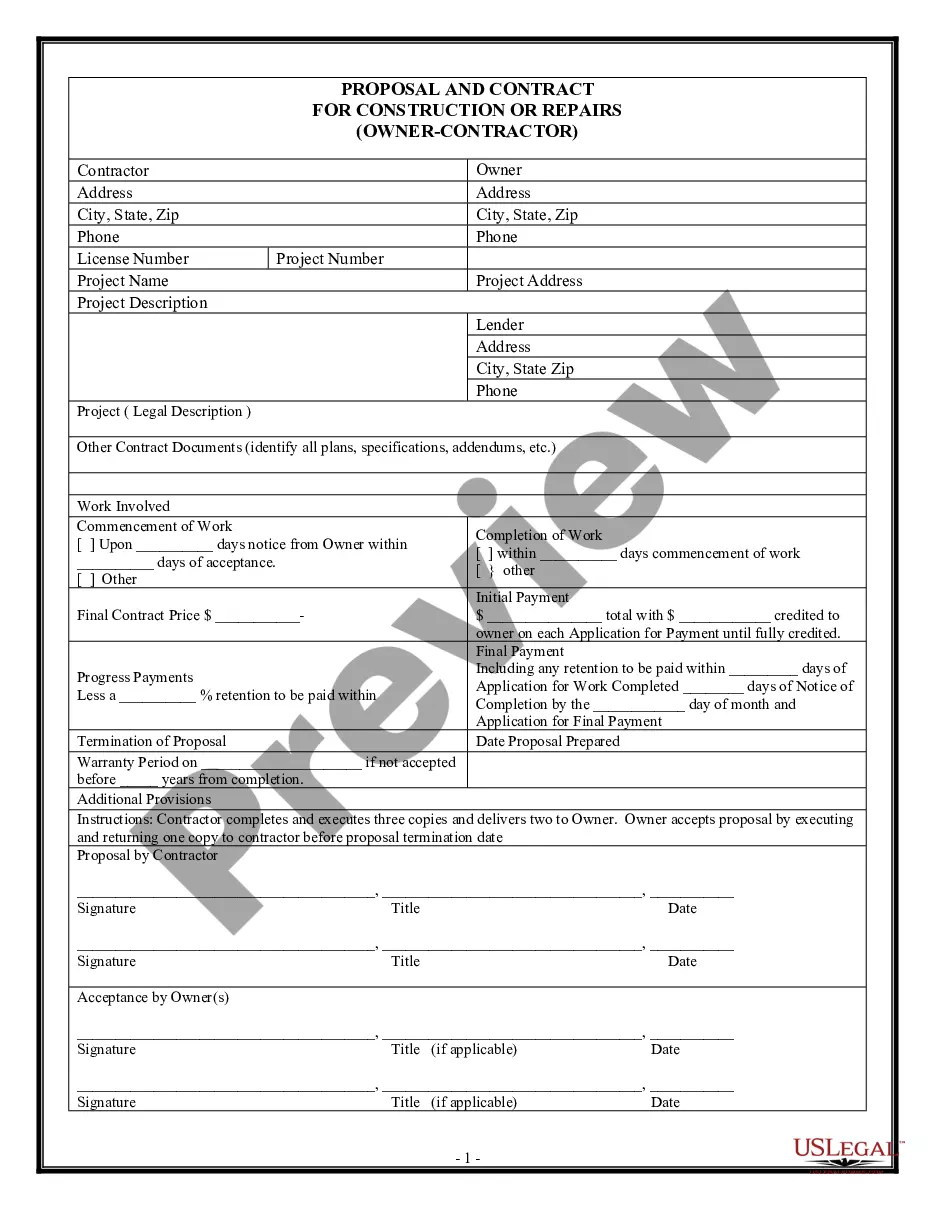
This office lease form states that the landlord and the tenant will fulfill, observe and comply with all of the terms and provisions of all applicable environmental laws.
California Environmental Matters Hazardous Substances
Description
How to fill out Environmental Matters Hazardous Substances?
Choosing the best legal record template can be a battle. Obviously, there are tons of templates available online, but how can you obtain the legal form you need? Make use of the US Legal Forms website. The services gives a huge number of templates, like the California Environmental Matters Hazardous Substances, that you can use for organization and private needs. All the forms are examined by professionals and fulfill state and federal demands.
When you are presently registered, log in to the accounts and click on the Obtain option to obtain the California Environmental Matters Hazardous Substances. Utilize your accounts to look with the legal forms you possess purchased in the past. Proceed to the My Forms tab of your respective accounts and acquire an additional version of the record you need.
When you are a new customer of US Legal Forms, here are simple recommendations that you can stick to:
- Initial, make certain you have selected the proper form for your personal city/state. You may examine the form utilizing the Review option and read the form description to make certain this is the right one for you.
- If the form fails to fulfill your requirements, utilize the Seach area to discover the correct form.
- When you are positive that the form is suitable, click the Acquire now option to obtain the form.
- Opt for the rates plan you desire and enter the essential information. Create your accounts and pay money for an order making use of your PayPal accounts or charge card.
- Select the document file format and down load the legal record template to the device.
- Complete, modify and produce and indication the received California Environmental Matters Hazardous Substances.
US Legal Forms is the greatest collection of legal forms where you can discover various record templates. Make use of the service to down load appropriately-made paperwork that stick to status demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
The California Department of Public Health (CDPH) Environmental Management Branch regulates the collection, storage, transportation and disposal of sharps and medical wastes from businesses.
NFPA 30 defines hazardous material or hazardous chemical as a ?material presenting dangers beyond the fire problems relating to flash point and boiling point.? The annex material goes on to explain that the other dangers could include things like toxicity, reactivity, instability, or corrosivity.
What are Environmentally Hazardous Substances? Environmentally Hazardous Substances (or Marine {Pollutants) are materials that can pose a risk to aquatic ecosystems such as marine mammals, fish, crustaceans and algae. Marine Pollutant is a supplementary classification requirement that applies only to transport by sea.
HazMat are products that pose a risk to health, safety, and property during transportation. The term often is shortened to HazMat, which you may see on road signs or to HM in government regulations. HazMat include explosives, various types of gas, solids, flammable and combustible liquid, and other materials.
Common industrial materials that are considered non hazardous in most states include ash, sludges, antifreeze, grinding dusts and liquids contaminated with non-hazardous chemicals.
Examples of other listed air toxics include dioxin, asbestos, toluene, and metals such as cadmium, mercury, chromium, and lead compounds.
Often, the first step towards determining whether a consumer product is hazmat is to locate the Safety Data Sheet (SDS), formerly known as the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), prepared by the manufacturer. This document provides the product's hazard classification in its 'Transportation Information' section.
Any solid, liquid, or gaseous material that is radioactive, toxic, explosive, flammable, corrosive, or otherwise physically or biologically threatening to health.