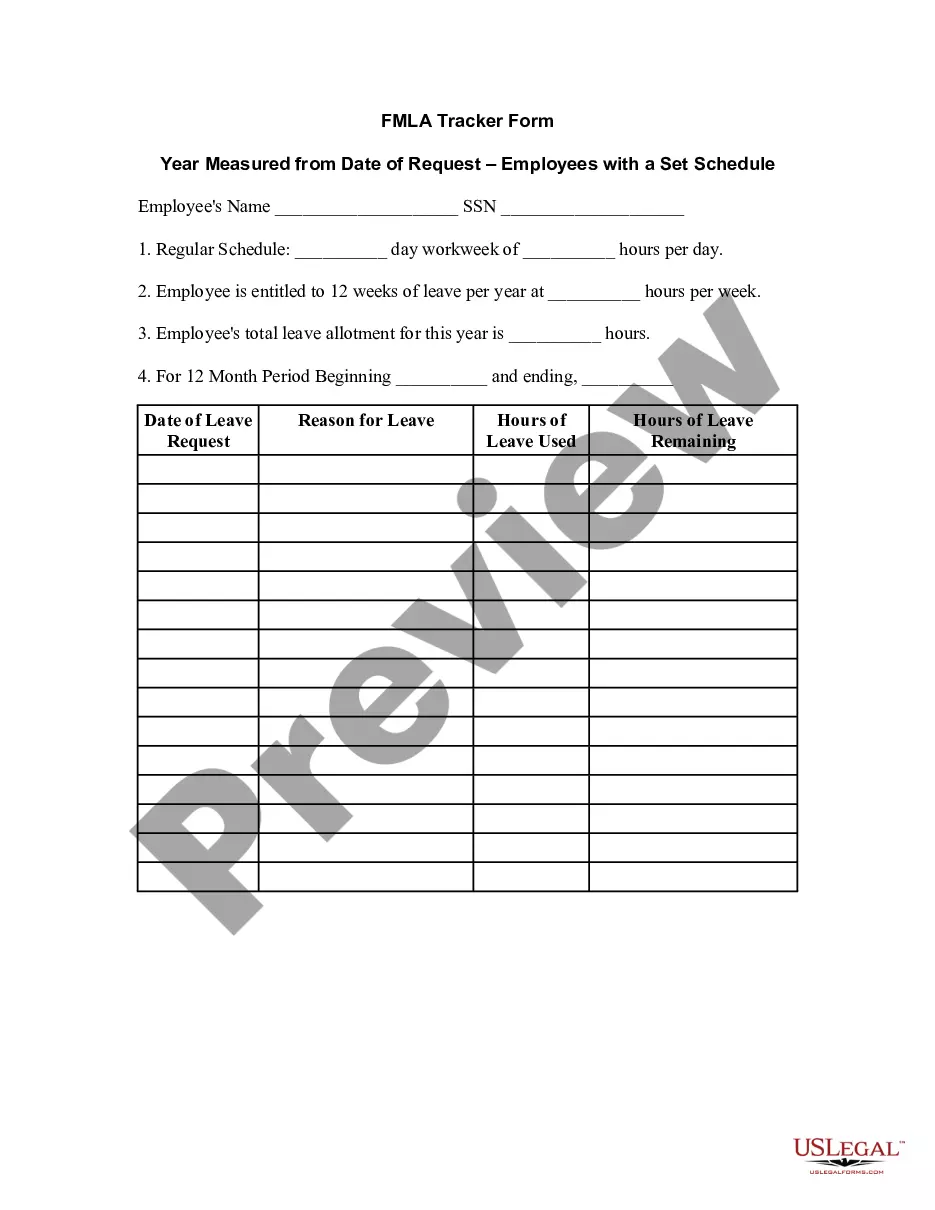
The rolling 12-month period for Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) is an important aspect to understand for both employees and employers. FMLA provides eligible employees with up to 12 weeks of job-protected unpaid leave per year to handle family or medical situations without risking their job. To determine the 12-month period, employers typically use either the calendar year or a rolling backward method from the date an employee's FMLA leave begins. Here are two types of rolling 12-month periods often used for FMLA calculations: 1. Calendar Year Rolling Period: — In this method, the rolling 12-month period starts on January 1st and ends on December 31st of each year. — This approach provides a clear and predictable 12-month FMLA period for all employees, regardless of their individual hire date. 2. The "Look-Back" Rolling Period: — With this method, the 12-month rolling period is determined by looking back from the first day of FMLA leave for the employee. — For instance, if an employee requests FMLA leaves on May 1st, the employer will examine the previous 12 months (May 1st of the previous year to April 30th of the current year) to determine their FMLA eligibility. — This method ensures that employees can access FMLA leave based on their specific circumstances, regardless of the calendar year. Through these two examples, it is essential to note that employers must clearly communicate which rolling 12-month period they follow to avoid confusion among employees. Some relevant keywords to consider for this topic are: — FMLA rolling 12-montperiodio— - FMLA leave calculation — FMLA calendar yeamethodho— - Rolling backward FMLA period — Determining FMLeligibilityit— - FMLA leave start date — "Look-Back" methoformalML— - FMLA employee rights — Job-protected FMLleadav— - FMLA policy explanation Proper understanding of the FMLA rolling 12-month period is crucial for both employees and employers to ensure fair treatment, adherence to legal obligations, and effective management of leave requests.
Example Of Rolling 12 Month Period For Fmla
Description rolling 12 month fmla calculator excel
How to fill out Example Of Rolling 12 Month Period For Fmla?
Handling legal paperwork and operations could be a time-consuming addition to the day. Example Of Rolling 12 Month Period For Fmla and forms like it usually need you to search for them and navigate the way to complete them appropriately. As a result, whether you are taking care of financial, legal, or personal matters, using a extensive and hassle-free online library of forms on hand will greatly assist.
