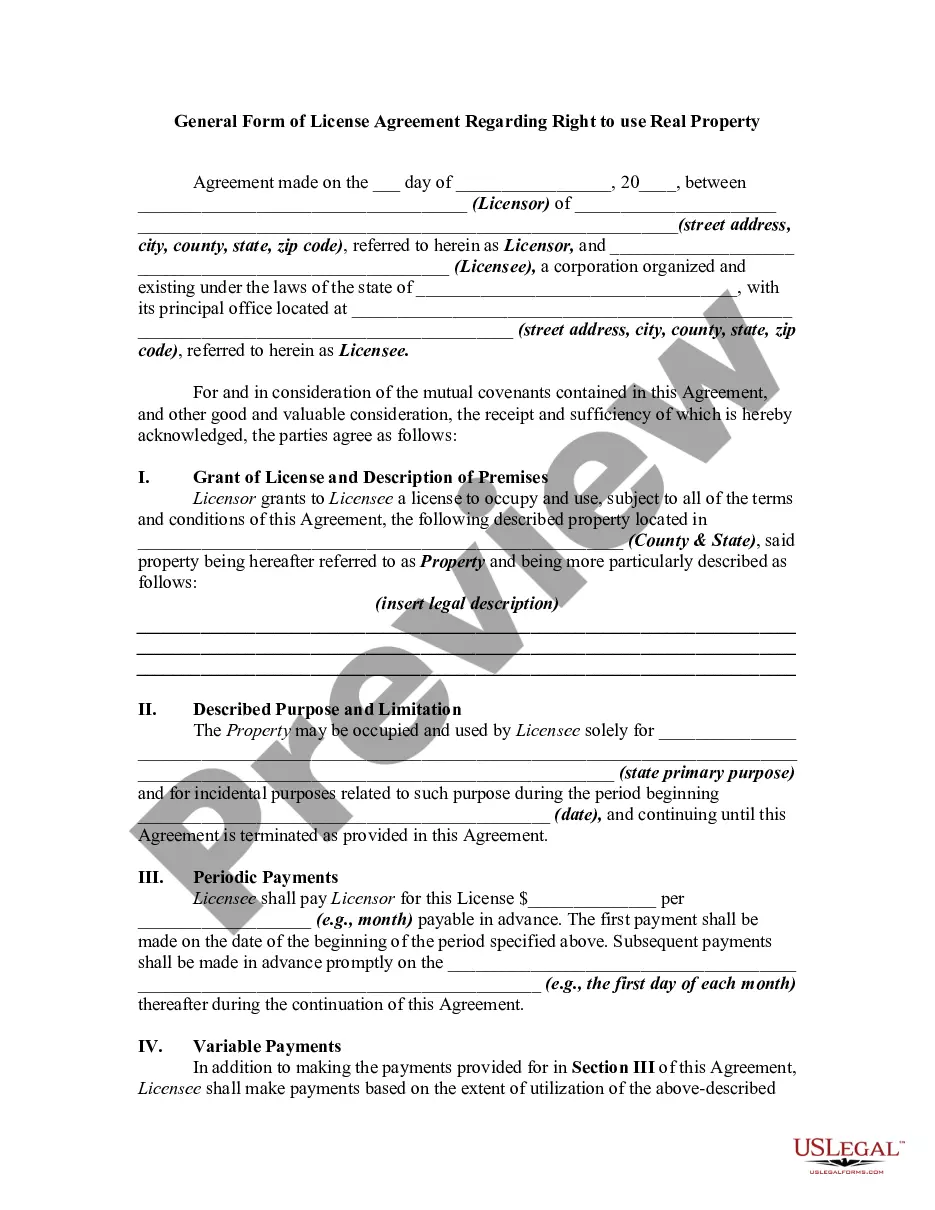
An easement is a right in the land of another. The right is often described as the right to use the land of another for a special purpose. An easement gives one party the right to go onto another party's property. That property may be owned by a private person, a business entity, or a group of owners. Utilities often get easements that allow them to run pipes or phone lines beneath private property. An easement is a real property interest, but separate from the legal title of the owner of the underlying land. This form is a generic example that may be referred to when preparing such a form for your particular state.
California General Form of Easement Agreement
Description
How to fill out General Form Of Easement Agreement?
It is feasible to spend time online attempting to locate the legal document format that complies with the federal and state regulations you require.
US Legal Forms offers a vast selection of legal documents that are reviewed by experts.
You can download or print the California General Form of Easement Agreement from the platform.
To find another variation of the form, use the Search field to locate the format that meets your needs and specifications. Once you have found the format you require, click Get now to proceed. Select the pricing plan you prefer, enter your details, and create your account on US Legal Forms. Complete the purchase using your credit card or PayPal account to acquire the legal document. Choose the format of the file and download it to your device. Make changes to your document if necessary. You can complete, modify, sign, and print the California General Form of Easement Agreement. Access and print numerous document templates using the US Legal Forms website, which offers the largest collection of legal documents. Utilize professional and state-specific templates to address your business or personal needs.
- If you already have a US Legal Forms account, you can Log In and click the Obtain button.
- Afterward, you can complete, modify, print, or sign the California General Form of Easement Agreement.
- Each legal document you purchase is yours permanently.
- To create an additional backup of the acquired form, go to the My documents section and click the corresponding button.
- If you are accessing the US Legal Forms website for the first time, follow the simple steps below.
- First, make sure you have selected the correct document format for the state/city of your choice.
- Review the form description to confirm you have chosen the right document.
Form popularity
FAQ
Prescriptive Easement ? A prescriptive easement is produced when someone utilizes another person's property in a specific way for a lengthy period without their consent. To establish a prescriptive easement in California, the adverse use of the land must be open, notorious, and continuous for at least five years.
Any landowner contemplating the grant of a new easement over his property should consider whether he wants the grantee to assume a portion of the property taxes. By statute, property taxes are usually assessed to the landowner.
This can lead to conflicts between parties involved. Negligent maintenance is another issue. The servient estate owner is typically responsible for maintaining the easement, and when this duty is neglected, it can result in disputes. Poorly maintained easements can affect property values and functionality.
This grant of Easement is made on the express condition that Grantor is to be free from all liability by reason of injury or death to persons or injury to property from whatever cause arising out of Grantee's, its contractors', agents', officers', employees', invitees', or licensees' exercise of rights granted pursuant ...
To establish a prescriptive easement in California, certain legal requirements must be met. These include open and notorious use, continuous and uninterrupted use for a specific period of time, hostile use without the owner's permission, and exclusive use by the claimant.
Sometimes homeowners want to understand if they can remove an easement from their property or can a property owner block an easement. If the intent is to prevent or obstruct the use of the easement, the answer is probably no.
An easement grants the right to utilize another person's land for a certain purpose, such as exit and entry. However, it is crucial to understand that easements do not grant holders a possessory right. They also do not provide the holder the right to profit from the land or the right to inhabit the property.
Parties claiming rights pursuant to an implied easement must demonstrate that: (1) the owner of the property conveyed or transferred one part of that property to another; (2) ?the owner's prior existing use of the property was of a nature that the parties must have intended or believed the use would continue,? in other ...