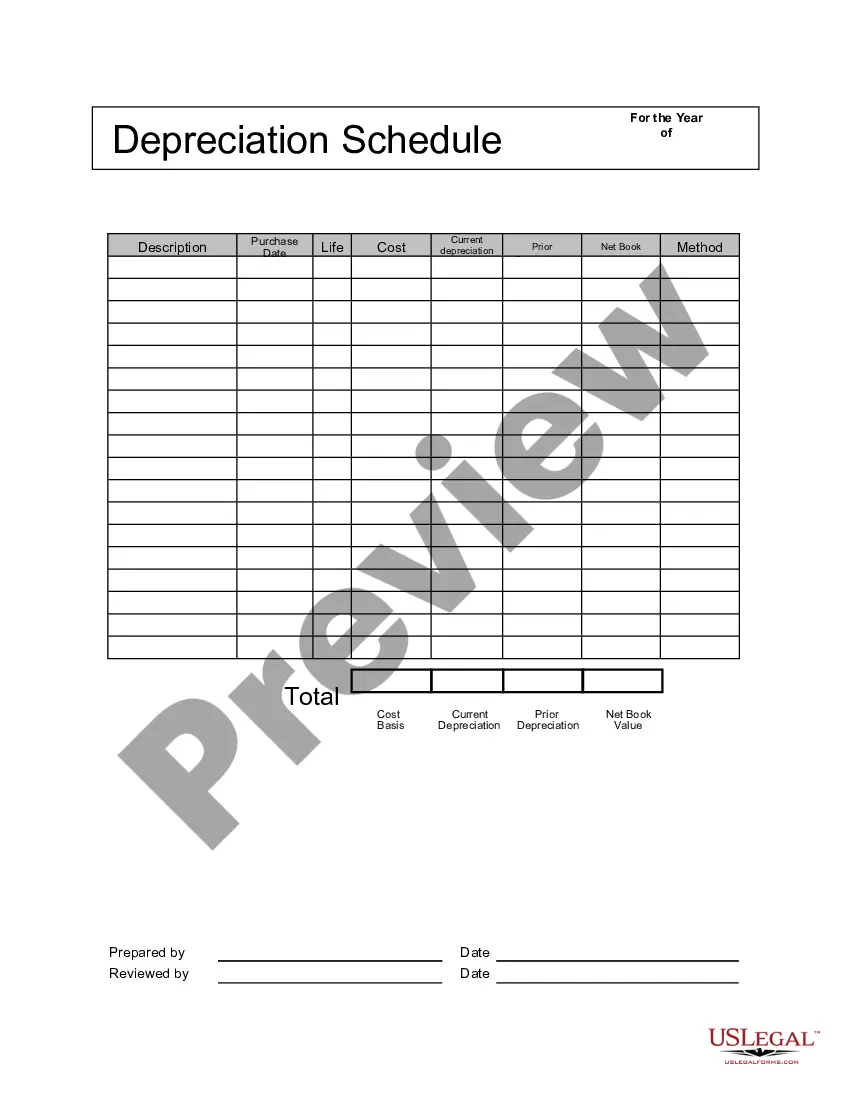
A California Depreciation Schedule is a document that outlines the allocated depreciation expenses for an asset or property in the state of California. It helps individuals and businesses in California accurately calculate the decrease in value of their assets over time, usually for tax and accounting purposes. One type of California Depreciation Schedule commonly used is the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MARS). MARS is a method approved by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) that allows businesses to recover the cost of certain assets over a specific period. It classifies assets into various categories with designated recovery periods and depreciation methods, ensuring tax deductions are claimed appropriately. Another type of California Depreciation Schedule is the Straight-Line Depreciation method. In this method, the asset's value is spread evenly over its useful life, resulting in a consistent annual depreciation expense. This method is simpler to calculate and is often used for assets that lose value at a consistent rate. Additionally, the California Depreciation Schedule may include other methods, such as the Double Declining Balance method or the Units of Production method, depending on the asset and industry-specific requirements. It is crucial to accurately maintain the California Depreciation Schedule to comply with state laws and ensure correct reporting of financial information. Failure to report depreciation correctly may lead to penalties or potential inaccuracies in tax filings. Therefore, individuals and businesses should consult tax professionals or use specialized software to ensure accurate and up-to-date records of their depreciation schedules. Overall, a California Depreciation Schedule is a vital tool used by individuals and businesses in the state to track and calculate the decrease in value of assets over time. By adhering to specific methods and guidelines, asset owners can accurately calculate their annual depreciation expenses, ensure tax compliance, and effectively manage their financial records.
California Depreciation Schedule
Description
How to fill out California Depreciation Schedule?
Choosing the right authorized papers web template could be a have a problem. Naturally, there are a variety of templates available online, but how will you get the authorized develop you need? Make use of the US Legal Forms site. The support delivers 1000s of templates, including the California Depreciation Schedule, that you can use for organization and personal demands. Every one of the forms are examined by professionals and meet up with state and federal needs.
Should you be previously signed up, log in in your profile and click on the Down load key to obtain the California Depreciation Schedule. Make use of your profile to look throughout the authorized forms you possess ordered previously. Proceed to the My Forms tab of your respective profile and get one more copy in the papers you need.
Should you be a whole new user of US Legal Forms, allow me to share simple instructions that you should follow:
- Initial, ensure you have selected the correct develop for your area/region. You are able to look over the form utilizing the Review key and browse the form description to ensure this is basically the right one for you.
- If the develop will not meet up with your preferences, take advantage of the Seach discipline to get the right develop.
- Once you are certain the form is acceptable, click on the Buy now key to obtain the develop.
- Opt for the rates plan you want and enter in the needed information and facts. Make your profile and purchase the order making use of your PayPal profile or bank card.
- Select the document format and acquire the authorized papers web template in your gadget.
- Complete, edit and print out and signal the received California Depreciation Schedule.
US Legal Forms may be the most significant library of authorized forms in which you can see numerous papers templates. Make use of the service to acquire professionally-made papers that follow express needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
A depreciation schedule charts the loss in value of an asset over the period you've designated as its useful life, using the accounting method you've chosen. The point of having a depreciation schedule is to give you the ability to track what you've already deducted and stay on top of the process.
Special and Bonus Depreciation. California does not conform to the federal special or bonus depreciation for qualified property acquired and placed in service.
California does not conform to the federal special or bonus depreciation for qualified property acquired and placed in service.
The only acceptable methods of depreciation for California tax purposes are: Straight-line. Declining balance.
The only acceptable methods of depreciation for California tax purposes are: Straight-line. Declining balance. Sum-of-the-years-digits method.
There is no adjustment for California AMT purposes. basis of the property at the end of the taxable year is a tax preference item for both federal and state purposes.
Schedule C FilersEnter the depreciation deduction on Schedule C, Line 13, Depreciation and section 179 expense deduction (not included in Part III). Attach Schedule C and Form 4562 to your Form 1040.
On or after January 1, 1987. California provides special credits and accelerated write-offs that affect the California basis for qualifying assets. California does not conform to all the changes to federal law enacted in 1993.
MACRS usually follows the straight line or double declining method. IRS Publication 946 determines each asset's useful life and explains all the depreciation and amortization rules and regulations. Sole proprietorships and single-member LLCs deduct depreciation when they fill out Schedule C on Form 1040.
Use form FTB 3885A only if there is a difference between the amount of depreciation and amortization allowed as a deduction using California law and the amount allowed using federal law. California law and federal law have not always allowed the same depreciation methods, special credits, or accelerated write-offs.