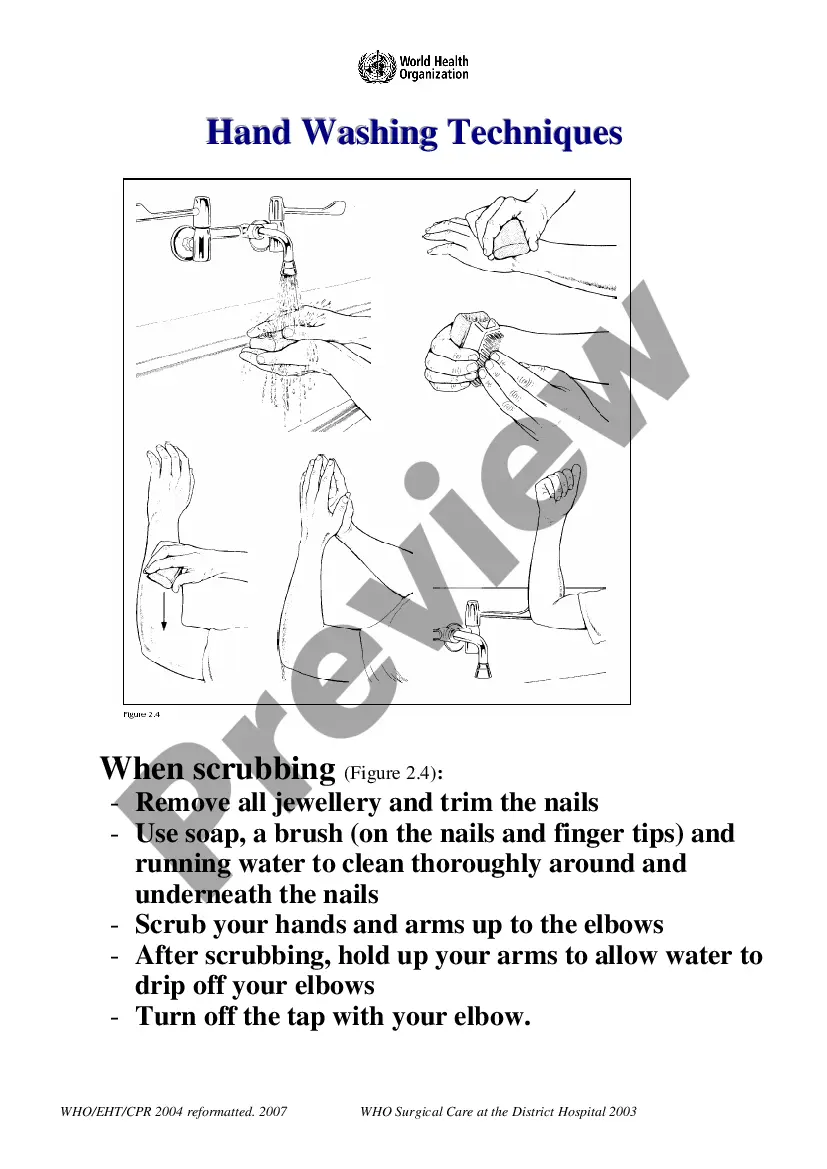
Connecticut Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety refers to a set of guidelines and procedures aimed at ensuring the safe and effective delivery of clinical care in Connecticut. These protocols are designed to optimize patient outcomes and prevent potential risks and errors in healthcare settings. They encompass various areas of clinical practice and establish standardized best practices being followed by healthcare professionals. Here are some types of Connecticut Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety: 1. Infection Control Protocols: These protocols outline measures to prevent the spread of infections within healthcare facilities, including hand hygiene, sterilization and disinfection of medical equipment, isolation precautions, and vaccination recommendations. 2. Medication Safety Protocols: These protocols focus on ensuring the safe and appropriate use of medications, including medication reconciliation, prescription guidelines, accurate dosage calculations, and strategies to prevent medication errors. 3. Surgical Safety Checklist: This protocol is specifically designed for surgical procedures to ensure patient safety throughout the perioperative period. It includes preoperative verification, site marking, and a checklist of essential safety measures to be followed during surgery. 4. Diagnostic Imaging Safety Protocols: These protocols aim to minimize radiation exposure and ensure the safe use of imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds. They cover factors like appropriateness criteria for ordering imaging tests, radiation dose optimization, and contrast material administration guidelines. 5. Emergency Care Protocols: These protocols define the management of various emergency situations, including cardiac arrest, stroke, trauma, and respiratory distress. They provide step-by-step instructions for immediate assessment, stabilization, and treatment of patients in critical conditions. 6. Quality Improvement Protocols: These protocols focus on continuously monitoring and improving the quality of clinical care provided. They establish benchmarks, data collection methods, and analysis techniques to identify areas for improvement and implement evidence-based interventions. 7. Patient Safety Protocols: These protocols emphasize the importance of patient-centered care and the prevention of harm to patients. They encompass various strategies such as fall prevention, pressure ulcer prevention, prevention of healthcare-associated infections, and patient and family engagement in care decisions. Overall, Connecticut Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety aim to promote a culture of safety in healthcare settings and provide healthcare professionals with standardized guidelines to deliver high-quality care while mitigating potential risks. These protocols are routinely updated and revised based on new scientific evidence and expert recommendations, ensuring that healthcare practices align with the latest advancements in patient safety.
Connecticut Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety
Description
How to fill out Connecticut Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety?
Are you presently inside a situation where you need to have files for both business or individual purposes almost every time? There are tons of lawful papers web templates available on the net, but locating kinds you can depend on is not easy. US Legal Forms provides thousands of form web templates, such as the Connecticut Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety, which are written in order to meet federal and state requirements.
If you are already acquainted with US Legal Forms internet site and get a merchant account, merely log in. Following that, you can download the Connecticut Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety design.
Should you not come with an bank account and would like to begin using US Legal Forms, follow these steps:
- Discover the form you will need and ensure it is for your right area/region.
- Use the Review switch to analyze the shape.
- See the explanation to actually have chosen the appropriate form.
- In case the form is not what you`re looking for, utilize the Lookup industry to find the form that suits you and requirements.
- Whenever you get the right form, simply click Get now.
- Choose the prices prepare you desire, fill out the necessary information to make your bank account, and purchase your order making use of your PayPal or charge card.
- Decide on a practical file file format and download your version.
Find every one of the papers web templates you might have bought in the My Forms menus. You can obtain a extra version of Connecticut Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety at any time, if needed. Just go through the needed form to download or produce the papers design.
Use US Legal Forms, the most considerable assortment of lawful varieties, in order to save efforts and steer clear of errors. The assistance provides appropriately produced lawful papers web templates which you can use for a selection of purposes. Generate a merchant account on US Legal Forms and initiate making your daily life easier.