US Legal Forms is the top online platform of legal templates, featuring over 85,000 state-specific forms and a number of tools to help you complete your paperwork quickly. Explore the library of relevant papers available with just one click.
US Legal Forms provides you with state- and county-specific forms available at any time for downloading. Protect your papers managing operations having a high quality services that allows you to prepare any form within minutes without having extra or hidden charges. Just log in to the profile, identify Example Of Rolling 12 Month Period For Fmla and download it straight away within the My Forms tab. You can also access formerly saved forms.
Would it be the first time utilizing US Legal Forms? Register and set up up your account in a few minutes and you will get access to the form library and Example Of Rolling 12 Month Period For Fmla. Then, adhere to the steps below to complete your form:
- Make sure you have found the correct form by using the Review feature and reading the form description.
- Choose Buy Now when ready, and choose the subscription plan that is right for you.
- Press Download then complete, sign, and print out the form.
US Legal Forms has twenty five years of expertise helping consumers control their legal paperwork. Find the form you want right now and improve any operation without breaking a sweat.
fmla types of leave Form popularity
FAQ
The next 12-month period would then begin the first time FMLA leave is taken after completion of any previous 12-month period. For example, if any employee requests leave on June 3, 2009, the 12-month period for this employee and this occasion would be June 3, 2009 until June 2, 2010.
Under the ''rolling'' 12-month period, each time an employee takes FMLA leave, the remaining leave entitlement would be the balance of the 12 weeks which has not been used during the immediately preceding 12 months. Example 1: Michael requests three weeks of FMLA leave to begin on July 31st.
The calendar year; Any fixed 12-month "leave year" The 12-month period measured forward from the date any employee's first FMLA leave begins; or. A "rolling" 12-month period measured backward from the date an employee uses any FMLA leave.
If this is the first FMLA leave request, the 12-month period will begin on the first date of this FMLA leave. If the employee's request for leave is more than 12 months after a previous FMLA leave, the first date of the current FMLA leave will be the beginning of the new 12-month period.
The 12-month period measured forward from the date any employee's first FMLA leave begins; or. A "rolling" 12-month period measured backward from the date an employee uses any FMLA leave.