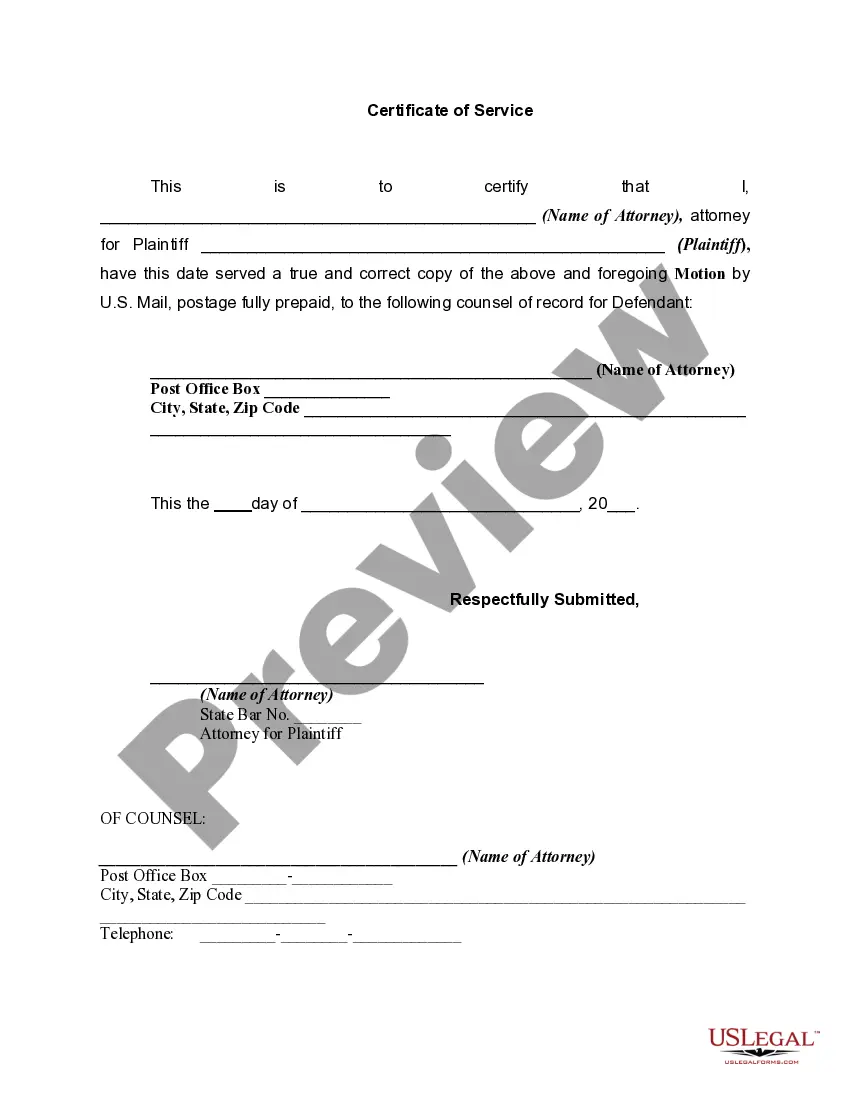
A motion is an application to a judge or court requesting a specific order directing performance of an act for the benefit of the applicant. Generally, where there is a procedural defect in a proceeding, a motion is an appropriate remedy. However, it is usually used to obtain relief not available through other pleadings. An order is a direction by a judge or court that certain actions should or should not be performed, and is usually, although not always, made in response to a party's motion.
This form is a generic example that may be referred to when preparing such a form for your particular state. It is for illustrative purposes only. Local laws should be consulted to determine any specific requirements for such a form in a particular jurisdiction.
