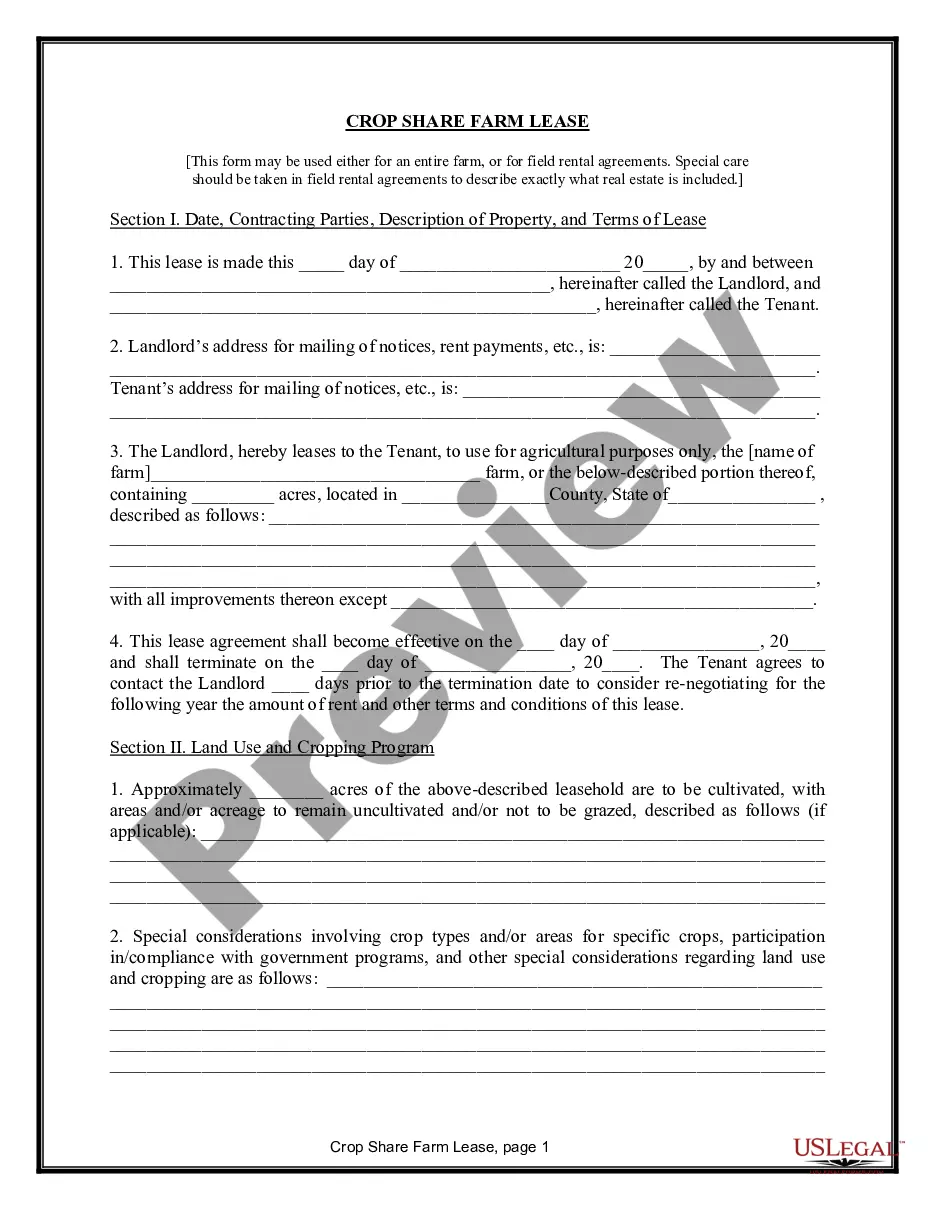
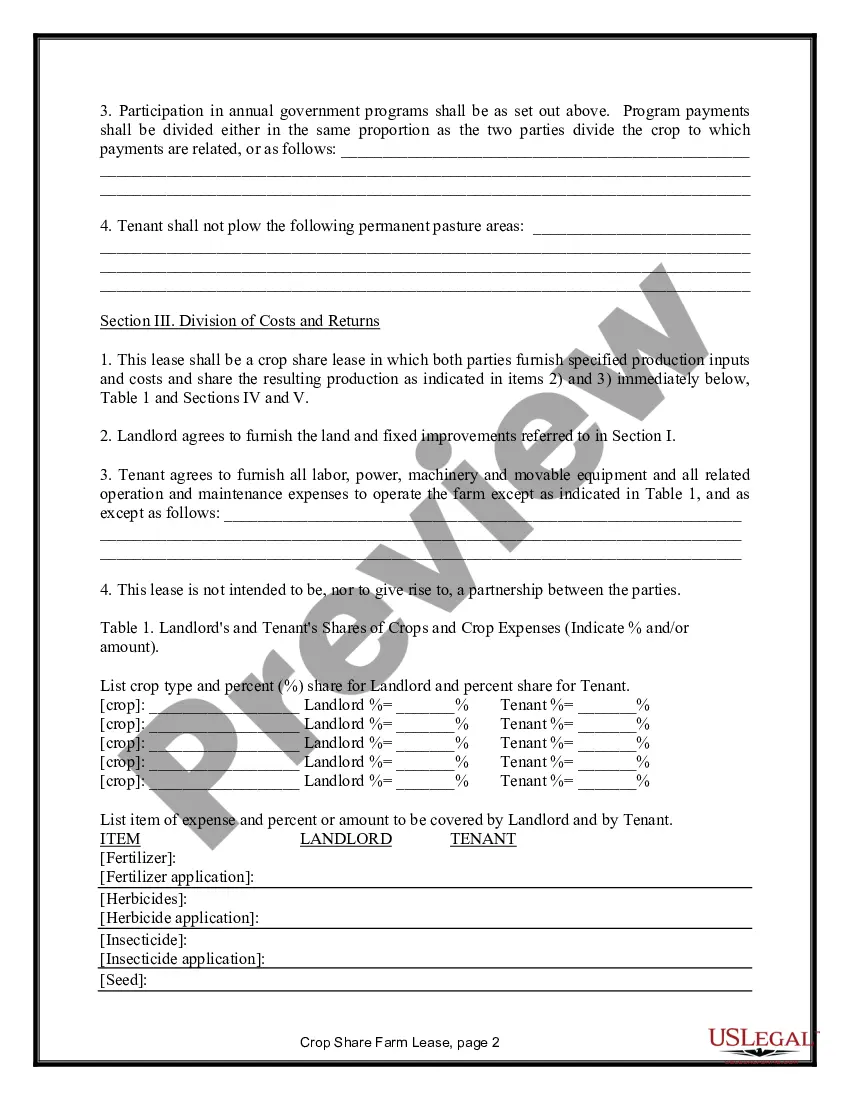
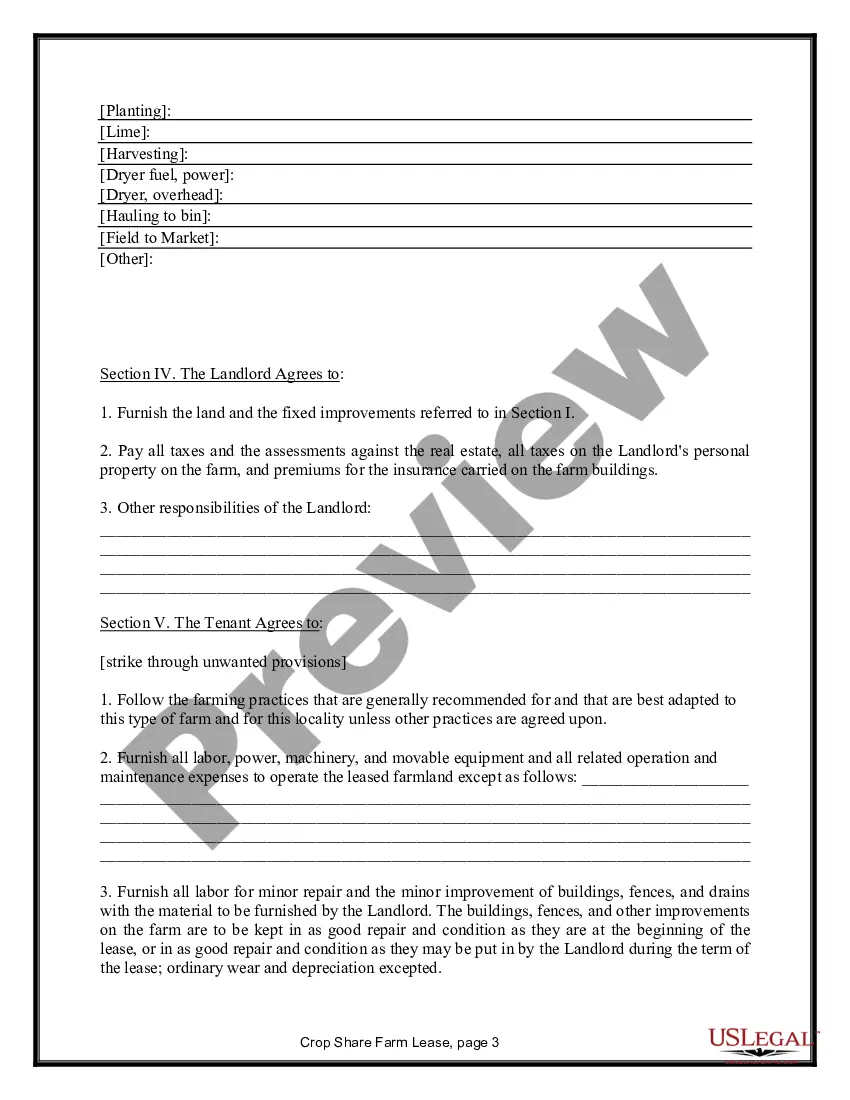
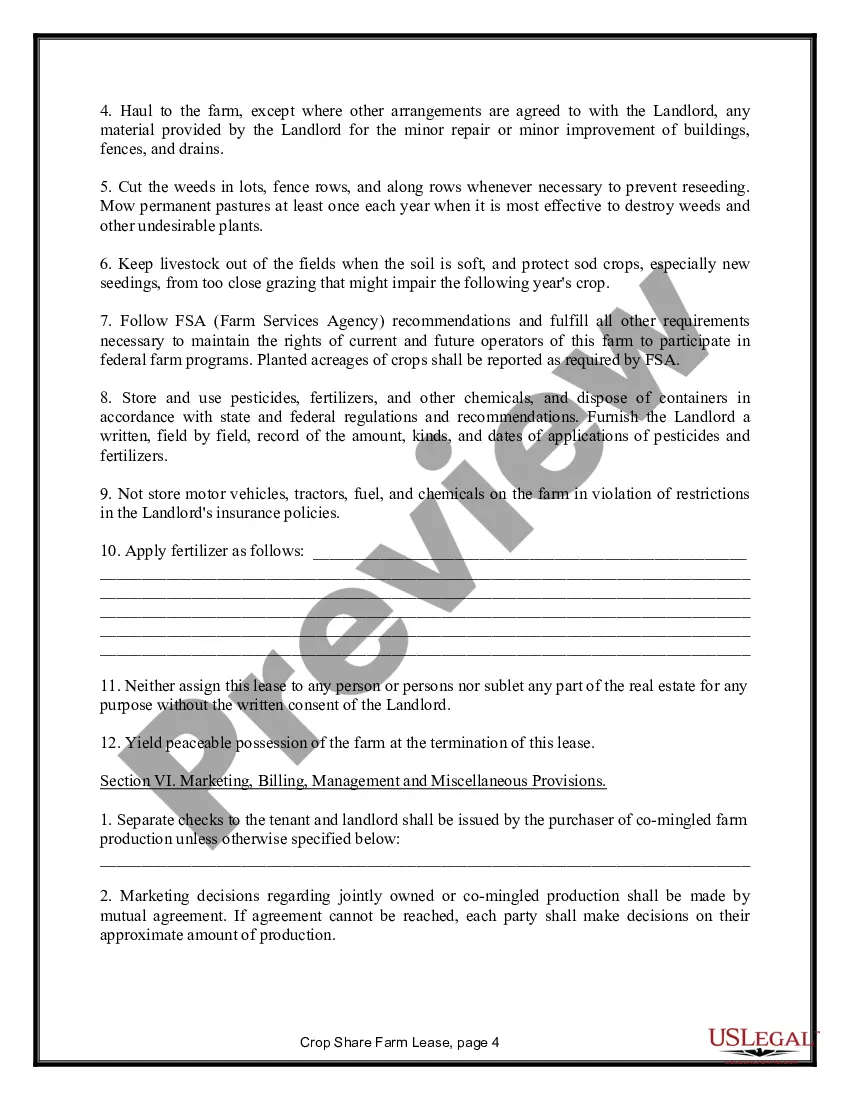
Alaska Farm Lease or Rental — Crop Share is an agricultural arrangement wherein a landowner leases their property to a farmer in exchange for a share of the crops grown. This collaborative approach allows both parties to share the risks and benefits of farming, fostering a mutually beneficial partnership. Alaska, known for its vast and diverse landscapes, offers unique opportunities for agricultural activities, and the Farm Lease or Rental — Crop Share option provides a sustainable and efficient way for farmers to access land without significant upfront costs. Various types of Alaska Farm Lease or Rental — Crop Share arrangements exist, each with its own characteristics tailored to different farming needs and preferences. These may include: 1. Traditional Crop Share Lease: In this arrangement, the landowner and farmer agree to divide the crop proceeds at a predetermined ratio. Typically, the landowner provides the land, while the farmer provides labor, machinery, and inputs such as seeds and fertilizers. The crop share ratio could vary, depending on various factors like land fertility, infrastructure availability, and market conditions. 