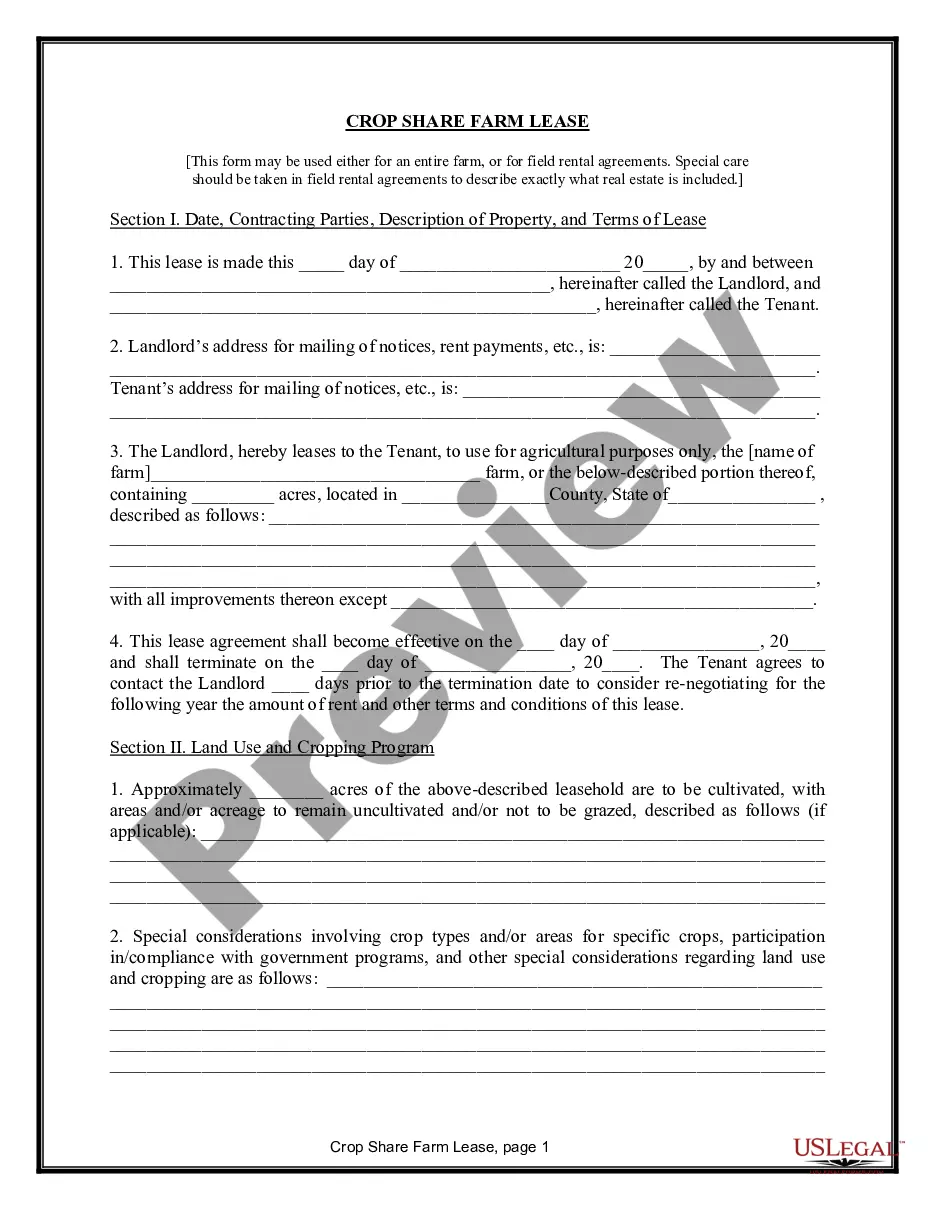
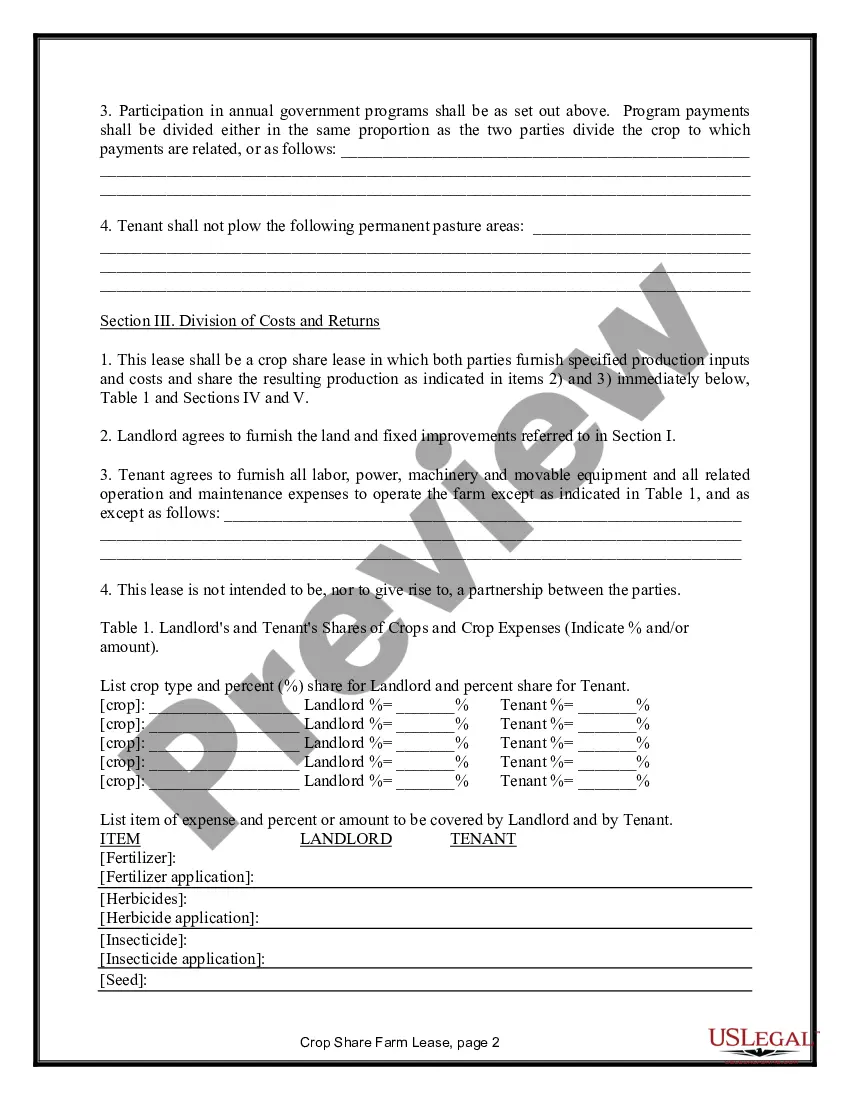
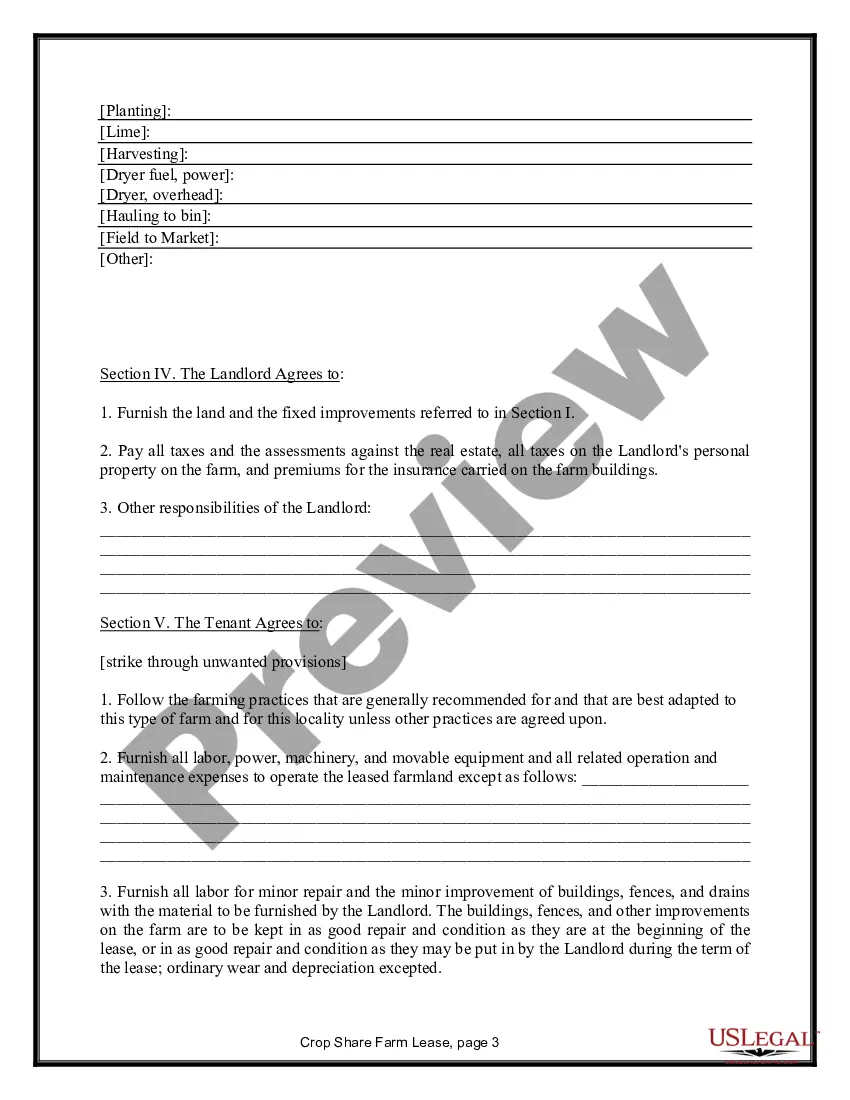
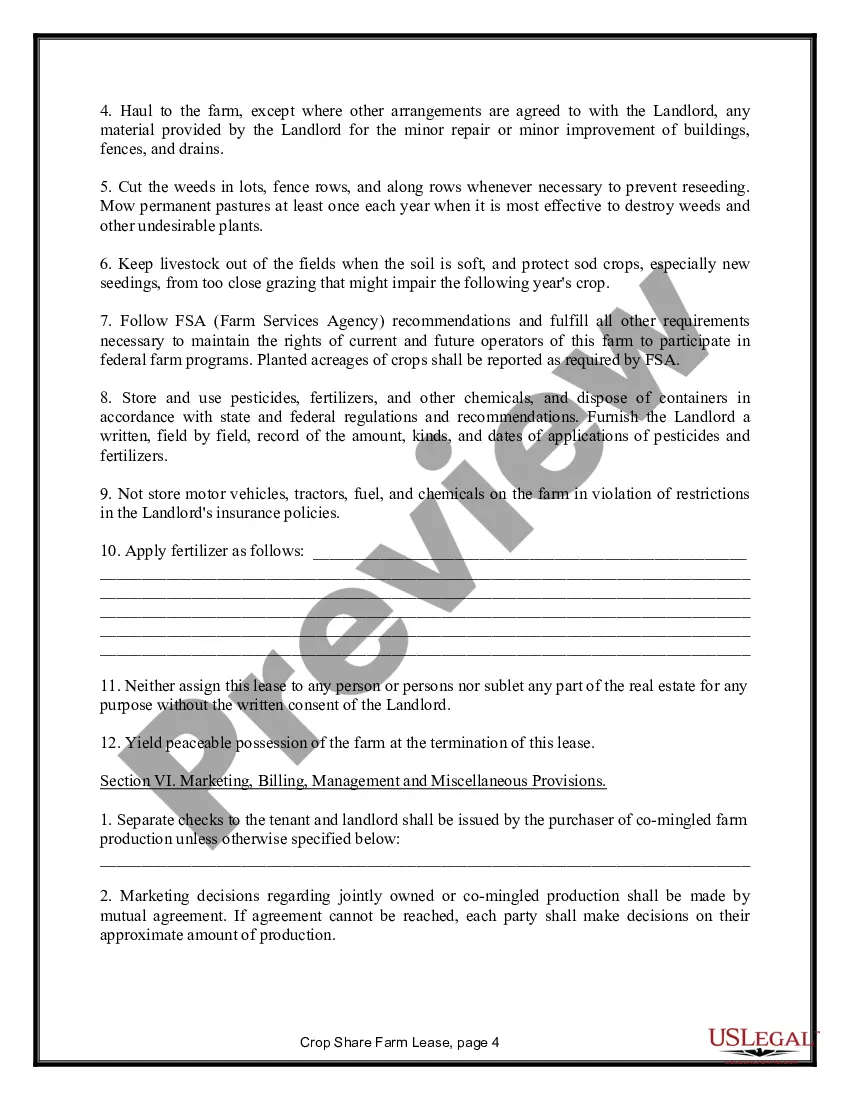
Title: California Farm Lease or Rental — Crop Share: An In-Depth Overview Introduction: In California, the Farm Lease or Rental — Crop Share agreement is a widely practiced arrangement between landowners and tenants. This type of agricultural lease establishes an agreement where the tenant (farmer) pays for their rent through a predetermined percentage of the crop harvest rather than a fixed amount of money. This detailed description aims to explain the California Farm Lease or Rental — Crop Share agreement, its benefits, and the various types of agreements available. Types of California Farm Lease or Rental — Crop Share: 1. Custom Farming Lease: A custom farming lease is a type of crop-share agreement where the landowner hires a producer to cultivate and manage the land. Under this arrangement, the landowner typically covers the expenses of inputs (e.g., seeds, fertilizers, and chemicals), machinery, and labor, while the tenant provides their expertise. The crop harvest is then divided based on a pre-determined percentage agreed upon by both parties. 