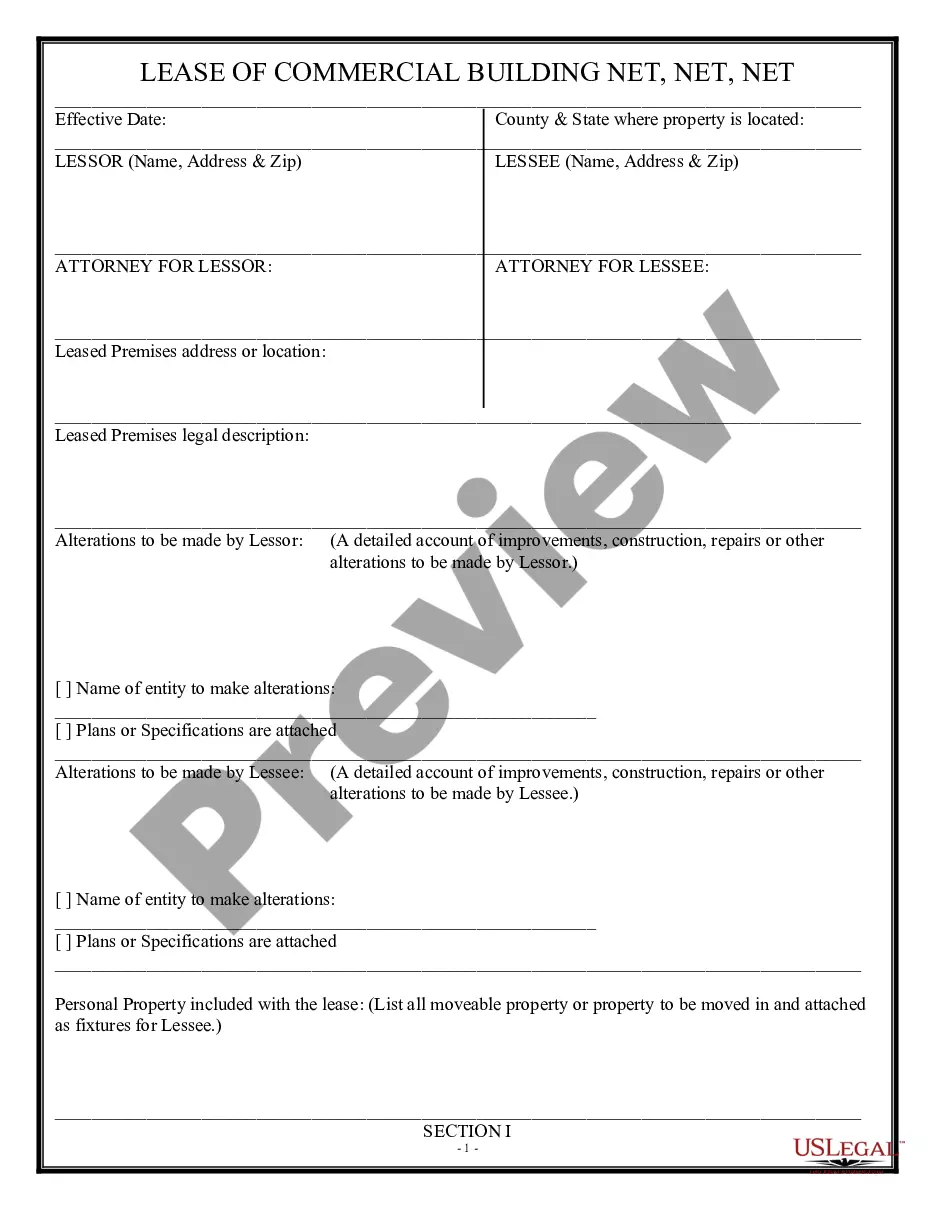
California Triple Net Lease for Residential Property
Description
How to fill out Triple Net Lease For Residential Property?
US Legal Forms - one of the premier collections of legal documents in the United States - offers a variety of legal form templates that you can download or print.
