California Hospital National Patient Safety Goals refer to a set of guidelines established by the California Department of Public Health (CDP) to improve patient safety and reduce the risk of adverse events in healthcare facilities across the state. These goals aim to provide a framework for hospitals and healthcare organizations to ensure the highest standards of patient safety by addressing potential risks and implementing effective strategies. The California Hospital National Patient Safety Goals are designed to align with and complement the National Patient Safety Goals set by The Joint Commission, a leading accrediting organization for healthcare institutions in the United States. While the specific requirements may vary slightly from year to year, the common objective remains unchanged: to enhance patient safety and foster a culture of continuous improvement in healthcare facilities. Key areas addressed by the California Hospital National Patient Safety Goals include: 1. Patient identification: Ensuring accurate patient identification through the use of at least two unique patient identifiers, such as full name and date of birth, to prevent errors in medication administration, specimen collection, and procedures. 2. Communication: Improving the effectiveness of communication among healthcare providers to minimize the occurrence of errors. This includes standardized hand off protocols during patient transfers and the use of read-back verification for critical test results and medication orders. 3. Medication safety: Reducing medication errors by implementing best practices such as medication reconciliation, labeling of medications, and appropriate storage and handling of high-alert medications. 4. Infection control: Preventing healthcare-associated infections by adhering to evidence-based guidelines for hand hygiene, proper disinfection and sterilization of equipment, and following isolation precautions. 5. Clinical alarms: Ensuring appropriate management of clinical alarms to prevent alarm fatigue and optimize patient safety. This involves setting alarm parameters based on individual patient needs and staff training on alarm recognition and response. 6. Surgical site infections: Implementing strategies to prevent surgical site infections, including the administration of appropriate prophylactic antibiotics, proper surgical site preparation, and post-operative wound care. It is essential for California hospitals to periodically review and update their processes to align with the most recent iteration of the California Hospital National Patient Safety Goals, as set forth by the CDP. Compliance with these goals is crucial for maintaining accreditation and improving patient outcomes. By prioritizing patient safety and actively working towards implementing these goals, healthcare organizations in California can create a safer environment for patients and promote continuous quality improvement.
California Hospital National Patient Safety Goals
Description
How to fill out California Hospital National Patient Safety Goals?
Are you within a placement in which you need to have paperwork for sometimes business or individual reasons virtually every day? There are tons of lawful papers web templates available on the Internet, but finding ones you can depend on isn`t straightforward. US Legal Forms delivers 1000s of form web templates, like the California Hospital National Patient Safety Goals, which can be published in order to meet state and federal needs.
Should you be already knowledgeable about US Legal Forms web site and get a merchant account, just log in. After that, you are able to obtain the California Hospital National Patient Safety Goals template.
If you do not provide an account and need to start using US Legal Forms, adopt these measures:
- Get the form you require and ensure it is for the correct area/state.
- Take advantage of the Preview option to review the shape.
- Browse the explanation to actually have selected the correct form.
- If the form isn`t what you are looking for, make use of the Research industry to discover the form that meets your requirements and needs.
- If you find the correct form, just click Buy now.
- Pick the prices prepare you would like, fill out the necessary info to make your bank account, and pay money for an order with your PayPal or charge card.
- Choose a hassle-free file file format and obtain your duplicate.
Find all the papers web templates you may have bought in the My Forms menu. You can aquire a extra duplicate of California Hospital National Patient Safety Goals whenever, if necessary. Just select the needed form to obtain or produce the papers template.