2. Flexible Crop Share Lease: A flexible crop share lease provides both parties the flexibility to adjust crop shares based on market conditions, input costs, and other factors. The percentage of crop share is not fixed but is rather determined annually or periodically. This allows farmers and landowners to adapt to changing circumstances in a mutually beneficial manner. 3. Simple Crop-Share Lease: A simple crop-share lease entails a straightforward arrangement where the landowner and tenant agree on a fixed percentage of the crop that the tenant will provide as rent. Typically, the landowner is not involved in the farm's daily operations, but they may provide guidance or expertise if requested by the tenant. This type of lease is commonly suitable for experienced and self-sufficient farmers. Key Elements of a California Farm Lease or Rental — Crop Share Agreement: 1. Duration: The lease agreement defines the specific time period during which the tenant has the right to use the land for agricultural purposes. It typically includes a start and end date, with the possibility of renewal or termination clauses. 2. Crop Sharing: The agreement details the percentage of crop share that the tenant will provide as rent. Clear provisions are made on how the crops will be harvested, sold, valued, and divided between the landowner and tenant. 3. Responsibilities and Obligations: The lease specifies the responsibilities and obligations of both parties, including maintenance, repairs, insurance, taxes, water rights, and compliance with relevant regulations. It is crucial to outline provisions for managing pests and diseases, maintaining soil health, and other sustainable farming practices. 4. Payment Schedule: The lease agreement outlines the payment schedule, including when and how the crop share will be calculated, shared, and delivered to the landowner. 5. Dispute Resolution: In case of disagreements or disputes, the lease agreement may include provisions for mediation, arbitration, or other methods of resolution. Benefits of California Farm Lease or Rental — Crop Share: 1. Risk Sharing: The crop-share arrangement allows both the tenant and the landowner to share risks associated with the uncertainties of farming, including yield variations, market prices, and weather conditions. 2. Investment Alignment: Crop sharing incentivizes tenants to optimize agricultural practices, as the success and profitability of the tenant's farm directly influence their income. 3. Landowner Involvement: The landowner can stay connected to their land, monitor its use, and potentially contribute their knowledge or guidance to maximize productivity. 4. Financial Stability: Tenant farmers benefit from reduced upfront costs, as they do not need to pay fixed rent amounts. This facilitates access to land and allows them to invest in operational expenses or expansion. Conclusion: The California Farm Lease or Rental — Crop Share agreement serves as an effective means for landowners and tenants to form mutually beneficial partnerships within the state's agricultural industry. By understanding the various types of crop-share arrangements available and the key elements involved, landowners and farmers can establish successful, sustainable, and long-term agreements, contributing to the continued growth and productivity of California's vibrant farming sector.
