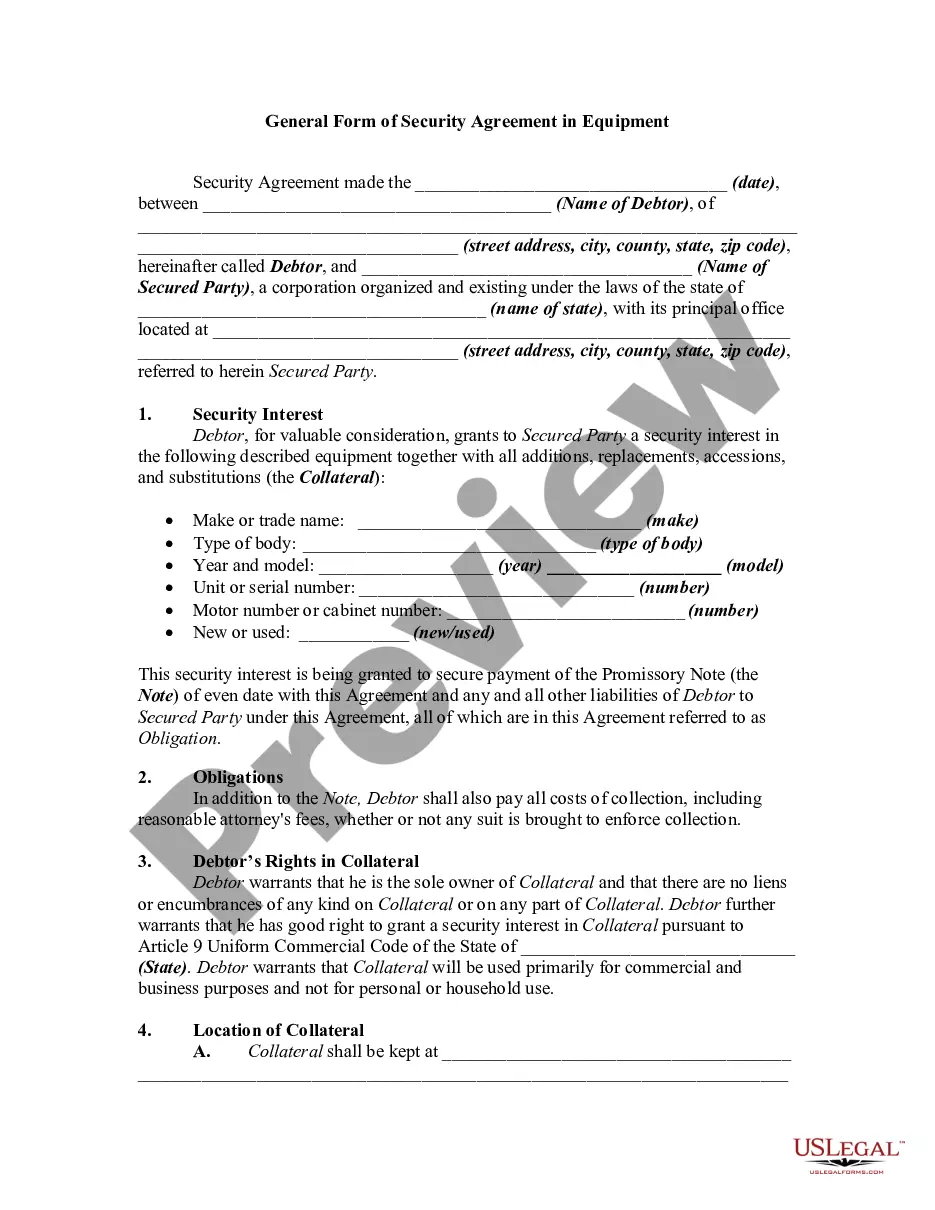
A secured transaction is created when a buyer or borrower (debtor) grants a seller or lender (creditor or secured party) a security interest in personal property (collateral). A security interest allows a creditor to repossess and sell the collateral if a debtor fails to pay a secured debt.
The Truth-in-Lending Act (TILA) is part of the Federal Consumer Credit Protection Act. The purpose of the TILA is to make full disclosure to debtors of what they are being charged for the credit they are receiving. The Act merely asks lenders to be honest to the debtors and not cover up what they are paying for the credit. Regulation Z is a federal regulation prepared by the Federal Reserve Board to carry out the details of the Act. TILA applies to consumer credit transactions. Consumer credit is credit for personal or household use and not commercial use or business purposes.
Alabama General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment is a legally binding document that outlines the terms and conditions pertaining to the pledge of equipment as collateral in a loan agreement. This agreement is commonly used in a variety of business transactions and helps protect the lender's interests in case of default by the borrower. The keywords relevant to this topic include "Alabama General Form of Security Agreement," "equipment," "collateral," "loan agreement," and "borrower." In Alabama, there are several variations or types of General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment, including: 1. Alabama General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment for Business Loans: This type of agreement is commonly used when a business secures a loan using its equipment as collateral. It outlines the details of the equipment being pledged, including its description, condition, and value. The agreement also defines the terms of the loan, such as repayment schedule, interest rate, and default provisions. 2. Alabama General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment for Construction Projects: In construction projects, equipment plays a vital role. This specific type of agreement focuses on securing loans for construction projects by using the construction equipment as collateral. It includes provisions specific to the construction industry, such as project timelines, payment milestones, and provisions for equipment maintenance and insurance. 3. Alabama General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment for Leases: When equipment is leased rather than owned, a different type of security agreement comes into play. This agreement outlines the terms and conditions of leasing equipment, including equipment description, duration of the lease, lease payment terms, and provisions for equipment maintenance and damage. 4. Alabama General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment for Agricultural Loans: Farmers and agricultural businesses often require loans to purchase or maintain equipment necessary for their operations. This type of agreement is designed specifically for securing loans by pledging agricultural equipment as collateral. It includes provisions related to agricultural practices, such as crop cycles, livestock management, and provisions for equipment upkeep. These different types of Alabama General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment cater to various industries and loan scenarios. Each agreement follows a common structure and contains similar elements, including details on the equipment being pledged, loan terms, default provisions, and conditions for releasing the equipment upon loan repayment. It is essential to consult legal professionals or specialized advisers while drafting or entering into such agreements to ensure compliance with Alabama's legal requirements and best protect the interests of both parties involved.