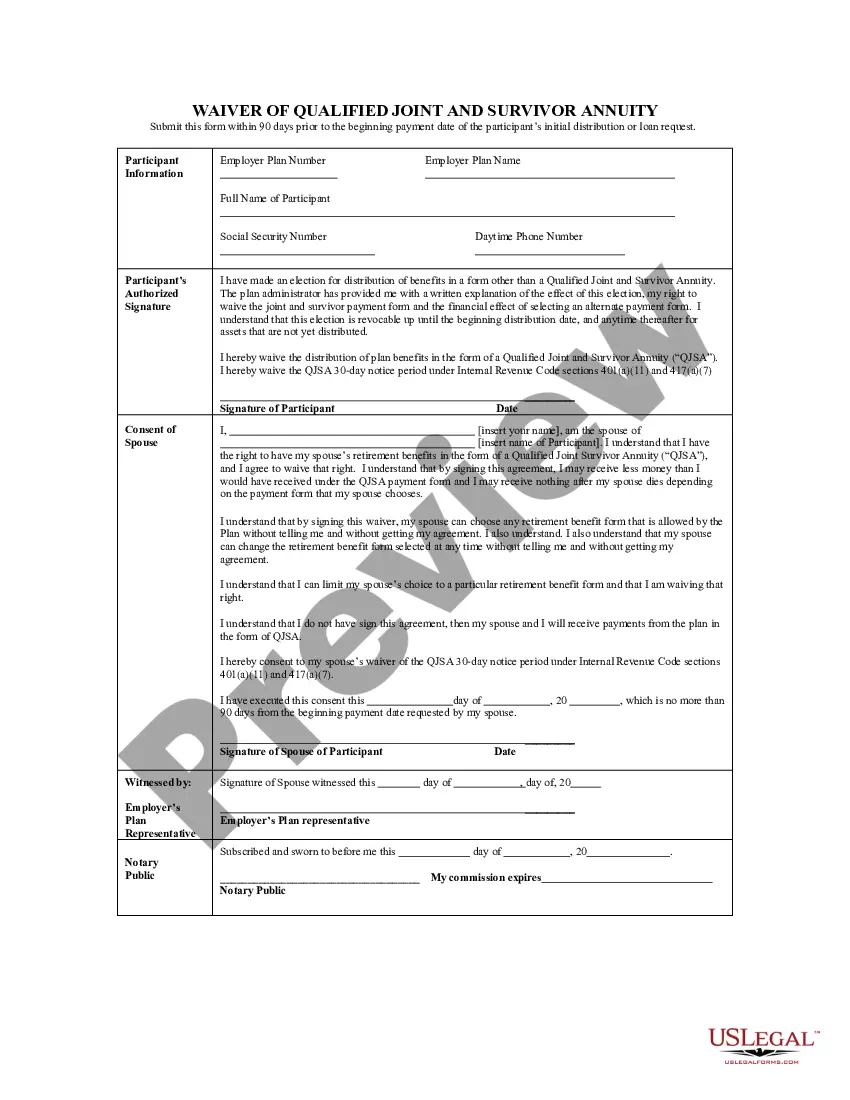
Alaska Waiver of Qualified Joint and Survivor Annuity - QJSA
Description
How to fill out Waiver Of Qualified Joint And Survivor Annuity - QJSA?
If you desire to complete, acquire, or print valid document templates, utilize US Legal Forms, the largest collection of legal forms available online.
Take advantage of the website's straightforward and convenient search to locate the documents you require.
Various templates for business and personal purposes are categorized by types and regions, or keywords.
Every legal document format you purchase belongs to you permanently.
You can access every form you acquired with your account. Select the My documents section and choose a form to print or download again.
- To obtain the Alaska Waiver of Qualified Joint and Survivor Annuity - QJSA with just a few clicks, use US Legal Forms.
- If you are an existing US Legal Forms customer, Log Into your account and click the Download option to find the Alaska Waiver of Qualified Joint and Survivor Annuity - QJSA.
- You can also access forms you previously acquired from the My documents tab in your account.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, follow these instructions.
- Step 1. Make sure you have selected the form for the correct city/state.
- Step 2. Use the Preview option to review the form's content. Don't forget to read the summary.
- Step 3. If you are not satisfied with the form, use the Search field at the top of the screen to find other forms of your legal form type.
- Step 4. Once you have found the form you need, choose the Buy Now option. Select the pricing plan you prefer and provide your information to register for an account.
- Step 5. Process the transaction. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to complete the transaction.
- Step 6. Select the format of your legal document and download it to your device.
- Step 7. Fill out, edit, and print or sign the Alaska Waiver of Qualified Joint and Survivor Annuity - QJSA.
Form popularity
FAQ
This benefit provides payments to the participant's spouse for his or her lifetime equal to a percentage (as specified in the Pension Plan) not less than one-half of the annuity that would have been payable during their joint lives. The participant may waive the Qualified Preretirement Survivor Annuity.
A QJSA is when retirement benefits are paid as a life annuity (a series of payments, usually monthly, for life) to the participant and a survivor annuity over the life of the participant's surviving spouse (or a former spouse, child or dependent who must be treated as a surviving spouse under a QDRO) following the
This special payment form is often called a qualified joint and survivor annuity or QJSA payment form. This benefit is paid to the participant each year and, on the participant's death, a survivor annuity is paid to the surviving spouse.
This benefit provides payments to the participant's spouse for his or her lifetime equal to a percentage (as specified in the Pension Plan) not less than one-half of the annuity that would have been payable during their joint lives. The participant may waive the Qualified Preretirement Survivor Annuity.
The Survivor Benefit Plan (SBP) allows a retiree to ensure, after death, a continuous lifetime annuity for their dependents. The annuity which is based on a percentage of retired pay is called SBP and is paid to an eligible beneficiary. It pays your eligible survivors an inflation-adjusted monthly income.
A joint and survivor annuity is an insurance product designed for couples that continues to make regular payments as long as one spouse lives. A joint and survivor annuity has the advantage of providing income if one or both people live longer than expected. This is not a good choice for a younger couple.
life annuity provides the largest monthly payment but pays only during your lifetime. It's a poor choice if your spouse will need income from your pension to pay routine expenses. A jointandsurvivor annuity pays you during your lifetime and then continues to pay your spouse or other named beneficiary.
QJSA rules apply to money-purchase pension plans, defined benefit plans, and target benefits. They can also apply to profit-sharing and 401(k) and 403(b) plans, but only if so elected under the plan.
Qualified Joint and Survivor AnnuityIf your spouse consents to change the way the Plan's retirement benefits are paid, your spouse gives up his or her right to the QJSA payments. This is referred to as a waiver of the QJSA payment form.
When the participant dies, the spouse will receive lifetime payments in the same or reduced amount. The participant may waive the Qualified Joint and Survivor Annuity with spousal consent and elect to receive another form of payment.