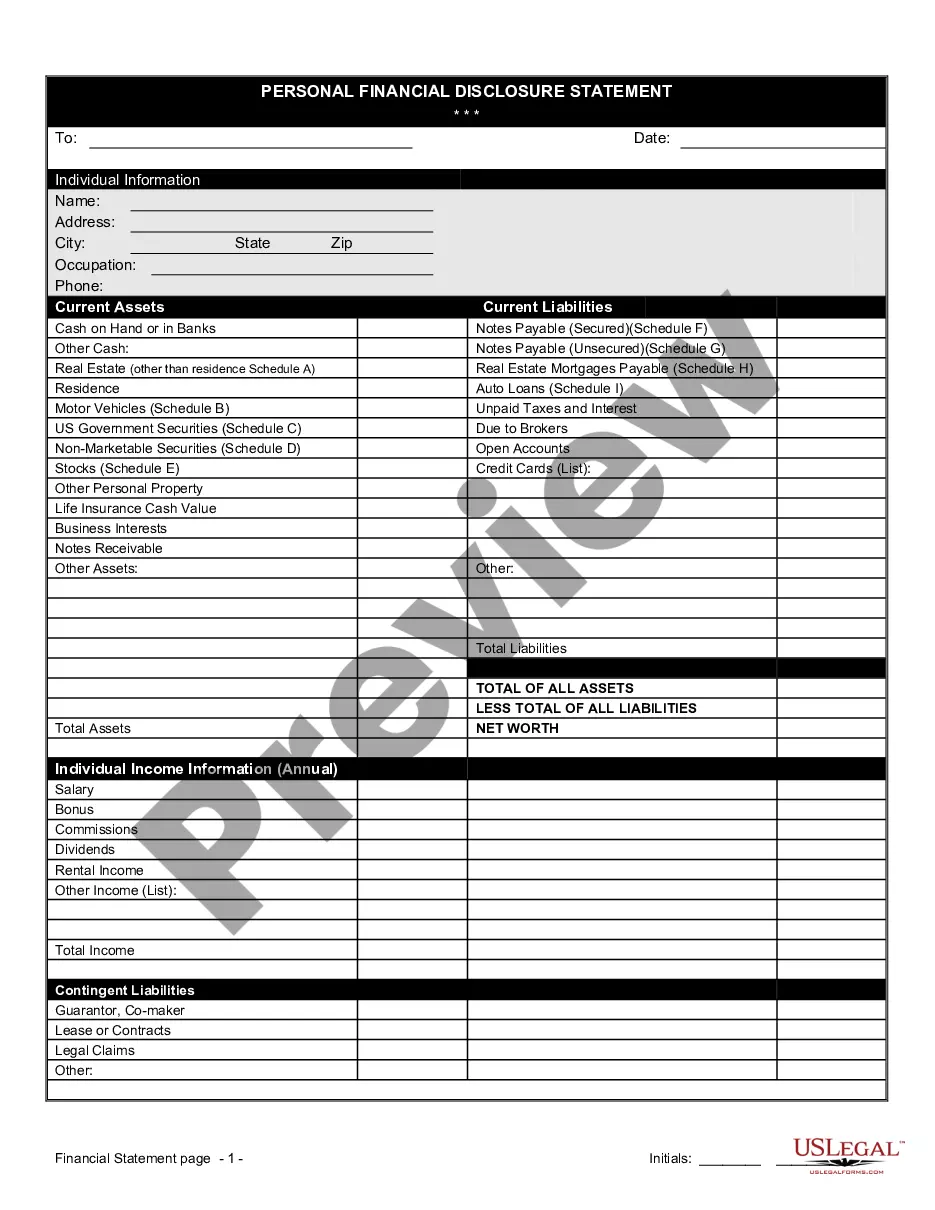
This office lease form states that a guaranty in which a corporate guarantor has the authority of the signatory to bind a corporation. This guaranty gives the guarantor full power, authority and legal right to execute and deliver this guaranty and that this guaranty constitutes the valid and binding obligation of the guarantor.
Alabama Authority of Signatory to Bind the Guarantor
Description
How to fill out Authority Of Signatory To Bind The Guarantor?
Are you currently in the place the place you need to have files for either organization or individual functions virtually every time? There are a lot of legitimate record templates available on the net, but finding types you can trust is not effortless. US Legal Forms provides a large number of kind templates, much like the Alabama Authority of Signatory to Bind the Guarantor, that happen to be created to meet state and federal requirements.
In case you are presently knowledgeable about US Legal Forms internet site and also have your account, simply log in. Following that, you can acquire the Alabama Authority of Signatory to Bind the Guarantor design.
If you do not offer an account and need to begin using US Legal Forms, adopt these measures:
- Discover the kind you want and ensure it is for the appropriate metropolis/state.
- Make use of the Preview key to review the form.
- Read the outline to ensure that you have chosen the right kind.
- When the kind is not what you are looking for, make use of the Research industry to discover the kind that meets your needs and requirements.
- If you obtain the appropriate kind, simply click Purchase now.
- Select the rates strategy you need, complete the required information and facts to make your account, and pay for the order utilizing your PayPal or bank card.
- Choose a hassle-free data file format and acquire your version.
Locate all the record templates you have bought in the My Forms menus. You may get a additional version of Alabama Authority of Signatory to Bind the Guarantor anytime, if required. Just select the required kind to acquire or produce the record design.
Use US Legal Forms, probably the most substantial selection of legitimate forms, to conserve time and avoid blunders. The support provides professionally manufactured legitimate record templates that you can use for a selection of functions. Produce your account on US Legal Forms and begin making your lifestyle a little easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
A guarantor is a person who ?guarantees? your identity. This person must have known you for at least 2 years and well enough to confirm the information in your application is true.
The "guarantor" is the person guarantying the debt while the party who originally incurred the debt is the "principle" and the creditor is the "guaranteed party." Under California law, if properly drafted, a guaranty is a fully enforceable obligation which allows the guaranteed party to proceed directly against the ...
Answer and Explanation: A guarantor's signature may refer to the actual signature of the guarantor whom the principal party or debtor may have acquired to secure his or her obligations.
A guarantor is a person who agrees to be responsible for the debt of another person. Being a guarantor is a serious obligation.
The guarantor unconditionally guarantees the payment obligations of the obligor (the borrower or debtor) for the benefit of the beneficiary (the lender or creditor). This Standard Clause has integrated notes with important explanations and drafting and negotiating tips.
A guarantor is someone who vouches for you financially and can be a friend, family member or even a third-party service. The guarantor signs the rental agreement with you and ensures rent payments are made on time if you fall behind or can no longer make the payments yourself.
The Guarantor agrees that, if any of the Obligations are not paid when due, the Guarantor will, upon demand by the Bank, forthwith pay such Obligations, or if the maturity thereof shall have been accelerated by the Bank, the Guarantor will forthwith pay all Obligations of the Borrower.
A guarantor is a person who can confirm your identity when you are applying for registration under the Indian Act or a secure status card as an adult or as the parent or legal guardian of a child or dependent adult.