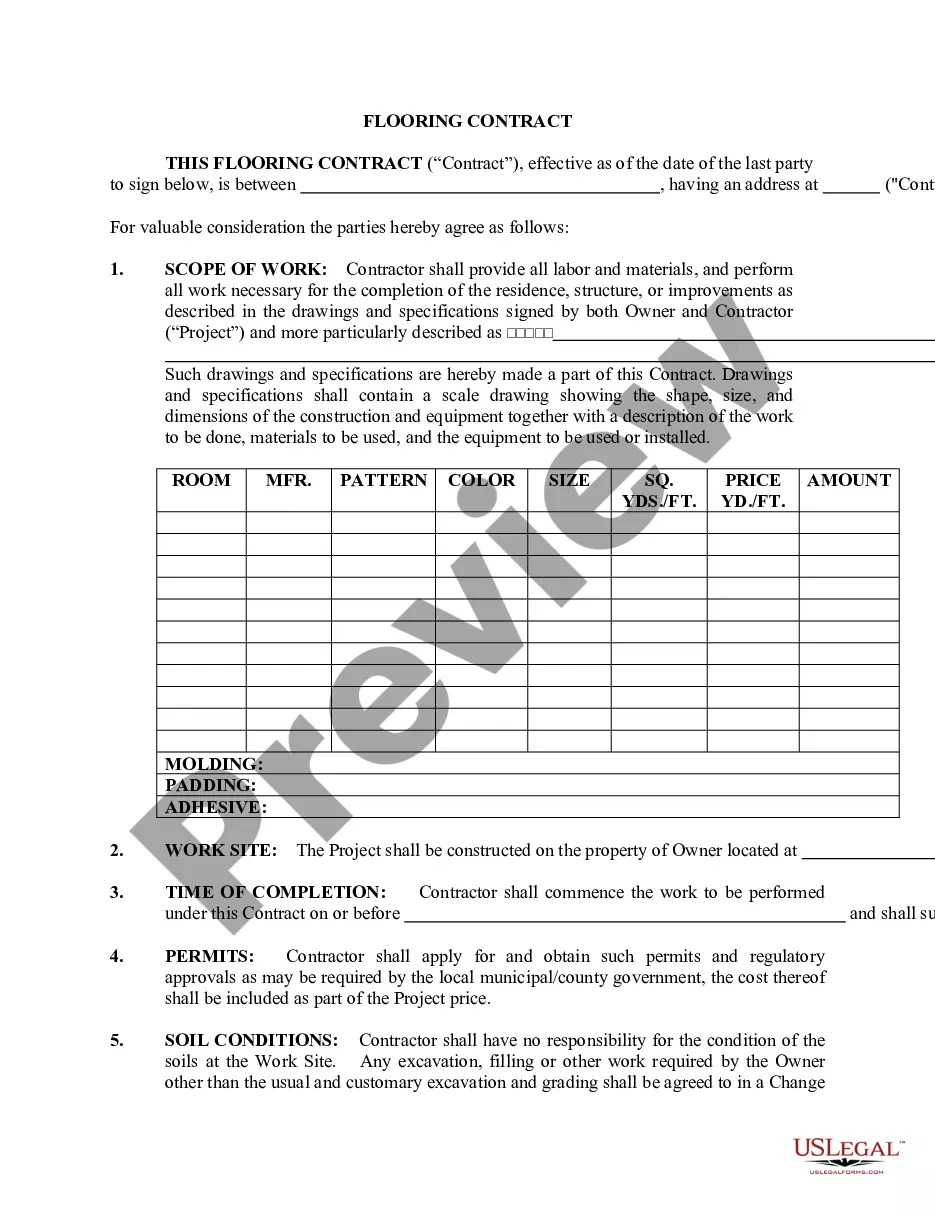
Barter is the trading of goods or services directly for other goods or services, without using money or any other similar unit of account or medium of exchange. Bartering is sometimes used among business as the method for the exchange of goods and services. This form is a generic example that may be referred to when preparing such a form for your particular state. It is for illustrative purposes only. Local laws should be consulted to determine any specific requirements for such a form in a particular jurisdiction.
