catalogue and Evaluation Criteria For Software Vendor Selection. Then, stick to the steps listed below to complete your form:
- Make sure you have the correct form by using the Review option and reading the form information.
- Choose Buy Now when all set, and choose the subscription plan that fits your needs.
- Press Download then complete, eSign, and print out the form.
US Legal Forms has 25 years of experience supporting users handle their legal documents. Get the form you need right now and improve any operation without breaking a sweat.
Form popularity
FAQ
A notary acknowledgement ensures that the signer of the document is indeed the person named in the document. The function of the notary in this case is to verify the identity of the signer. On the other hand, a notary is asked to perform a Jurat, when the signer takes an oath or makes an affirmation.
A notary public in and for said state, (name of officer signing document) who signed to the writing above, bearing the date of _____(date) (name of corporation) has this day acknowledged before me the said writing to be the act and deed of said corporation.
An Acknowledgement of Signature or Acknowledgement of Execution is a notary which verifies that a particular person signed a given document. It is often used for legal agreements, business documents, etc.
A Georgia notary acknowledgment is used to verify an individual's signature on a legal document before a notary public. It includes the signer's name, the notarization date, and the type of identification they provide to the notary public.
An acknowledgment requires the following steps: The signer must physically appear before you. You as the notary must positively identify the signer ing to your state's rules. The signer may either sign the document before appearing before you, or in your presence.
The usual notary acknowledgment language does not state that the notary actually saw the signor execute the document in their presence. The requirement in Georgia is that the notary must attest, or in plain terms, actually witness the signing of the document for it to be valid and recordable.
This record was acknowledged before me on _______________ by ___________________. Signed (or attested) before me on _______________ by _____________________. If the document you are handed to notarize does not have any notary wording, you must ask the customer which notary act they want you to perform.
The purpose of an acknowledgment is for a signer, whose identity has been verified, to declare to a Notary or notarial officer that he or she has willingly signed a document.