Use US Legal Forms, by far the most comprehensive selection of lawful forms, to conserve time as well as prevent blunders. The service delivers appropriately created lawful papers web templates which you can use for a variety of reasons. Generate a merchant account on US Legal Forms and initiate creating your way of life a little easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
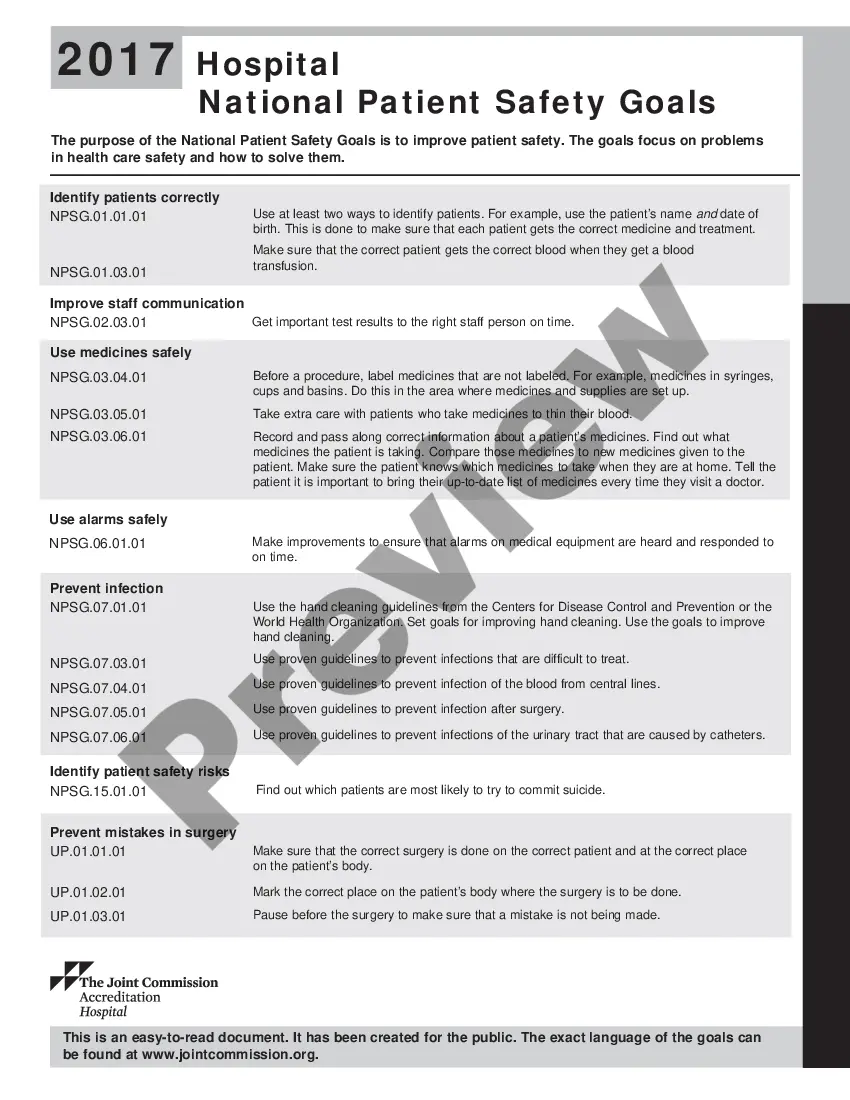
2022 Joint Commission National Patient Safety Goals1 Identify Patients Correctly.2 Improve Staff Communication.3 Use Medicines Safely.4 Use Alarms Safely.5 Prevent Infection.6 Surgery Verification.
Goal 6: Reduce patient harm associated with clinical alarm systems.
20172021 versionsGoal 1: Identify patients correctly.Goal 2: Improve effective communication.Goal 3: Improve the safety of high-alert medications.Goal 4: Ensure safe surgery.Goal 5: Reduce the risk of health care-associated infections.Goal 6: Reduce the risk of patient harm resulting from falls.
The idea is, over time, to have all those numbered goals migrate into standards.Goal 1: Improve the Accuracy of Patient Identification.Goal 2: Improve Communication.Goal 3: Improve the Safety of Using Medications.Goal 6: Reduce the Harm Associated with Clinical Alarm Systems.More items...
This is done to make sure that each patient gets the correct medicine and treatment.Identify patients correctly.Prevent infection.Improve staff communication.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.Use medicines safely.Use alarms safely.
The initiative recommends that care providers make sure that all drugs are labeled clearly. The Hospital National Patient Safety Goals also call for increased caution when treating individuals with different diagnosis. An example of this would be for someone who requires medication to thin their blood.
What Are the 7 National Patient Safety Goals for Hospitals in 2021?Identify patients correctly.Improve staff communication.Use medicines safely.Use alarms safely.Prevent infection.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.
This is done to make sure that each patient gets the correct medicine and treatment.Identify patients correctly.Prevent infection.Improve staff communication.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.
The idea is, over time, to have all those numbered goals migrate into standards.Goal 1: Improve the Accuracy of Patient Identification.Goal 2: Improve Communication.Goal 3: Improve the Safety of Using Medications.Goal 6: Reduce the Harm Associated with Clinical Alarm Systems.More items...