California Farm Lease or Rental - Crop Share
Description
How to fill out California Farm Lease Or Rental - Crop Share?
Are you currently inside a placement in which you need files for sometimes company or person functions nearly every working day? There are plenty of lawful file layouts available on the Internet, but discovering ones you can depend on is not effortless. US Legal Forms offers a huge number of kind layouts, just like the California Farm Lease or Rental - Crop Share, which can be published in order to meet state and federal demands.
In case you are previously familiar with US Legal Forms web site and possess your account, simply log in. Afterward, you are able to acquire the California Farm Lease or Rental - Crop Share format.
Unless you provide an profile and would like to begin to use US Legal Forms, follow these steps:
- Get the kind you will need and ensure it is for the correct city/area.
- Use the Review key to examine the form.
- Read the description to actually have chosen the appropriate kind.
- When the kind is not what you`re looking for, utilize the Look for area to find the kind that meets your requirements and demands.
- Whenever you obtain the correct kind, click Get now.
- Opt for the costs strategy you need, complete the specified information to produce your bank account, and purchase the order utilizing your PayPal or charge card.
- Pick a practical paper structure and acquire your copy.
Get all the file layouts you possess bought in the My Forms menus. You can aquire a more copy of California Farm Lease or Rental - Crop Share whenever, if necessary. Just click on the needed kind to acquire or print out the file format.
Use US Legal Forms, by far the most considerable collection of lawful forms, in order to save time as well as avoid mistakes. The support offers professionally produced lawful file layouts that you can use for a variety of functions. Make your account on US Legal Forms and start producing your life a little easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
For pastureland, the average rental rate per acre remained unchanged at $12.50. Source: USDA NASS. Rates ranged from $72 in Oklahoma to $528 in California for irrigated cropland; from $26.50 in Montana to $231 in Iowa for non-irrigated cropland; and from $6.30 in Montana to $54 in Iowa for pastureland.
A crop share lease is an agreement where the landowner and tenant split the expenses of farming as well as the production. Because of this, both parties to experience the risk associated with high and lows of price and production.
Description. Farm layout involves the location of the fields with respect to the farmstead and public highways, the size, shape and number of fields, and the location of hog-lots, feed yards, etc. In arranging or re-arranging a farm layout the most important considerations are convenience and economy of operation.
Most farmers find that a combination of both ownership and leasing is desirable, especially when capital is limited. For many new farmers, especially in areas where land is quite expensive, leasing land is often the best option.
How a CSA Works. The main purpose of a CSA is to define and record the collateral offered by both parties in a derivatives transaction in order to ensure that they can cover any losses.
Farm share programs provide a direct link between local farmers and consumers by allowing members to purchase a share of a farmer's crop before it is grown each season.
Farmland has historically been a good investment. Unfortunately, not many investors have been able to benefit from this asset class, given the high upfront costs of buying farmland.
With a land lease agreement (also known as a ground lease), you purchase the home but rent the land. One of the main advantages is the lower price of this unique arrangement. One of the main disadvantages is that you will not be able to build valuable equity in the land on which you live.
A farm lease is a written agreement between a landowner and a tenant farmer. Through a farm lease, the landowner grants the tenant farmer the right to use the farm property. Key terms of basic leases include the length of the lease, rent amounts and frequency of payment, how to renew or end the lease, and more.
The advantages of the first are that the tenant in many cases is free to manage the farm as he pleases, and as a long-time proposition he may pay less rent than under crop-sharing arrangements. The chief disadvantage is that the tenant agrees to pay a definite sum before he knows what his income will be.