By using the website, you will have access to thousands of forms for business and personal use, organized by categories, states, or keywords. You can find the latest versions of forms such as the California Triple Net Lease for Residential Properties in just moments.
If you already possess a subscription, Log In and download the California Triple Net Lease for Residential Property from the US Legal Forms library. The Download button will appear on every form you view. You can access all previously downloaded forms from the My documents tab of your account.
Make modifications. Complete, edit, print, and sign the downloaded California Triple Net Lease for Residential Property.
Each template you add to your account does not have an expiration date and is yours permanently. Therefore, if you wish to download or print another copy, simply go to the My documents section and click on the form you need. Access the California Triple Net Lease for Residential Property with US Legal Forms, the most extensive library of legal document templates. Utilize thousands of professional and state-specific templates that meet your business or personal needs.
- If you want to use US Legal Forms for the first time, here are simple instructions to get started.
- Ensure you have selected the correct form for your city/state. Click on the Preview button to review the form's content. Check the form overview to confirm you have chosen the right one.
- If the form does not meet your requirements, use the Search field at the top of the screen to locate the one that does.
- If you are satisfied with the form, validate your selection by clicking the Get now button. Then, select the pricing plan you prefer and provide your details to create an account.
- Complete the transaction. Use your credit card or PayPal account to finalize the purchase.
- Choose the format and download the form to your device.
Form popularity
FAQ
When you enter a California Triple Net Lease for Residential Property, certain expenses are typically excluded from the NNN costs. Commonly not included are utility costs and tenant improvements, which can be the responsibility of the tenant. Additionally, property management fees may also be separate from the NNN obligations. For a clear understanding of what is or isn't covered, tools and templates available on uslegalforms can assist in outlining these details.
To get approved for a California Triple Net Lease for Residential Property, start by ensuring your finances are in order. Landlords look for reliable tenants, so providing proof of income, good credit scores, and previous rental history can strengthen your application. You should also familiarize yourself with the terms of a California Triple Net Lease, as this lease type includes responsibilities for property expenses. Being prepared and showing your understanding of the lease will make you a more attractive tenant.
To qualify for a California Triple Net Lease for Residential Property, you typically need to demonstrate a stable income and solid credit history. Property owners often look for tenants with reliable financial backgrounds to ensure timely rent payments. Additionally, showing a genuine interest in maintaining the property can strengthen your position as a qualified candidate. Using platforms like US Legal Forms can help you understand the necessary documentation and requirements for securing a triple net lease.
Filling out a California residential lease agreement requires attention to specific details. Start by entering the landlord's and tenant's information, then specify the property address. Include the lease term, rental amount, and any additional clauses related to a California Triple Net Lease for Residential Property. Using platforms like US Legal Forms can simplify this process by providing templates and guidance.
A triple net lease, also known as a net-net-net lease, requires the tenant to pay rent plus all three additional expenses. Rents are generally lower with net leases than traditional leasesthe more expenses a tenant has to bear, the lower base rent a landlord charges.
To determine the triple net lease amount for each renter, add those monthly expenses and the monthly rental per square foot charges and multiply it by the number of square feet a renter is leasing. That is the monthly triple net lease amount.
A triple net lease includes property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs, in addition to the base rent. Tenants may attempt to get out of a triple net lease because of the high costs associated with them, so landlords generally use a bondable net lease.
Cons of a Triple Net Lease-TenantsTax Liabilities: Because the tenant is responsible for annual property taxes in a triple net lease, this also means that they will be prone to all the liabilities of taxes as well, including fines and penalties for late or incorrect tax remittance.
Example of Calculating Monthly Rent in a NNN Lease The estimated operating expenses (aka NNN) are $10 per square foot per year. The total yearly rent you would pay equals $40 sf per year. So if you are leasing 3,000 sf then your yearly rent would be $120,000 or $10,000 per month.
There are many areas where a tenant can negotiate a NNN lease to make it more favorable. First, the base rental amount becomes a key negotiating term. If the tenant is taking on all responsibility and risk of the landlord's overhead, then the tenant may be able to negotiate a more favorable base rental amount.