2. Variable Crop Share Lease: This type of lease adjusts the crop share ratio based on yearly yield variations or changes in market prices. It allows for a more equitable distribution of risks and rewards between the landowner and farmer, ensuring both parties are fairly compensated and motivated to improve farming practices. 3. Organic Crop Share Lease: With growing consumer demand for organic produce, organic farming has gained popularity in Alaska. This type of lease specifically focuses on organic farming practices, where farmers follow strict guidelines to cultivate crops without synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). The landowner may prioritize the conservation of soil health and biodiversity, making this lease suitable for farmers interested in sustainable agricultural practices. 4. Livestock Crop Share Lease: Apart from crop cultivation, some farmers in Alaska engage in livestock production, particularly raising cattle, pigs, or poultry. In this lease arrangement, the landowner allows the farmer to utilize the land for grazing, feeding, and maintaining livestock, while both parties share the profits derived from the sale of livestock or related products. Alaska Farm Lease or Rental — Crop Share agreements offer an attractive option for both landowners and farmers, facilitating sustainable and profitable farming operations while promoting land utilization and economic growth in Alaska's agricultural sector.
Alaska Farm Lease or Rental - Crop Share
Description
How to fill out Alaska Farm Lease Or Rental - Crop Share?
You can devote several hours on the Internet searching for the legal document template that suits the federal and state needs you want. US Legal Forms offers a large number of legal forms that happen to be reviewed by professionals. It is possible to down load or produce the Alaska Farm Lease or Rental - Crop Share from your services.
If you already have a US Legal Forms profile, it is possible to log in and then click the Down load option. After that, it is possible to total, change, produce, or sign the Alaska Farm Lease or Rental - Crop Share. Every legal document template you acquire is the one you have forever. To acquire yet another backup of any acquired type, proceed to the My Forms tab and then click the related option.
If you use the US Legal Forms website the first time, stick to the easy recommendations listed below:
- Very first, be sure that you have selected the best document template to the county/town of your choosing. Look at the type description to ensure you have picked the correct type. If offered, utilize the Review option to look with the document template too.
- In order to locate yet another edition of the type, utilize the Lookup discipline to get the template that meets your requirements and needs.
- When you have discovered the template you would like, just click Buy now to move forward.
- Select the rates plan you would like, key in your credentials, and sign up for your account on US Legal Forms.
- Complete the purchase. You can utilize your Visa or Mastercard or PayPal profile to cover the legal type.
- Select the formatting of the document and down load it in your device.
- Make modifications in your document if needed. You can total, change and sign and produce Alaska Farm Lease or Rental - Crop Share.
Down load and produce a large number of document layouts utilizing the US Legal Forms Internet site, that offers the most important collection of legal forms. Use expert and state-distinct layouts to tackle your company or individual demands.