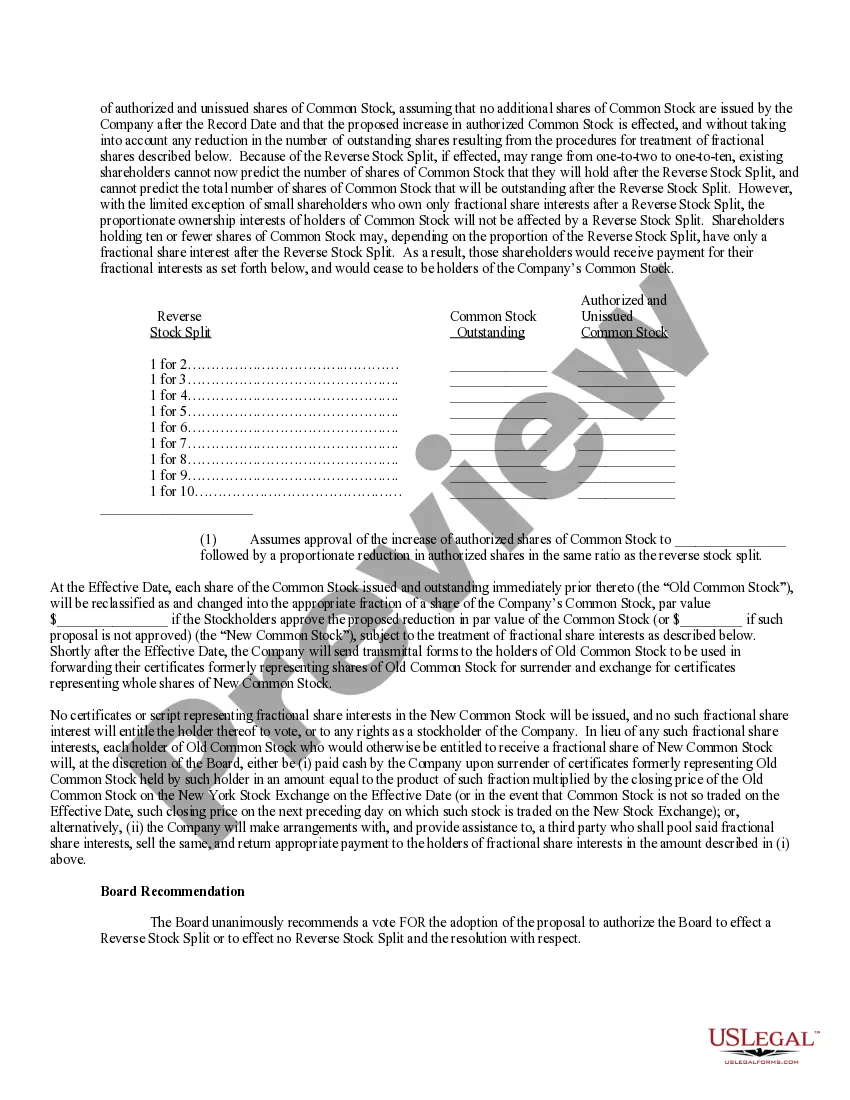
Par Value For Stock
State:
Multi-State
Control #:
US-CC-3-213F
Format:
Word;
Rich Text
Instant download
Description Authorized Stock With
This sample form, a detailed Proposal to Amend Certificate to Reduce Par Value, Increase Authorized Common Stock and Reverse Stock Split w/Exhibit document, is a model for use in corporate matters. The language is easily adapted to fit your specific circumstances. Available in several standard formats.
Free preview Par Value Common Stock