California Bartering Contract or Exchange Agreement
Description
How to fill out Bartering Contract Or Exchange Agreement?
You have the capacity to spend hours online searching for the legal document template that meets your state and federal requirements.
US Legal Forms offers a multitude of legal forms that are reviewed by professionals.
You can obtain or print the California Bartering Contract or Exchange Agreement from our service.
If available, take advantage of the Review button to browse through the document template as well.
- If you have a US Legal Forms account, you can Log In and click the Download button.
- Afterward, you can complete, modify, print, or sign the California Bartering Contract or Exchange Agreement.
- Every legal document template you receive is yours indefinitely.
- To get another copy of the purchased form, visit the My documents tab and click the corresponding button.
- If you are using the US Legal Forms website for the first time, follow the simple instructions below.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct document template for the county/town of your choice.
- Review the form description to ensure you have chosen the appropriate type.
Form popularity
FAQ
Yes, barter agreements are legal in most jurisdictions, including California, as long as they meet contractual requirements. These agreements, including California Bartering Contracts or Exchange Agreements, must clearly outline the terms and conditions of the exchange. Always ensure that both parties understand their obligations and rights under the law to make the barter transaction valid and enforceable.
Writing a barter agreement requires you to clarify your exchange terms. Begin by identifying all parties involved, listing the items or services exchanged, and specifying the terms of the exchange to create a solid foundation. Utilize a California Bartering Contract or Exchange Agreement template from US Legal Forms for a reliable and legally sound approach to your barter transactions.
An example of a barter agreement could involve two parties exchanging services, such as a graphic designer providing design work in exchange for legal consultation. This type of arrangement would fall under a California Bartering Contract or Exchange Agreement, detailing the services offered and the terms of the exchange to avoid misunderstandings.
Writing an agreement deal involves outlining the specifics of the transaction clearly. Ensure the document includes relevant parties, the items or services involved, and the terms of the exchange. Use the format of a California Bartering Contract or Exchange Agreement to provide a clear framework for both parties to honor their commitments.
To write an agreement between a buyer and a seller, start with the title, clearly stating it as a California Bartering Contract or Exchange Agreement. Include essential elements like the names of both parties, a detailed description of the items being exchanged, and the terms of the exchange. Be sure to specify any additional conditions, payment methods, and deadlines to ensure a smooth transaction.
When it comes to taxes, bartering is treated like any other form of income. According to the IRS, the value of the goods or services received in a barter must be reported as income. This is where a California Bartering Contract or Exchange Agreement becomes important, as it provides documentation of the transaction's value. To navigate the complexities of bartering and taxes, consider using a platform like USLegalForms for guidance.
To properly record a barter transaction, you should create a clear California Bartering Contract or Exchange Agreement. This contract should describe the items or services exchanged and their agreed-upon values. Additionally, maintaining a written record of the transaction will help with accounting and tax purposes. You may also want to consult with a tax professional to ensure compliance.
The primary rule of bartering is that both parties must agree on the value of the goods or services being exchanged. A California Bartering Contract or Exchange Agreement typically details the value assessment to ensure fairness and clarity. This agreement helps prevent disputes by providing a clear framework for what each party receives in the exchange. Keeping written records is essential for accountability.
When participating in bartering, it’s essential to follow specific rules to ensure that the transaction is legal and beneficial for both parties. First, create a detailed California Bartering Contract or Exchange Agreement outlining each party's responsibilities. Secondly, make sure you report any income derived from the barter to tax authorities. By adhering to these rules, you can enjoy the advantages of bartering while staying compliant.
The IRS considers bartering as a taxable transaction. When you engage in a barter through a California Bartering Contract or Exchange Agreement, you must report the fair market value of the exchanged goods or services as income. This means keeping accurate records of your trades is crucial for tax purposes to ensure compliance with IRS regulations.