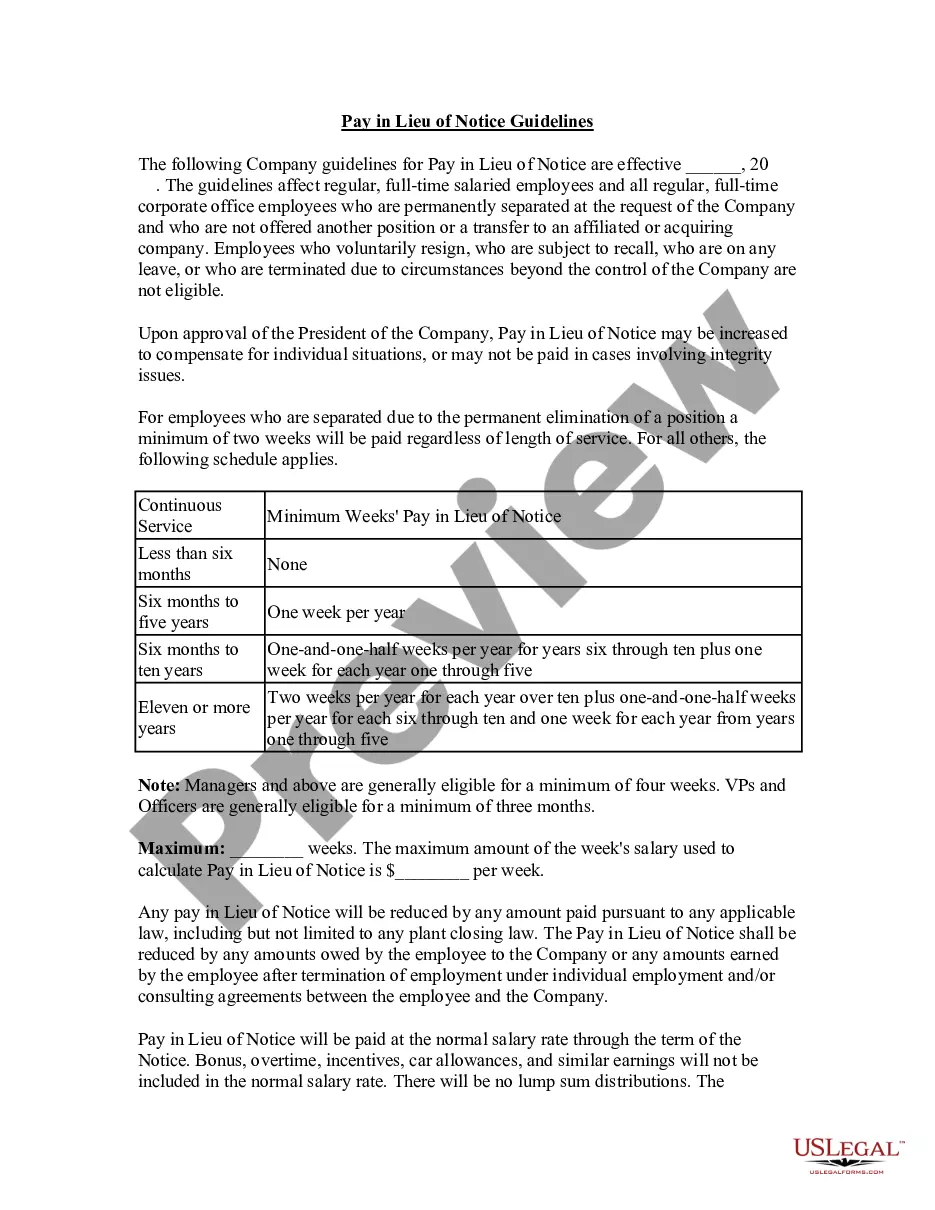
Alaska Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines serve as a legal framework determining the compensation an employee is entitled to receive when their employment is terminated without a proper notice period. Pay in Lieu of Notice (PILOT) refers to payment made by an employer to an employee whose services are terminated without providing the required notice period. Under Alaska state law, employers must adhere to specific regulations regarding PILOT. The Alaska Department of Labor and Workforce Development establishes these guidelines to protect employees' rights and ensure fair treatment in termination situations. The regulations aim to provide employees with financial stability during a transitional period after sudden termination. There are primarily two types of Alaska Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines: 1. Statutory Guidelines: These guidelines are established by state statutes and regulations, providing a baseline for what employees are entitled to in terms of payment when their employment is terminated without adequate notice. According to Alaska law, employees must be compensated for all wages earned and unpaid as of the termination date. Additionally, unpaid wages should be released within three working days. 2. Contractual Guidelines: These guidelines are determined by the terms of an employment contract or collective bargaining agreement between the employer and the employee. If the employment contract explicitly outlines specific PILOT provisions, such as a notice period or payment terms, those provisions take precedence. Employers must follow the contractual guidelines established by the employment agreement. However, Alaska does not have a specific statutory provision for Pay in Lieu of Notice. Instead, employers and employees are expected to mutually agree upon such terms in the employment contract. Hence, the specific guidelines and terms regarding PILOT may vary from one employer to another, depending on the employment agreement in place. To summarize, Alaska Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines ensure that terminated employees receive appropriate compensation for the lack of a notice period. While statutory guidelines provide a baseline, contractual provisions listed in the employment agreement may supersede them. By following these guidelines, employers demonstrate their commitment to fair employment practices and protect employees' rights.
Alaska Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines
Description
How to fill out Alaska Pay In Lieu Of Notice Guidelines?
If you have to complete, download, or print out lawful record themes, use US Legal Forms, the greatest selection of lawful forms, which can be found online. Take advantage of the site`s simple and easy practical lookup to obtain the papers you need. A variety of themes for company and specific functions are sorted by types and says, or keywords and phrases. Use US Legal Forms to obtain the Alaska Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines with a few mouse clicks.
Should you be presently a US Legal Forms buyer, log in in your account and click on the Download key to have the Alaska Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines. You can also entry forms you previously downloaded in the My Forms tab of your own account.
If you are using US Legal Forms the first time, refer to the instructions listed below:
- Step 1. Ensure you have chosen the shape to the appropriate city/region.
- Step 2. Make use of the Review choice to look through the form`s information. Do not forget to learn the information.
- Step 3. Should you be not satisfied with the develop, make use of the Look for area at the top of the monitor to get other types of the lawful develop design.
- Step 4. Once you have found the shape you need, click on the Purchase now key. Choose the rates program you choose and add your credentials to sign up for an account.
- Step 5. Process the transaction. You may use your credit card or PayPal account to accomplish the transaction.
- Step 6. Choose the structure of the lawful develop and download it on the device.
- Step 7. Total, modify and print out or indicator the Alaska Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines.
Every single lawful record design you purchase is yours eternally. You may have acces to each develop you downloaded within your acccount. Go through the My Forms area and select a develop to print out or download again.
Remain competitive and download, and print out the Alaska Pay in Lieu of Notice Guidelines with US Legal Forms. There are many expert and state-certain forms you can use for the company or specific requires.