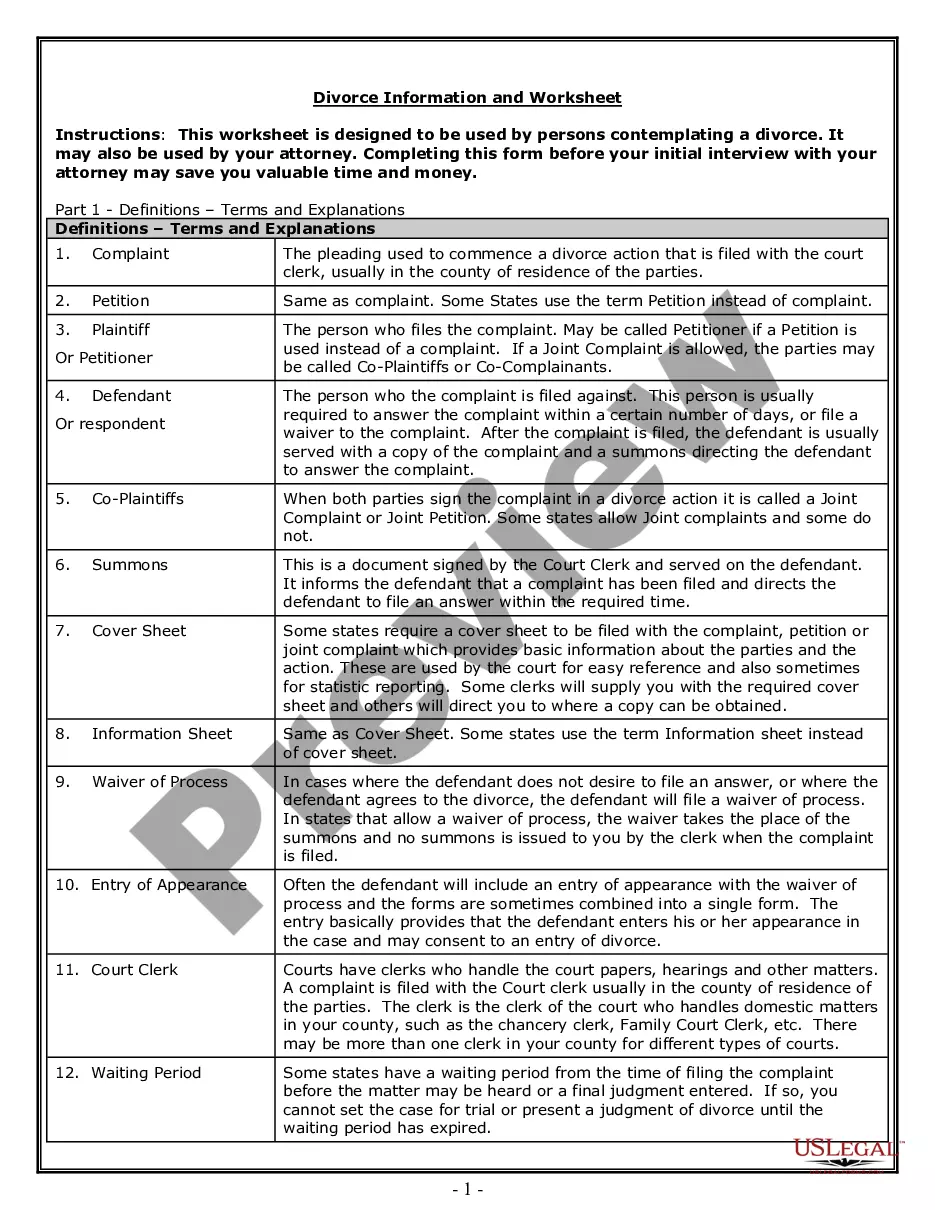
A bond placement is the process of selling a new bond issue often to an intitutional investor. For a company in need of financing, this a typical transaction arranged through an investment banker.
Colorado Bond placement agreement
Description
How to fill out Bond Placement Agreement?
Selecting the optimal legitimate document template can be a challenge. Of course, there are numerous templates available online, but how can you locate the legitimate version you need? Utilize the US Legal Forms website. The platform offers a vast array of templates, including the Colorado Bond placement agreement, suitable for both business and personal purposes. All documents are vetted by experts and adhere to state and federal regulations.
If you are currently registered, Log In to your account and click the Obtain button to retrieve the Colorado Bond placement agreement. Use your account to search through the legal forms you have previously purchased. Visit the My documents section of your account to download another copy of the document you require.
If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are straightforward instructions that you should follow: First, ensure you have chosen the correct form for your region/area. You can review the form using the Preview button and read the form description to confirm it is the suitable one for you. If the form does not meet your needs, use the Search field to find the appropriate form. Once you are confident that the form is acceptable, click the Acquire now button to obtain the form. Select the pricing plan you prefer and enter the necessary information. Create your account and complete the purchase using your PayPal account or credit card. Choose the file format and download the legal document template to your device. Complete, modify, print, and sign the obtained Colorado Bond placement agreement.
- US Legal Forms is the largest collection of legal forms available where you can find a variety of document templates.
- Utilize the service to download professionally crafted documents that comply with state regulations.
- The templates available are designed for both personal and business use.
- All documents are reviewed to ensure they meet legal standards.
- User-friendly interface for easy navigation and access to forms.
- Secure payment options for a hassle-free transaction.
Form popularity
FAQ
The act requires a court to hold a bond setting hearing within 48 hours after an arrestee's arrival at a jail or holding center beginning on April 1, 2022. Under current law, a person is allowed to post bond within 2 hours after the sheriff receives the bond information.
If you operate an appraisal management company (AMC) or collection agency in Colorado, you must be properly bonded in order to receive your business license. General contractors, mortgage brokers, motor vehicle dealers, and motor vehicle salespeople in the state must also post surety bonds to obtain licensure.
When your loved one is arrested in Colorado, it may be possible to secure their release by posting a bail bond with the court. A bail bond serves as a monetary promise that your loved one will show up to all future court proceedings in return for getting to remain out of custody during the case.
The amount and type of bail are fixed by the judge at the first appearance before the court. A court will consider the defendant's individual circumstances when the amount of bail is set. The bail amount must be sufficient to ensure that the defendant will appear for all scheduled proceedings.
The primary purpose of bail is to ensure that the defendant appears for trial. A bond is an agreement between the defendant and the court under which the defendant agrees to comply with all of the conditions of release and to pay the bail amount if he or she does not appear in court.
Cash Bail. Cash bail is paid directly to the court. The money will be returned minus any court fees and fines if the defendant appears at all court dates. If the defendant does not attend court, the bail money is forfeited.
A PR bond is a signature bond that involves no money or property as long as the defendant appears at all future court dates. The defendant's signature acts as the promise to appear in court. A judge may require additional persons to sign the bond as well, to ensure the appearance of the defendant in court.