The District of Columbia General Form of a Motion of Plaintiff and Notice to Defendant of Hearing on Motion is an essential legal document used in legal proceedings within the District of Columbia jurisdiction. This form serves to inform the defendant about the plaintiff's motion and the subsequent hearing regarding the matter at hand. By understanding the purpose and details of this document, parties involved can better navigate the legal process. A "motion" refers to a formal request made by one party (the plaintiff) seeking a specific action or ruling from the court. In the District of Columbia, there are different types of motions that can be filed, each with its specific purpose and requirements. Some common types include: 1. Motion for Summary Judgment: This motion asks the court to rule in favor of the plaintiff without going to trial, based on the belief that there are no genuine disputes of material fact to be resolved. 2. Motion to Dismiss: This motion seeks the immediate dismissal of the case, as the defendant argues that the plaintiff fails to state a claim upon which relief can be granted, lacks jurisdiction, or presents other legal deficiencies. 3. Motion for Preliminary Injunction: This motion requests the court to issue a temporary order restraining the defendant from engaging in certain actions until the final judgment is rendered. Regardless of the specific type, the District of Columbia General Form of a Motion of Plaintiff and Notice to Defendant of Hearing on Motion essentially consists of several key elements: 1. Caption: The document starts with a caption that includes the names of the parties involved, the case number, and the court's name. 2. Introduction: This section identifies the party filing the motion (the plaintiff) and the party being served (the defendant). It also briefly mentions the subject of the motion. 3. Statement of Facts: The plaintiff presents a concise overview of the relevant facts underlying the motion. This section aims to provide the court with an understanding of the context and basis for the request being made. 4. Legal Argument: The plaintiff articulates a clear and persuasive legal argument supporting the motion. This may include references to applicable statutes, regulations, or previous case law. It is crucial to present a strong legal basis for the requested action. 5. Relief Requested: The plaintiff explicitly states the specific relief sought from the court, such as the granting of a summary judgment, dismissal of the case, or issuance of a preliminary injunction. 6. Notice of Hearing: The document notifies the defendant of the scheduled date, time, and courtroom for the motion hearing. It is crucial to adhere to any specific timing and notice requirements set by the court. When filing the District of Columbia General Form of a Motion of Plaintiff and Notice to Defendant of Hearing on Motion, it is essential to consult the relevant court rules and procedures to ensure compliance. Additionally, it is advisable to seek legal counsel to tailor the document to the specific circumstances of the case and enhance the chances of a favorable outcome.The District of Columbia General Form of a Motion of Plaintiff and Notice to Defendant of Hearing on Motion is an essential legal document used in legal proceedings within the District of Columbia jurisdiction. This form serves to inform the defendant about the plaintiff's motion and the subsequent hearing regarding the matter at hand. By understanding the purpose and details of this document, parties involved can better navigate the legal process. A "motion" refers to a formal request made by one party (the plaintiff) seeking a specific action or ruling from the court. In the District of Columbia, there are different types of motions that can be filed, each with its specific purpose and requirements. Some common types include: 1. Motion for Summary Judgment: This motion asks the court to rule in favor of the plaintiff without going to trial, based on the belief that there are no genuine disputes of material fact to be resolved. 2. Motion to Dismiss: This motion seeks the immediate dismissal of the case, as the defendant argues that the plaintiff fails to state a claim upon which relief can be granted, lacks jurisdiction, or presents other legal deficiencies. 3. Motion for Preliminary Injunction: This motion requests the court to issue a temporary order restraining the defendant from engaging in certain actions until the final judgment is rendered. Regardless of the specific type, the District of Columbia General Form of a Motion of Plaintiff and Notice to Defendant of Hearing on Motion essentially consists of several key elements: 1. Caption: The document starts with a caption that includes the names of the parties involved, the case number, and the court's name. 2. Introduction: This section identifies the party filing the motion (the plaintiff) and the party being served (the defendant). It also briefly mentions the subject of the motion. 3. Statement of Facts: The plaintiff presents a concise overview of the relevant facts underlying the motion. This section aims to provide the court with an understanding of the context and basis for the request being made. 4. Legal Argument: The plaintiff articulates a clear and persuasive legal argument supporting the motion. This may include references to applicable statutes, regulations, or previous case law. It is crucial to present a strong legal basis for the requested action. 5. Relief Requested: The plaintiff explicitly states the specific relief sought from the court, such as the granting of a summary judgment, dismissal of the case, or issuance of a preliminary injunction. 6. Notice of Hearing: The document notifies the defendant of the scheduled date, time, and courtroom for the motion hearing. It is crucial to adhere to any specific timing and notice requirements set by the court. When filing the District of Columbia General Form of a Motion of Plaintiff and Notice to Defendant of Hearing on Motion, it is essential to consult the relevant court rules and procedures to ensure compliance. Additionally, it is advisable to seek legal counsel to tailor the document to the specific circumstances of the case and enhance the chances of a favorable outcome.