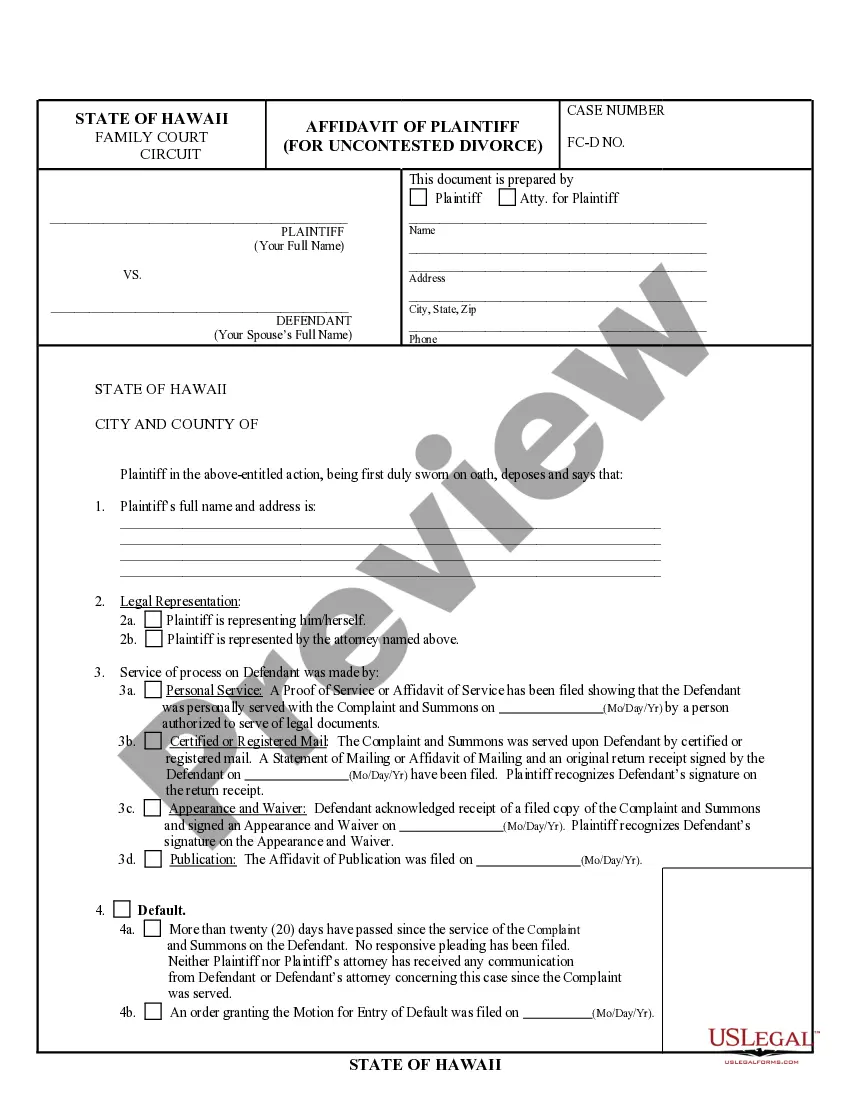
This form is used if any party fails or is unable to pay its proportionate share of the costs for the operation, the Operator shall have the right to enforce the lien, or the Operator shall have the right, exercised before or after Completion of the operation.
The Arizona Rights of Operator Against A Defaulting Party Pre-1989 Agreements refer to the legal provisions and remedies available to operators who enter into agreements before 1989 with defaulting parties in the state of Arizona. These agreements typically involve the exploration, production, or development of natural resources or the operation of a joint venture. In such agreements, operators have certain rights and recourse against defaulting parties who fail to meet their contractual obligations. These rights are essential to protect the interests of operators and ensure the smooth functioning of joint ventures or resource development projects. Here are some key aspects of the Arizona Rights of Operator Against A Defaulting Party Pre-1989 Agreements: 1. Lien Rights: Operators often have the right to assert a lien on the defaulting party's share of production or proceeds. This allows the operator to recover the costs and expenses incurred due to the defaulting party's failure to fulfill their obligations. 2. Financial Remedies: Operators may be entitled to seek financial remedies, such as damages or specific performance, if the defaulting party's breach causes monetary losses. These remedies aim to compensate the operator for the economic harm suffered as a result of the default. 3. Injunctive Relief: In certain situations, operators can seek injunctive relief to prevent the defaulting party from further impeding the progress of the joint venture or exploiting shared resources. This may be granted by the court to protect the operator's interests until the dispute is resolved. 4. Suspension or Termination of Defaulting Party's Participation: In some cases, operators have the right to suspend or terminate the defaulting party's participation in the joint venture or resource development project. This action can be taken when the defaulting party's breach is severe or persistent, threatening the overall success or stability of the endeavor. 5. Dispute Resolution: Agreements may include provisions for resolving disputes between operators and defaulting parties. This could involve arbitration or mediation procedures aimed at reaching a fair and expeditious resolution, avoiding lengthy court proceedings. It is important to note that the Arizona Rights of Operator Against A Defaulting Party Pre-1989 Agreements may have different variations and types depending on the specific terms and conditions outlined in each agreement. These variations may encompass additional rights and remedies, duration and renewal provisions, and allocation of costs and expenses among parties. In conclusion, the Arizona Rights of Operator Against A Defaulting Party Pre-1989 Agreements provide operators with a range of legal tools to protect their interests when dealing with defaulting parties. These rights include lien rights, financial remedies, injunctive relief, suspension or termination of participation, and dispute resolution procedures. Understanding these rights is crucial for operators engaged in joint ventures or resource development projects in Arizona to navigate potential default scenarios and enforce their rights effectively.