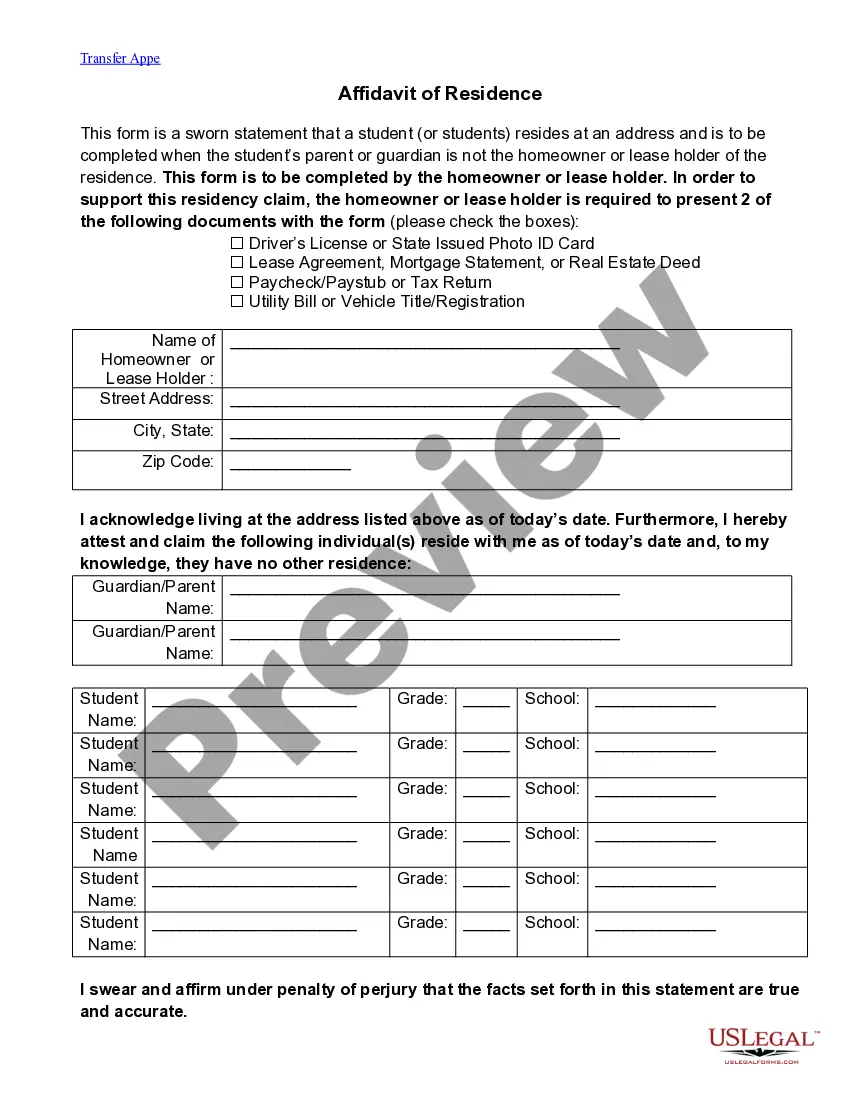
Alaska Proof of Residency for College
Description
How to fill out Proof Of Residency For College?
US Legal Forms - one of several biggest libraries of legal kinds in the USA - gives an array of legal file layouts you are able to down load or print out. While using web site, you can find thousands of kinds for business and personal purposes, categorized by categories, states, or key phrases.You will find the most recent versions of kinds such as the Alaska Proof of Residency for College in seconds.
If you already possess a registration, log in and down load Alaska Proof of Residency for College from the US Legal Forms catalogue. The Download option can look on each and every type you view. You have access to all formerly downloaded kinds inside the My Forms tab of your own bank account.
In order to use US Legal Forms initially, listed here are basic guidelines to get you started:
- Be sure to have selected the correct type for the town/state. Click the Preview option to check the form`s content. Browse the type information to actually have selected the proper type.
- In the event the type doesn`t match your demands, use the Research field near the top of the monitor to obtain the one which does.
- If you are content with the shape, affirm your option by clicking on the Acquire now option. Then, choose the rates plan you want and provide your accreditations to sign up to have an bank account.
- Procedure the transaction. Make use of Visa or Mastercard or PayPal bank account to complete the transaction.
- Select the format and down load the shape on your product.
- Make adjustments. Complete, change and print out and signal the downloaded Alaska Proof of Residency for College.
Every single design you included with your bank account does not have an expiration day and is the one you have eternally. So, in order to down load or print out an additional duplicate, just go to the My Forms section and then click on the type you will need.
Obtain access to the Alaska Proof of Residency for College with US Legal Forms, one of the most considerable catalogue of legal file layouts. Use thousands of specialist and state-distinct layouts that fulfill your company or personal demands and demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
1. Tuition Reciprocity RegionParticipating StatesWesternAlaska, Arizona, California, Colorado, Hawaii, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oregon, South Dakota, Utah, Washington, Wyoming, and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands3 more rows
An Alaska resident, defined as a person who is a United States citizen or eligible non-citizen that has been physically present in Alaska for at least the past one year.
You have been physically present in Alaska for one or more years and provide the following: Documentation that you moved your household goods to Alaska prior to one year ago; or. Documentation of your lease, rental, or ownership of real property in Alaska for at least the prior year; or.
415(a): "resident" means a person (including an alien) who is physically present in Alaska with the intent to remain indefinitely and make a home here, has maintained that person's domicile in Alaska for the 12 consecutive months immediately preceding this application for a license, and is not claiming residency or ...
Alaska's universities are consistently rated as some of the most affordable in the United States. In-state undergraduate tuition and fees are approximately $6,500 (2023-24); out-of-state undergraduate tuition and fees are $22,000 (2023-24).
Residential Address Utility bill. Alaska voter registration card. Alaska title and/or registration (Issued at least 30 days prior to application) Paycheck Stub.
An individual's intent to establish residency, remain indefinitely in Alaska, or to return to Alaska and remain indefinitely is demonstrated through the establishment and maintenance of customary ties indicative of Alaska residency and the absence of those ties in another state or country.
The Alaska Permanent Fund pays out annual dividends, called the Permanent Fund Dividend (PFD). To qualify for a dividend, the Alaska residents must have lived a full calendar year in the state and must intend to remain in Alaska.